Abstract
Background Context
Chronic neck pain is a prevalent and disabling condition among older adults. Despite the large burden of neck pain, little is known regarding the cost-effectiveness of commonly used treatments.
Purpose
To estimate the cost-effectiveness of home exercise and advice (HEA), spinal manipulative therapy (SMT) plus HEA, and supervised rehabilitative exercise (SRE) plus HEA.
Study Design/Setting
Cost-effectiveness analysis conducted alongside a randomized clinical trial (RCT).
Patient Sample
241 older adults (≥65 years) with chronic mechanical neck pain.
Outcome Measures
Direct and indirect costs, neck pain, neck disability, SF-6D-derived quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios over a one-year time horizon.
Methods
This work was supported by grants from the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (#F32AT007507), National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (#P60AR062799), and Health Resources and Services Administration (#R18HP01425). The RCT is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (#NCT00269308). The primary analysis adopted a societal perspective, a healthcare perspective was adopted as a sensitivity analysis. Cost-effectiveness was a secondary aim of the RCT which was not powered for differences in costs or QALYs. Differences in costs and clinical outcomes were estimated using generalized estimating equations and linear mixed models, respectively. Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves were calculated to assess the uncertainty surrounding cost-effectiveness estimates.
Results
Total costs for SMT+HEA were 5% lower than HEA (mean difference: −$111; 95%CI -$1,354 to $899) and 47% lower than SRE+HEA (mean difference: −$1,932; 95%CI −$2,796 to −$1,097). SMT+HEA also resulted in a greater reduction of neck pain over the year relative to HEA (0.57; 95%CI 0.23 to 0.92) and SRE+HEA (0.41; 95%CI 0.05 to 0.76). Differences in disability and QALYs favored SMT+HEA. The probability that adding SMT to HEA is cost-effective at willingness to pay thresholds of $50,000 to $200,000 per QALY gained ranges from 0.75 to 0.81. If adopting a healthcare perspective, costs for SMT+HEA were 66% higher than HEA (mean difference: $515; 95%CI $225 to $1,094), resulting in an ICER of $55,975 per QALY gained.
Conclusions
On average, SMT+HEA resulted in better clinical outcomes and lower total societal costs relative to SRE+HEA and HEA alone, with a 0.75 to 0.81 probability of cost-effectiveness for willingness to pay thresholds of $50,000 to $200,000 per QALY.
Keywords: Chronic neck pain, Spinal manipulative therapy, Exercise, Home exercise, Cost-effectiveness, Older adults
Introduction
Chronic pain affects more U.S. adults than heart disease, diabetes, and cancer combined.[1] Although often considered benign and self-limiting, chronic neck pain is a substantial burden to society. Neck pain is the third most common chronic pain condition in the U.S.[2] and the fourth leading cause of disability worldwide.[3] Disability from neck pain has increased by 29% in the U.S. over the past two decades, largely due to population growth and aging.[4] Up to 22% of older adults experience neck pain, which is associated with diminished physical function and overall health.[5, 6]
The economic burden of spine pain in the U.S. is substantial, accounting for 9% of total healthcare expenditures[7] and nearly $20 billion in reduced productivity.[8] Annual healthcare expenditures for spine pain increased by 95% from 1999 to 2008, largely due to rising costs for specialty care.[9] Although older adults represent 18.5% of the adult population receiving care for spine pain, they account for an estimated 34% of healthcare expenditures.[10] Given the individual and economic burden of neck pain in our aging society, the identification of safe and cost-effective interventions has become paramount.
Spinal manipulative therapy and exercise are commonly used for the management of neck pain.[11, 12] While emerging evidence supports the use of these treatments,[13–17] there is a paucity of research addressing their effectiveness within older populations. A recent randomized clinical trial (RCT) by our group found spinal manipulative therapy with home exercise was well-tolerated among older adults and resulted in less neck pain compared to home exercise alone.[18, 19]
The number of RCT-based cost-effectiveness analyses (CEAs) of conservative treatments, including spinal manipulative therapy and exercise, for neck pain is limited.[20] To date, no trial-based CEAs of spinal manipulative therapy and exercise have been performed in the U.S., where healthcare costs dramatically differ from other industrialized countries.[21] Further, none of the existing analyses have focused on older adults, who account for a substantial share of healthcare costs.[10]
The purpose of this study was to estimate the cost-effectiveness of home exercise and advice (HEA), spinal manipulative therapy (SMT) plus HEA, and supervised rehabilitative exercise (SRE) plus HEA for older adults with chronic neck pain using cost data collected alongside a RCT.
Methods
The RCT methodology has been detailed previously. [18, 22]
Target Population
Older adults (≥65 years old) with chronic mechanical neck pain (≥3 months duration), a stable prescription pain medication plan, and independent ambulation were included. Neck pain needed to be accompanied by cervical spine stiffness or tenderness, with or without radiating arm pain and non-progressive neurologic deficits (Grades I and II from the Neck Pain Task Force classification[23]) for inclusion. Exclusion criteria included pain ratings less than 3 (0–10 scale), contraindications to study treatments (e.g. spinal infection, bleeding disorders), severe disabling health problems, substance abuse, neck pain litigation, or ongoing non-pharmacological healthcare for neck pain.
Setting and Location
The clinical trial was conducted within a University-based outpatient research clinic in the Minneapolis, Minnesota metropolitan area from 2004 to 2008. Participants were recruited from the general public using newspaper advertisements, direct mailings, and community posters.
Perspective
We adopted a societal perspective for the primary analysis which included costs for healthcare, patient time, transportation, and lost productivity. A healthcare perspective was adopted as a sensitivity analysis.
Interventions
Participants were randomly assigned to 12 weeks of treatment with the following interventions. Participant and provider blinding was not possible. Study interventions were provided by exercise therapists (with a minimum requirement of a bachelor’s degree in exercise science) and licensed chiropractors (with at least 5 years of clinical experience). All providers were trained on treatment delivery protocols and protocol compliance was monitored through chart audits, observations, and team meetings.
Home Exercise and Advice (HEA): Participants in the HEA group received four, one hour sessions with an exercise therapist or chiropractor. Patients were instructed to do daily neck and shoulder exercises at home. In addition to the home exercise instruction, information regarding neck pain and advice on self-management (e.g. ice, heat, ergonomics) was provided. The intervention was considered low dose due to the limited number of visits.
Spinal Manipulative Therapy (SMT) + HEA: Participants in the SMT+HEA group received four, one hour sessions of HEA in addition to a maximum of 20 sessions of SMT by a chiropractor. The number and frequency of treatments was determined by the provider. SMT consisted of high velocity, low amplitude manipulation or low velocity, variable amplitude mobilization to the cervical and thoracic spine.
Supervised Rehabilitative Exercise (SRE) + HEA: Participants in the SRE+HEA group received four, one hour sessions of HEA in addition to 20 one-on-one supervised one hour sessions of SRE by exercise therapists. The exercises consisted of neck and upper body strengthening using rubber tubing in addition to stretching, balance, and coordination exercises. Emphasis was placed on high repetitions and progressively increased resistance. Exercises were preceded by a light aerobic warm-up.
Time horizon & Discount Rate
Costs and clinical outcomes were collected for one year. No discount rate was applied.
Clinical Outcomes
Clinical outcomes were collected twice at baseline (one week apart) and at 4, 12, 26 and 52 weeks post-randomization.
Self-reported pain using the numerical rating scale (0 = no pain; 10 = worst possible pain) was the primary outcome for the clinical trial and the cost effectiveness analysis. The scale has been shown to be reliable and valid for older adults with persistent pain. [24]
Disability was measured using the Neck Disability Index (NDI), an instrument previously shown to be reliable and valid for adults with neck pain.[25, 26] A total NDI score was obtained by summing the responses from individual items and dividing by the maximum possible score resulting in a 0–100 scale, where 0 equals no disability.[27]
Health related quality of life was measured using the Medical Outcomes Study Short Form 36-item Health Survey (SF-36).[28] Quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) were estimated using the SF-6D, a multidimensional utility measure derived from the SF-36.[29] Preferences for SF-6D health states were obtained from a U.S. population using discrete choice experiments.[30] QALYs were additionally estimated using the Euroqol EQ-5D-3L as a sensitivity analysis. Preferences for EQ-5D-3L health states were calculated using published values from a representative sample of the US population elicited by time trade-off methods.[31]
Direct Healthcare Costs
Healthcare utilization was collected using a combination of standardized study provider forms, telephone interviews, and patient self-report questionnaires. Study treatments were recorded at each visit by the provider. Non-study related healthcare use for neck pain was collected by self-report questionnaires and telephone interviews. Participants also reported the number of days and types of medication taken in the past week using self-report questionnaires.
We estimated costs of healthcare resources using 2006 Medicare national allowable payments or relative value units with constant 2006 U.S. dollars (see table 1). Medication costs were estimated using the average cost per prescription day reported within Medicare’s 2008 prescription drug profiles public use file.[32] Cost estimates from years other than 2006 were adjusted for inflation using the annual chained consumer price index.
Table 1.
Unit cost of healthcare resources
| Healthcare resource | Source (2006 Medicare Allowed Charges) | |
|---|---|---|
| Study Treatments | ||
| Spinal manipulative therapy visit | $30.74 | Average resource use from random sample of 20 participants (301 visits) |
| Supervised rehabilitative exercise visit (60 minutes) | $112.80 | HCPCS 97110 (4 units) |
| Home exercise and advice visit (60 minutes) | $115.09 | HCPCS 97110 (3 units) & 97535 (1 unit) |
| Non-study Treatments | ||
| Chiropractic evaluation | $37.07 | HCPCS 99212 |
| Spinal manipulative therapy | $25.37 | HCPCS 98940 |
| Heat | $13.40 | HCPCS 97010 (1 unit) |
| Ultrasound | $12.30 | HCPCS 97035 (1 unit) |
| Acupuncture (60 minutes) | $119.00 | HCPCS 97810 (1 unit) & 97811 (3 units) |
| Manual therapy | $26.52 | HCPCS 97140 (1 unit) |
| Physician evaluation | $51.26 | HCPCS 99213 |
| Physical therapy evaluation | $75.57 | HCPCS 97001 |
| Exercise therapy (30 minutes) | $56.39 | HCPCS 97110 (2 units) |
| Traction | $14.55 | HCPCS 97012 (1 unit) |
| Massage (30 minutes) | $45.79 | HCPCS 97124 (2 units) |
| Cervical spine radiographs | $33.93 | HCPCS 72040 Global |
| Epidural injection | $431.51 | 2006 Average for HCPCS 62310 |
| CT | $251.22 | HCPCS 70490 Global |
| MRI | $500.84 | HCPCS 72141 Global |
| Fusion | $15,181.14 | (Facility + Anesthesiologist + Surgeon Costs) |
| Facility Costs | $12,157.44 | Average reimbursement for DRG's 471–3 |
| Anesthesiologist Costs | $218.68 | 2006 Average for HCPCS 00630 |
| Surgeon Costs | $3,023.70 | (Arthrodesis + Discectomy + Autograft + Instrumentation) |
| - Arthrodesis | $734.35 | HCPCS 22554 |
| - Discectomy | $1,048.68 | HCPCS 63075 |
| - Autograft | $203.62 | HCPCS 20938 |
| - Anterior Instrumentation | $818.37 | HCPCS 22845 |
HCPCS = Healthcare common procedure coding system; DRG = Diagnosis-related group
Indirect Costs
Participant time costs for healthcare utilization and transportation were included using an opportunity cost approach. Standardized time estimates for healthcare resources were multiplied by the U.S. median wage rate for adults 65 and older.[33] Costs for healthcare-related transportation were valued using the average travel distance and time for medical care in the U.S.[34] The U.S. Internal Revenue Service’s2006 standard mileage deduction rate for operating an automobile ($0.445/mile) was used to value travel distance.
Lost productivity costs for paid and unpaid labor were estimated using an adapted question from the U.S. National Health Interview Survey. [35] Participants reported the number of days in the past month they were unable to carry out their daily work (in or away from home) due to neck pain. Productivity costs were valued using the U.S. national median wage rate for adults 65 and older.[33]
Analysis
Intention-to-treat analyses, including all trial participants according to their allocated treatment assignment were used. The cost-effectiveness evaluation was a secondary objective of the clinical trial, which was primarily designed to determine differences in pain between treatment groups after 12 weeks. Accordingly, an estimation approach was used for the cost-effectiveness analysis rather than hypothesis testing.[36] Treatment effectiveness was estimated using linear mixed effect models. Baseline measures of the respective outcomes were included as covariates.[37, 38] Pain, disability and QALYs over the one year study duration were calculated using time weighted averages via linear interpolation.[39]
Generalized estimating equations specifying a poisson distribution and identity link were used to estimate mean costs over the year.[40, 41] Separate models were performed to estimate cost rates for medication use (one week) and lost productivity (one month). Mean costs for medication use and lost productivity over the one-year time horizon were estimated by multiplying the cost rate at each measurement period by the appropriate time interval using linear interpolation. To estimate the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER), treatment strategies were ranked by mean costs. We estimated the mean difference in cost divided by the mean difference in effects (i.e. neck pain, neck disability, QALYs) for treatment strategies that were both more costly and more effective. ICERs were not calculated for “dominated” treatments (i.e. greater mean costs and worse mean effects).[39, 42]
We assessed the uncertainty of cost-effectiveness estimates using the following methods. Bias-corrected bootstrap confidence intervals were calculated using 5000 samples taken with replacement with the subject as the unit of observation.[43] Bootstrapped cost-effect pairs were displayed graphically on the cost effectiveness plane.[36] Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves were created to illustrate the probability of cost-effectiveness at different willingness to pay (WTP) thresholds for a QALY.[44]
Missing Data Analysis
Linear mixed model analyses provide unbiased estimates provided data is missing at random.[45, 46] To explore the potential for data missing not at random we compared mean clinical outcomes for participants with missing and complete primary outcome data at week 52. Sensitivity analyses for data missing not at random were performed using pattern mixture methods.[47, 48] Missing clinical outcome and cost data were imputed separately for each treatment group using multiple imputation (Procedure MI in STATA). Five imputed data sets were created using a multivariate normal model for clinical outcomes and predictive mean matching for costs. The imputation models included clinical outcomes in addition to baseline covariates associated with missing data. The sensitivity analyses for data missing not at random assumed the imputed clinical outcomes and costs were worse by 1) 10% and 2) 50%.
Sensitivity analyses
We assessed the impact of deriving QALYs with the commonly used EQ-5D, the adoption of a healthcare perspective, and the potential for data missing not at random on cost-effectiveness results.
Results
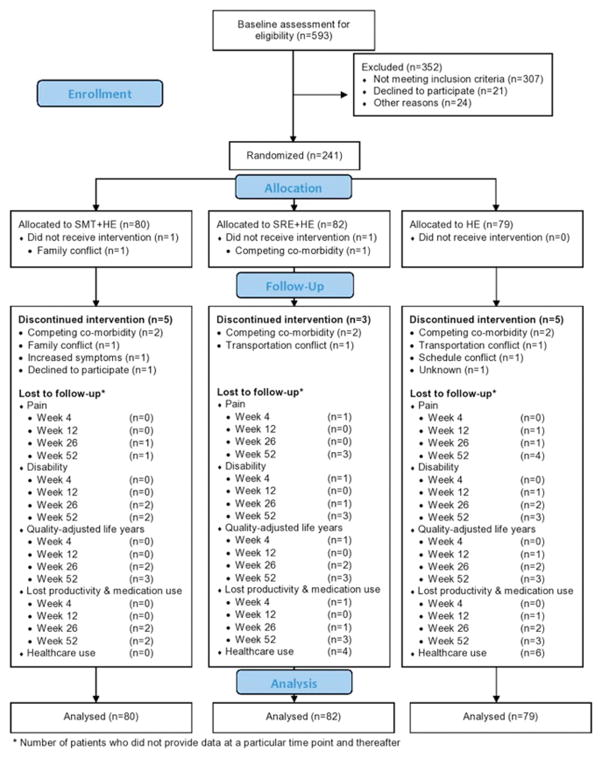
A Consort flow diagram[49] is provided in Figure 1. The number of participants and reasons for discontinuing treatment were similar between groups. Over the one-year time horizon, a total of 17 participants were lost to follow up across the three groups. Baseline clinical and demographic characteristics were similar across groups (Table 2). Approximately one-quarter of participants received care for their neck pain in the three months prior to enrollment.
Figure 1.
CONSORT Flow diagram for clinical outcomes, lost productivity, and healthcare use
Table 2.
Baseline clinical and demographic characteristics
| HEA | SMT + HEA | SRE + HEA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Participants, n | 79 | 80 | 82 |
| Mean age (SD), years | 72.7 (5.3) | 71.7 (5.2) | 72.6 (5.6) |
| Women, n (%) | 35 (44.3) | 36 (45.0) | 42 (51.2) |
| Median duration neck pain (IQR), years | 5.0 (2.0–15.0) | 6.5 (2.0–19.0) | 7.5 (1.8–20.0) |
| Pain radiating to upper extremity, n (%) | 17 (21.5) | 13 (16.3) | 11 (13.4) |
| Timed up & go test (SD), seconds | 11.3 (2.4) | 10.8 (2.1) | 11.3 (2.4) |
| Neck pain (SD), [0–10] | 4.95 (1.26) | 5.33 (1.49) | 4.89 (1.34) |
| Neck disability (SD), [0–100] | 24.23 (9.88) | 22.78 (9.37) | 22.85 (9.20) |
| SF6D-derived quality adjusted life years (SD), [0.1–1] | 0.76 (0.12) | 0.77 (0.12) | 0.77 (0.13) |
| EQ5D-derived quality adjusted life years (SD), [−0.1−1] | 0.80 (0.07) | 0.79 (0.06) | 0.80 (0.09) |
| Employment status | |||
| - Employed, n (%) | 12 (12.5) | 16 (16.8) | 17 (17.7) |
| - Retired, n (%) | 65 (67.7) | 57 (60.0) | 59 (61.5) |
| - Homemaker, n (%) | 8 (8.3) | 7 (7.4) | 8 (8.3) |
| - Other (e.g. unemployed, disabled), n (%) | 11 (11.5) | 15 (15.8) | 12 (12.5) |
| Education level, n (%) | |||
| - Less than high school | 1 (1.3) | 2 (2.5) | 1 (1.2) |
| - High school degree | 23 (29.1) | 24 (30.0) | 23 (28.1) |
| - Some college | 20 (25.3) | 14 (17.5) | 21 (25.6) |
| - Associate or technical degree | 11 (13.9) | 6 (7.5) | 8 (8.5) |
| - College degree | 12 (15.2) | 18 (22.5) | 17 (20.7) |
| - Post-graduate degree | 12 (15.2) | 16 (20.0) | 13 (15.9) |
| Previous Treatment (prior 3 months), n (%) | 18 (22.8) | 27 (33.8) | 19 (23.2) |
| - Medical Doctor | 6 (7.6) | 8 (10.0) | 9 (11.0) |
| - Specialist | 1 (1.3) | 3 (3.8) | 5 (6.1) |
| - Chiropractor | 10 (12.7) | 14 (17.5) | 12 (14.6) |
| - Physical Therapy | 1 (1.3) | 6 (7.5) | 1 (1.2) |
| - Massage | 5 (6.3) | 9 (11.3) | 3 (3.7) |
Outcomes
Group differences in clinical outcomes are provided in Table 3. Overall, SMT+HEA resulted in the greatest reduction of neck pain and disability, and the most gains in QALYs. In terms of neck pain, the primary outcome of the clinical trial, group differences favored SMT+HEA over HEA (0.57 95%CI 0.23 to 0.92) and SRE+HEA (0.41 95%CI 0.05 to 0.76). Results also favored SMT+HEA for reductions of neck disability and QALY gains over HEA (disability = 1.67 95%CI −0.15 to 3.41; QALYs = 0.009 95%CI −0.011 to 0.029) and SRE+HEA (disability = 1.85 95%CI 0.06 to 3.57; QALYs = 0.009 95%CI −0.009 to 0.027). Group differences favored SRE+HEA over HEA for neck pain (0.17 95%CI −0.20 to 0.52), but not neck disability (−0.18 95%CI −1.92 to 1.63) nor QALYs (−0.0001; 95%CI −0.018 to 0.018). 95% confidence intervals for the SMT+HEA vs SRE+HEA neck pain and disability estimates and the SMT+HEA vs HEA neck pain estimate did not cross 0. Other treatment effectiveness estimates had greater uncertainty with 95% confidence intervals that crossed 0.
Table 3.
One year time-weighted clinical outcomes and cumulative costs
| HEA | SMT+HEA | SRE+HEA | SMT+HEA HEA | SMT+HEA - SRE+HEA | SRE+HEA HEA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD)* | Mean (SD)* | Mean (SD)* | Mean (95% CI)† | Mean (95% CI)† | Mean (95% CI)† | |
| Clinical Outcomes | ||||||
|
| ||||||
| Pain Reduction [0–10] | 1.6 (1.9) | 2.4 (2.1) | 1.8 (1.9) | 0.57 (0.23 to 0.92) | 0.41 (0.05 to 0.76) | 0.17 (−0.20 to 0.52) |
| Disability Reduction [0–100] | 6.1 (8.8) | 7.4 (9.9) | 5.6 (8.5) | 1.67 (–0.15 to 3.41) | 1.85 (0.06 to 3.57) | –0.18 (–1.92 to 1.63) |
| QALY Gain (SF6D) [0.1–1] | 0.031 (0.101) | 0.039 (0.106) | 0.030 (0.084) | 0.009 (–0.011 to 0.029) | 0.009 (–0.009 to 0.027) | −0.0001 (−0.018 to 0.018) |
| QALY Gain (EQ5D) [−0.1−1] | 0.020 (0.090) | 0.027 (0.110) | 0.011 (0.090) | 0.007 (−0.012 to 0.025) | 0.015 (−0.004 to 0.033) | −0.009 (−0.025 to 0.009) |
|
| ||||||
| Costs (2006 US $) | ||||||
|
| ||||||
| Healthcare | 779 (281) | 1,297 (1,792) | 2,556 (505) | 515 (225 to 1,094) | −1,260 (−1,562 to −682) | 1,775 (1,590 to 1,948) |
| Lost productivity | 1,390 (1,596) | 548 (844) | 1,042 (1,299) | −842 (−2,194 to −33) | −495 (−1,362 to 104) | −348 (−1,646 to 643) |
| Total indirect | 1,526 (1,597) | 901 (848) | 1,573 (1,302) | −625 (−1,837 to 245) | −672 (−1,481 to −22) | 47 (−1,170 to 1,111) |
| Total | 2,305 (1,634) | 2,198 (2,040) | 4,129 (1,438) | −111 (−1,354 to 899) | −1,932 (−2,796 to −1,097) | 1,821 (592 to 2,912) |
Unadjusted mean (SD);
Model-based results with baseline outcome included as a covariate for clinical outcomes, 95% bias-corrected bootstrap confidence intervals, positive values favor the first treatment contrast;
HEA = Home exercise and advice; SMT = Spinal manipulation therapy; SRE = Supervised rehabilitative exercise; Pain reduction = numerical rating scale, higher scores indicate more improvement; Disability reduction = neck disability index, higher scores indicate more improvement; QALY = Quality-adjusted life year, higher scores indicate more quality adjusted life years; Total indirect costs = lost productivity + time + transportation costs.
Costs
Healthcare, lost productivity, total indirect, and total costs are detailed in Table 3. From the societal perspective, SMT+HEA resulted in the lowest mean costs ($2,198) followed by HEA ($2,305) and SRE+HEA ($4,129). Total costs for SMT+HEA were 47% lower compared to SRE+HEA (mean difference: −$1,932 95%CI −$2,796 to −$1,097), and 5% lower than HEA alone (mean difference: −$111 95%CI −$1,354 to $899). The HEA group reported the lowest mean healthcare costs ($779) followed by SMT+HEA ($1,297) and SRE+HEA ($2,556). Mean lost productivity costs were smallest for SMT+HEA ($548) followed by SRE+HEA ($1,042) and HEA ($1,390). The majority of indirect costs were due to lost productivity. Further details on resource use and costs by treatment group are provided in table 4. Study related treatments accounted for the majority of healthcare costs (HEA: 58%, SMT+HEA: 71%, SRE+HEA: 91%). Over one-quarter of participants were unable to carry out their daily work (in or away from home) for at least one day. Less than 20% of the older adults participating in the trial were employed, and unpaid labor accounted for approximately 75% of lost productivity costs.
Table 4.
Resource use and associated cost over one year
| HEA | SMT+HEA | SRE+HEA | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % use | Mean use (SD) | Mean $ (SD) | % use | Mean use (SD) | Mean $ (SD) | % use | Mean use (SD) | Mean $ (SD) | |
| Study Treatments | |||||||||
| HEA | 100 | 3.9 (0.4) | 449 (44) | 99 | 3.9 (0.5) | 455 (51) | 100 | 3.9 (0.5) | 446 (61) |
| SMT | -- | -- | -- | 99 | 15.1 (3.5) | 463 (107) | -- | -- | -- |
| SRE | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 99 | 16.6 (3.4) | 1,868 (379) |
| Non-study Treatments | |||||||||
| SMT | 13 | 1.0 (4.1) | 25 (103) | 15 | 1.3 (4.3) | 32 (110) | 14 | 0.5 (1.6) | 14 (41) |
| Exercise Therapy | 7 | 0.4 (2.2) | 23 (125) | -- | -- | -- | 9 | 0.7 (2.8) | 41 (159) |
| Physician Evaluation | 7 | 0.1 (0.5) | 5 (26) | 9 | 0.1 (0.3) | 5 (17) | 9 | 0.1 (0.3) | 5 (18) |
| Heat | -- | -- | -- | 1 | 0.01 (0.1) | 0.2 (2) | 3 | 0.1 (1.1) | 2 (15) |
| Ultrasound | 3 | 0.3 (2.1) | 4 (26) | 3 | 0.1 (1.1) | 2 (14) | 3 | 0.1 (0.8) | 2 (10) |
| Massage | 4 | 0.4 (2.3) | 12 (73) | 3 | 0.4 (2.9) | 19 (131) | 1 | 0.04 (0.3) | 2 (15) |
| Acupuncture | 4 | 0.2 (1.3) | 26 (160) | 1 | 0.01 (0.1) | 1 (13) | 1 | 0.06 (0.6) | 8 (67) |
| X-rays | 1 | 0.01 (0.1) | 0.4 (4) | 1 | 0.01 (0.1) | 0.4 (4) | -- | -- | -- |
| CT | 1 | 0.01 (0.1) | 3 (29) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| MRI | 1 | 0.01 (0.1) | 7 (57) | 1 | 0.01 (0.1) | 6 (56) | -- | -- | -- |
| Injection | 3 | 0.03 (0.2) | 11 (69) | -- | -- | -- | 3 | 0.03 (0.2) | 11 (68) |
| Fusion | -- | -- | -- | 1 | 0.01 (0.1) | 190 (1697) | -- | -- | -- |
| Medication | 85 (32) | 110 (57) | 133 (63) | ||||||
| Indirect Costs | |||||||||
| Lost productivity | % | Mean days (SD) | Mean $ (SD) | % | Mean days (SD) | Mean $ (SD) | % | Mean days (SD) | Mean $ (SD) |
| Paid labor | 6 | 3.5 (8.1) | 407 (945) | 6 | 2.0 (6.5) | 235 (752) | 2 | 0.4 (0.9) | 42 (102) |
| Unpaid labor | 19 | 8.4 (11.2) | 976 (1,308) | 19 | 2.7 (3.4) | 312 (395) | 32 | 8.5 (11.1) | 995 (1,293) |
| Total | 25 | 11.9 (13.7) | 1,390 (1,596) | 25 | 4.7 (7.2) | 548 (844) | 34 | 8.9 (11.1) | 1,042 (1,299) |
| Patient time | 74 (34) | 147 (63) | 311 (62) | ||||||
| Transportation | 63 (45) | 206 (53) | 220 (51) | ||||||
HEA = Home exercise and advice; SMT = Spinal manipulation therapy; SRE = Supervised rehabilitative exercise
Cost-effectiveness
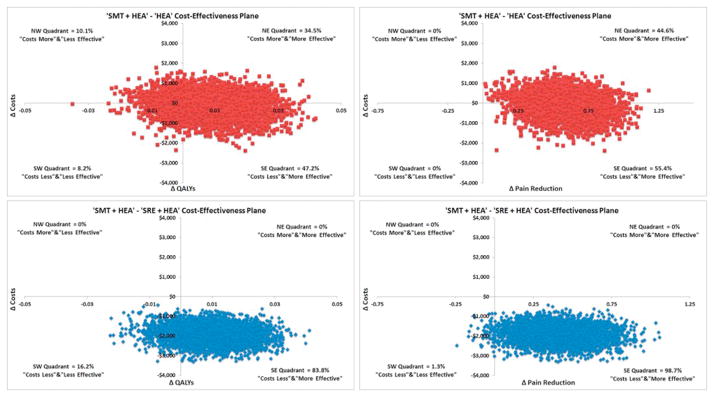
Cost-effectiveness results are provided in Table 5. From the societal perspective, SMT+HEA resulted in lower costs, and greater improvements in pain, disability, and QALYs relative to SRE+HEA and HEA, leading to treatment dominance. Figure 2 displays the 5000 bootstrap replicates of the SMT+HEA treatment contrasts on the cost-effectiveness planes for QALYs and pain. All bootstrap replicates found SMT+HEA was less expensive than SRE+HEA, and 84% and 99% of the replicates favored SMT+HEA for QALYs and pain, respectively. When adding SMT to HEA, bootstrap replicates crossed all four quadrants of the cost-effectiveness plane for QALYs. 47% of replicates found SMT+HEA to be dominant, 10% revealed HEA to be dominant, and the remaining 45% found adding SMT to HEA was either more expensive and more effective or less expensive and less effective. For pain, 55% of the bootstrap replicates found adding SMT to HEA was less expensive and more effective.
Table 5.
Cost-effectiveness results
| Mean Costs (SD)* |
Δ Costs (95% CI)† |
Mean Outcome (SD)* |
Δ Outcomes (95% CI)† |
ICER (95% CI)† |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Societal Perspective | |||||
| Pain Reduction | |||||
|
| |||||
| SMT + HEA | $2,198 ($2,040) | - | 2.4 (2.1) | - | Reference |
| HEA | $2,305 ($1,634) | - | 1.6 (1.9) | - | Dominated‡ |
| SRE + HEA | $4,129 ($1,438) | - | 1.8 (1.9) | - | Dominated‡ |
|
| |||||
| Disability Reduction | |||||
|
| |||||
| SMT + HEA | $2,198 ($2,040) | - | 7.4 (9.9) | - | Reference |
| HEA | $2,305 ($1,634) | - | 6.1 (8.8) | - | Dominated‡ |
| SRE + HEA | $4,129 ($1,438) | - | 5.6 (8.5) | - | Dominated‡ |
|
| |||||
| QALYs Gained (SF-6D) | |||||
|
| |||||
| SMT + HEA | $2,198 ($2,040) | - | 0.039 (0.106) | - | Reference |
| HEA | $2,305 ($1,634) | - | 0.031 (0.101) | - | Dominated‡ |
| SRE + HEA | $4,129 ($1,438) | - | 0.030 (0.084) | - | Dominated‡ |
|
| |||||
| Sensitivity Analyses | |||||
| QALYs Gained (EQ-5D) | |||||
|
| |||||
| SMT + HEA | $2,198 ($2,040) | - | 0.027 (0.110) | - | Reference |
| HEA | $2,305 ($1,634) | - | 0.020 (0.090) | - | Dominated‡ |
| SRE + HEA | $4,129 ($1,438) | - | 0.011 (0.090) | - | Dominated‡ |
|
| |||||
| Healthcare Perspective | |||||
| Pain Reduction | |||||
|
| |||||
| HEA | $779 ($281) | - | 1.6 (1.9) | - | Reference |
| SMT + HEA | $1,297 ($1,792) | $515 ($225 to $1,094) | 2.4 (2.1) | 0.57 (0.23 to 0.92) | $895 ($317 to $3,178) ¥ |
| SRE + HEA | $2,556 ($505) | - | 1.8 (1.9) | - | Dominated‡ |
|
| |||||
| Disability Reduction | |||||
|
| |||||
| HEA | $779 ($281) | - | 6.1 (8.8) | - | Reference |
| SMT + HEA | $1,297 ($1,792) | $515 ($225 to $1,094) | 7.4 (9.9) | 1.67 (-0.15 to 3.41) | $308 ($97 to Dominated‡) ¥ |
| SRE + HEA | $2,556 ($505) | - | 5.6 (8.5) | - | Dominated‡ |
|
| |||||
| QALYs Gained (SF6D) | |||||
|
| |||||
| HEA | $779 ($281) | - | 0.031 (0.101) | - | Reference |
| SMT + HEA | $1,297 ($1,792) | $515 ($225 to $1,094) | 0.039 (0.106) | 0.009 (-0.011 to 0.029) | $55,975 ($18,733 to Dominated‡) ¥ |
| SRE + HEA | $2,556 ($505) | - | 0.030 (0.084) | - | Dominated‡ |
Unadjusted mean (SD);
Adjusted mean (95% bias-corrected bootstrap confidence intervals) from longitudinal model for treatments with higher costs and better outcomes;
Dominated = worse mean outcome and higher mean cost;
ICERs are calculated based on 7 digit accuracy of Δ in costs and outcomes, reported Δ in costs and outcomes were rounded for presentation;
HEA = Home exercise and advice; ICER = Incremental cost-effectiveness ratio; SMT = Spinal manipulation therapy; SRE = Supervised rehabilitative exercise; QALY = Quality-adjusted life year
Figure 2.
Cost-QALY and cost-pain reduction pairs for spinal manipulation therapy (SMT) when added to home exercise and advice (HEA), and SMT+HEA compared to supervise rehabilitative exercise (SRE) plus HEA plotted on the cost-effectiveness plane from the societal perspective
Results of sensitivity analyses are provided in Table 5. Group differences for QALYs derived with the commonly used EQ-5D were very similar to the base case analysis, and did not impact the cost-effectiveness results. If adopting a healthcare perspective, adding SMT to HEA resulted in 66% higher costs (mean difference: $515 95%CI $225 to $1,094) and ICERs of $895 for pain, $308 for disability, and $55,975 for QALYs.
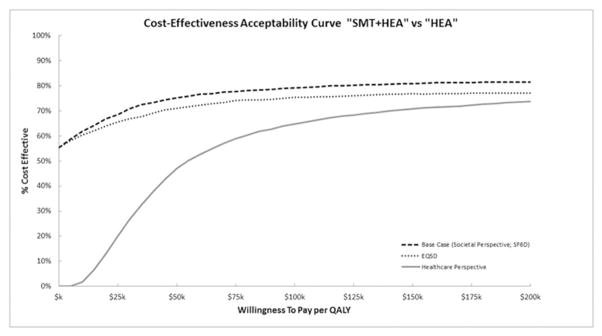
Figure 3 shows cost-effectiveness acceptability curves (CEAC) for adding SMT to HEA using sensitivity analyses. The most favorable CEAC for adding SMT to HEA was the base case analysis with a 75% probability of cost-effectiveness at a WTP threshold of $50k per QALY. Small increases in cost-effectiveness were observed at higher threshold values. Using the EQ-5D to value QALYs results in small decreases (<5%) in the probability of cost-effectiveness relative to the base case analysis. If a healthcare perspective is adopted, the probability of cost-effectiveness decreases to 47% at a WTP threshold of $50k, 65% at a WTP threshold of $100k, and 71% at a WTP threshold of $150k.
Figure 3.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for base case and sensitivity analyses when adding spinal manipulation therapy (SMT) to home exercise and advice (HEA) for QALYs
Missing data analyses
Study participants with missing data at week 52 reported higher pain and disability, and lower QALYs at prior assessments compared to participants with complete data, which suggests data may be missing not at random. Sensitivity analyses for data missing not at random produced very similar results to the primary analysis with minimal impact on the magnitude of group differences for both clinical outcomes and costs.
Discussion
This is the first reported RCT based cost-effectiveness analysis addressing the management of chronic mechanical neck pain in older adults. We collected self-report data on healthcare utilization and lost productivity to estimate the relative cost-effectiveness of home exercise and advice (HEA), spinal manipulative therapy (SMT) plus HEA, and supervised rehabilitative exercise (SRE) plus HEA. Adding SMT to HEA resulted in a 5% decrease in total societal costs and better outcomes. Although there is uncertainty surrounding the dominance of SMT+HEA from the societal perspective, the cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for adding SMT to HEA is favorable with a 0.75 probability of cost-effectiveness for willingness to pay thresholds greater than $50,000 per QALY. SMT+HEA also resulted in 47% lower costs and better outcomes relative to SRE+HEA. Overall, the additional exercise sessions (~16) attended by the SRE+HEA group conferred little advantage to 4 sessions of HEA alone. Mean annual healthcare costs for individuals within the HEA ($779) and SMT+HEA groups ($1297) were well below national estimates for spine pain (roughly $2600 in 2006 U.S. dollars).[7, 50]
The perspective from which cost-effectiveness analyses are performed can have an important impact. In this study, when the societal perspective was adopted (incorporating lost productivity), the addition of SMT to HEA was less costly. When the healthcare perspective was considered (excluding lost productivity), adding SMT to HEA was more costly. Whether the additional healthcare costs for SMT are worthwhile depends on how much insurers and patients are willing to pay for health outcomes. Currently, there is no consensus on threshold values for QALYs or other health outcomes within the U.S. [51, 52] The ICER of $55,975 for a QALY when adding SMT to HEA is below thresholds recommended by the World Health Organization (3 times the 2006 per-capita gross domestic product = $118,635)[53, 54] and Brathwaite and colleagues ($109,000 to $297,000; using 2003 U.S. dollars).[55] Inflating to 2014 U.S. dollars would result in an ICER of $65,731 per QALY gained which is still below the World Health Organizations’ recommended threshold (3 times the 2014 per-capita gross domestic product = $163,889).[54] The interpretation of ICERs for outcomes specific to neck pain can be aided by framing the additional costs needed for clinically important differences. Clinically important differences for individual improvement are estimated at 1 to 2.5 for neck pain (0–10 scale)[56, 57] and 7 to 19 for neck disability (0–100 scale)[57, 58]. Achieving similar mean group differences when adding SMT to HEA requires an additional $895 to $2,238 for neck pain and $2,156 to $5,852 for neck disability. Inflating costs to 2014 U.S. dollars results in an additional $1,060 to $2,649 for neck pain and $2,534 to $6,878 for neck disability. Individual patient estimates of clinically important differences are a conservative measure for interpreting ICERs, as the magnitude of clinically important group differences are likely smaller.[59]
The inclusion of lost productivity costs increases the value of SMT for older adults with chronic neck pain. The most appropriate method for including lost productivity within cost-effectiveness analyses has been contentiously debated.[60, 61] While recent evidence has shown that approximately half of the public includes lost productivity when valuing health states, their inclusion has little to no impact on QALYs.[62, 63] Accordingly, there have been recommendations to include lost productivity as a “cost” to ensure it is properly accounted for.[63] This is especially important for chronic pain conditions, where a substantial amount of societal burden is attributed to lost productivity.[8, 64]
Previously published RCT-based cost-effectiveness analyses for neck pain have included a limited number of older adults and none have been performed in the U.S. A 2012 systematic review of economic evaluations of conservative treatments for neck pain identified five cost-effectiveness analyses all performed within Europe.[20] Three studies share similar characteristics to our trial and are suitable for comparison.[65–67] All three studies found manual therapy to result in less total costs, and more QALYs relative to exercise. One study by Kortals de Bos also found similar advantages in terms of pain and disability;[65] however, the studies by Bosmans[67] and Lewis[66] did not. This discrepancy might be explained by differences in treatment content and dose, and the age of the population. We searched for additional studies published before March 2015 using the same search strategy reported in the 2012 systematic review which queried Medline, EMBASE, EconLit, EURONHEED, and NHS EED. Our updated literature search identified an additional trial by Manca et al.[68, 69] which found usual physiotherapy (which included exercise in 21% and manual therapy in 25% of visits) produced higher healthcare expenditures and total costs, but also more QALYs and less disability relative to a brief physiotherapy intervention.
The majority of cost-effectiveness analyses do not address lost productivity costs for work done outside the labor market (e.g. household or volunteer work), which is especially relevant for older adults.[61, 70] A strength of this study is that it included lost productivity costs related to both paid and unpaid work, reflecting meaningful impacts of chronic pain to older individuals and society. Other strengths of this study include the randomized design to limit selection bias when determining differences in healthcare resource use, lost productivity, and clinical outcomes, the limited amount of missing data, and the adoption of both societal and healthcare perspectives.
This study also has several limitations. Similar to other cost-effectiveness analyses conducted alongside RCTs [71], the economic analysis was a secondary aim of the primary clinical trial which was not powered for differences in costs or QALYs. Although cost-effectiveness analyses conducted alongside RCTs are often underpowered, they are the strongest study design for limiting bias when estimating differences in costs and outcomes, the primary goal of economic evaluations.[36, 71] Another limitation is the use of self-report for healthcare and medication utilization. Obtaining healthcare claims for trial participants would provide a more valid measure of healthcare use and cost; however, some level of self-reported utilization is necessary when including costs for non-covered services (e.g. massage, acupuncture) and over the counter medications. Finally, concerns may be raised about the generalizability of results from a single-center RCT. However, participants in this study were similar to other populations of older adults in the U.S. with neck or back pain.[72, 73]
Conclusions
On average, SMT+HEA resulted in better clinical outcomes and lower total societal costs relative to SRE+HEA and HEA alone, with a 0.75 to 0.81 probability of cost-effectiveness for willingness to pay thresholds of $50,000 to $200,000 per QALY.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Institute of Health (NIH) and Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA). The primary clinical trial was funded by the Health Resources and Services Administration (#R18HP01425). Brent Leininger is supported by a post-doctoral fellowship training grant through the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health at the NIH(#F32AT007507). Research reported in this publication was also supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (#P60AR062799) and the Dartmouth Clinical and Translational Science Institute, under award number UL1TR001086 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) of the NIH. The content is solely the responsibility of the author(s) and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH or HRSA.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Institute of Medicine. Relieving Pain in America: A Blueprint for Transforming Prevention, Care, Education, and Research. Washington (DC): National Academies Press; 2011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Johannes CB, Le TK, Zhou X, Johnston JA, Dworkin RH. The prevalence of chronic pain in United States adults: results of an Internet-based survey. The journal of pain : official journal of the American Pain Society. 2010;11(11):1230–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2010.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hoy D, March L, Woolf A, et al. The global burden of neck pain: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2014;73(7):1309–15. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Murray CJ, Atkinson C, Bhalla K, et al. The state of US health, 1990–2010: burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors. JAMA. 2013;310(6):591–608. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.13805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hartvigsen J, Christensen K, Frederiksen H. Back and neck pain exhibit many common features in old age: a population-based study of 4,486 Danish twins 70–102 years of age. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2004;29(5):576–80. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000099394.18994.2f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Patel KV, Guralnik JM, Dansie EJ, Turk DC. Prevalence and impact of pain among older adults in the United States: findings from the 2011 National Health and Aging Trends Study. Pain. 2013;154(12):2649–57. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.07.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Martin BI, Deyo RA, Mirza SK, et al. Expenditures and health status among adults with back and neck problems. JAMA. 2008;299(6):656–64. doi: 10.1001/jama.299.6.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Stewart WF, Ricci JA, Chee E, Morganstein D, Lipton R. Lost productive time and cost due to common pain conditions in the US workforce. JAMA. 2003;290(18):2443–54. doi: 10.1001/jama.290.18.2443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Davis MA, Onega T, Weeks WB, Lurie JD. Where the United States spends its spine dollars: expenditures on different ambulatory services for the management of back and neck conditions. Spine. 2012;37(19):1693–701. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182541f45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Luo X, Pietrobon R, Sun SX, Liu GG, Hey L. Estimates and patterns of direct health care expenditures among individuals with back pain in the United States. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2004;29(1):79–86. doi: 10.1097/01.BRS.0000105527.13866.0F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hurwitz EL. Epidemiology: spinal manipulation utilization. Journal of electromyography and kinesiology : official journal of the International Society of Electrophysiological Kinesiology. 2012;22(5):648–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jelekin.2012.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Freburger JK, Carey TS, Holmes GM, et al. Exercise prescription for chronic back or neck pain: who prescribes it? who gets it? What is prescribed? Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61(2):192–200. doi: 10.1002/art.24234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bronfort G, Evans R, Anderson AV, Svendsen KH, Bracha Y, Grimm RH. Spinal manipulation, medication, or home exercise with advice for acute and subacute neck pain: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2012;156(1 Pt 1):1–10. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-156-1-201201030-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Furlan AD, Yazdi F, Tsertsvadze A, et al. Complementary and alternative therapies for back pain II. Evidence report/technology assessment. 2010;(194):1–764. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gross A, Kay TM, Paquin JP, et al. Exercises for mechanical neck disorders. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;1:CD004250. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004250.pub5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gross A, Miller J, D'Sylva J, et al. Manipulation or mobilisation for neck pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;(1):CD004249. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004249.pub3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Miller J, Gross A, D'Sylva J, et al. Manual therapy and exercise for neck pain: A systematic review. Man Ther. 2010 doi: 10.1016/j.math.2010.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Maiers M, Bronfort G, Evans R, et al. Spinal manipulative therapy and exercise for seniors with chronic neck pain. The spine journal : official journal of the North American Spine Society. 2014;14(9):1879–89. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2013.10.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Maiers M, Evans R, Hartvigsen J, Schulz C, Bronfort G. Adverse events among seniors receiving spinal manipulation and exercise in a randomized clinical trial. Manual therapy. 2015;20(2):335–41. doi: 10.1016/j.math.2014.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Driessen MT, Lin CW, van Tulder MW. Cost-effectiveness of conservative treatments for neck pain: a systematic review on economic evaluations. European spine journal : official publication of the European Spine Society, the European Spinal Deformity Society, and the European Section of the Cervical Spine Research Society. 2012;21(8):1441–50. doi: 10.1007/s00586-012-2272-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Anderson GF, Reinhardt UE, Hussey PS, Petrosyan V. It's the prices, stupid: why the United States is so different from other countries. Health affairs (Project Hope) 2003;22(3):89–105. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.22.3.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Maiers MJ, Hartvigsen J, Schulz C, Schulz K, Evans RL, Bronfort G. Chiropractic and exercise for seniors with low back pain or neck pain: the design of two randomized clinical trials. BMC musculoskeletal disorders. 2007;8:94. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-8-94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Guzman J, Hurwitz EL, Carroll LJ, et al. A new conceptual model of neck pain: linking onset, course, and care: the Bone and Joint Decade 2000–2010 Task Force on Neck Pain and Its Associated Disorders. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2008;33(4 Suppl):S14–23. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181643efb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wood BM, Nicholas MK, Blyth F, Asghari A, Gibson S. Assessing Pain in Older People With Persistent Pain: The NRS Is Valid But Only Provides Part of the Picture. The Journal of Pain. 2010;11(12):1259–66. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2010.02.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vernon H, Mior S. The Neck Disability Index: a study of reliability and validity. Journal of manipulative and physiological therapeutics. 1991;14(7):409–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.McCarthy MJH, Grevitt MP, Silcocks P, Hobbs G. The reliability of the Vernon and Mior neck disability index, and its validity compared with the short form-36 health survey questionnaire. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(12):2111–7. doi: 10.1007/s00586-007-0503-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.MacDermid JC, Walton DM, Avery S, et al. Measurement properties of the neck disability index: a systematic review. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2009;39(5):400–17. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2009.2930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ware JE, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992;30(6):473–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Brazier J, Roberts J, Deverill M. The estimation of a preference-based measure of health from the SF-36. J Health Econ. 2002;21(2):271–92. doi: 10.1016/s0167-6296(01)00130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Craig BM, Pickard AS, Stolk E, Brazier JE. US valuation of the SF-6D. Medical decision making : an international journal of the Society for Medical Decision Making. 2013;33(6):793–803. doi: 10.1177/0272989X13482524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Shaw JW, Johnson JA, Coons SJ. US valuation of the EQ-5D health states: development and testing of the D1 valuation model. Medical care. 2005;43(3):203–20. doi: 10.1097/00005650-200503000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. CMS 2008 Prescription Drug Profiles Public Use File. Available from: http//:www.cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems/Statistics-Trends-and-Reports/BSAPUFS/Prescription_Drug_Profiles.html.
- 33.Bureau of Labor Statistics, US Department of Labor. Highlights of Women's Earnings in 2006. 2007. Report No.: 1000. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Probst JC, Laditka SB, Wang JY, Johnson AO. Mode of Travel and Actual Distance Traveled for Medical and Dental Care by Rural and Urban Residents. South Carolina Rural Health Research Center; 2006. [on 1 August 2015]. Accessed at http://rhr.sph.sc.edu/report/(6-1)%20Mode%20of%20Travel%20and%20Actual%20Distance%20Traveled.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Adams PF, Hendershot GE, Marano MA Centers for Disease C, Prevention/National Center for Health S. Current estimates from the National Health Interview Survey, 1996. Vital and health statistics Series 10, Data from the National Health Survey. 1999;(200):1–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Briggs AH, O'Brien BJ, Blackhouse G. Thinking outside the box: recent advances in the analysis and presentation of uncertainty in cost-effectiveness studies. Annual review of public health. 2002;23:377–401. doi: 10.1146/annurev.publhealth.23.100901.140534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Manca A, Hawkins N, Sculpher MJ. Estimating mean QALYs in trial-based cost-effectiveness analysis: the importance of controlling for baseline utility. Health Econ. 2005;14(5):487–96. doi: 10.1002/hec.944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Nixon RM, Thompson SG. Methods for incorporating covariate adjustment, subgroup analysis and between-centre differences into cost-effectiveness evaluations. Health Econ. 2005;14(12):1217–29. doi: 10.1002/hec.1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Drummond MF, Sculpher MJ, Torrance GW, O'Brien BJ, Stoddart GL. Methods for the Economic Evaluation of Health Care Programmes. Oxford University Press; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mihaylova B, Briggs A, O'Hagan A, Thompson SG. Review of statistical methods for analysing healthcare resources and costs. Health economics. 2011;20(8):897–916. doi: 10.1002/hec.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Barber J, Thompson S. Multiple regression of cost data: use of generalised linear models. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2004;9(4):197–204. doi: 10.1258/1355819042250249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hunink M, Weinstein M, Wittenberg E, et al. Decision making in health and medicine: integrating evidence and values. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Briggs AH, Wonderling DE, Mooney CZ. Pulling cost-effectiveness analysis up by its bootstraps: a non-parametric approach to confidence interval estimation. Health economics. 1997;6(4):327–40. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1099-1050(199707)6:4<327::aid-hec282>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Fenwick E, O'Brien BJ, Briggs A. Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves--facts, fallacies and frequently asked questions. Health economics. 2004;13(5):405–15. doi: 10.1002/hec.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Briggs A, Clark T, Wolstenholme J, Clarke P. Missing... presumed at random: cost-analysis of incomplete data. Health economics. 2003;12(5):377–92. doi: 10.1002/hec.766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Diggle P, Heagerty P, Liang K, Zeger S. Analysis of longitudinal data. Oxford University Press; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Faria R, Gomes M, Epstein D, White IR. A Guide to Handling Missing Data in Cost-Effectiveness Analysis Conducted Within Randomised Controlled Trials. PharmacoEconomics. 2014;32(12):1157–70. doi: 10.1007/s40273-014-0193-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Carpenter JR, Kenward MG. Missing data in randomised controlled trials—a practical guide. Birmingham, UK: National Institute for Health Researc; 2007. [on 1 August 2015]. Accessed at http://missingdata.lshtm.ac.uk/downloads/rm04_jh17_mk.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Schulz KF, Altman DG, Moher D CONSORT Group. CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomized trials. Ann Intern Med. 2010;152(11):726–32. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-152-11-201006010-00232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Pasquale MK, Dufour R, Schaaf D, et al. Pain conditions ranked by healthcare costs for members of a national health plan. Pain Pract. 2014;14(2):117–31. doi: 10.1111/papr.12066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Weinstein MC. How much are Americans willing to pay for a quality-adjusted life year? Med Care. 2008;46(4):343–5. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e31816a7144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Neumann PJ, Cohen JT, Weinstein MC. Updating cost-effectiveness--the curious resilience of the $50,000-per-QALY threshold. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(9):796–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1405158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hutubessy R, Chisholm D, Edejer TT. Generalized cost-effectiveness analysis for national-level priority-setting in the health sector. Cost Eff Resour Alloc. 2003;1(1):8. doi: 10.1186/1478-7547-1-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.The World Bank. [on 1 August 2015];GDP per capita (Current US$) Accessed at: http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.PCAP.CD.
- 55.Braithwaite RS, Meltzer DO, King JT, Jr, Leslie D, Roberts MS. What does the value of modern medicine say about the $50,000 per quality-adjusted life-year decision rule? Med Care. 2008;46(4):349–56. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e31815c31a7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Dworkin RH, Turk DC, Wyrwich KW, et al. Interpreting the clinical importance of treatment outcomes in chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. The journal of pain : official journal of the American Pain Society. 2008;9(2):105–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2007.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Pool JJ, Ostelo RW, Hoving JL, Bouter LM, de Vet HC. Minimal clinically important change of the Neck Disability Index and the Numerical Rating Scale for patients with neck pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007;32(26):3047–51. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31815cf75b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Cleland JA, Childs JD, Whitman JM. Psychometric properties of the Neck Disability Index and Numeric Pain Rating Scale in patients with mechanical neck pain. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2007.08.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dworkin RH, Turk DC, McDermott MP, et al. Interpreting the clinical importance of group differences in chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain. 2009;146:238–44. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.08.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Nyman JA. Productivity Costs Revisited: Toward a New US Policy. Health economics. 2012;21(12):1387–401. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Krol M, Brouwer W, Rutten F. Productivity costs in economic evaluations: past, present, future. PharmacoEconomics. 2013;31(7):537–49. doi: 10.1007/s40273-013-0056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Tilling C, Krol M, Tsuchiya A, Brazier J, Brouwer W. In or out? Income losses in health state valuations: a review. Value in health : the journal of the International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research. 2010;13(2):298–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2009.00614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Tilling C, Krol M, Tsuchiya A, Brazier J, Exel J, Brouwer W. Does the EQ-5D reflect lost earnings? PharmacoEconomics. 2012;30(1):47–61. doi: 10.2165/11539910-000000000-00000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Gaskin DJ, Richard P. The economic costs of pain in the United States. The journal of pain : official journal of the American Pain Society. 2012;13(8):715–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2012.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Korthals-de Bos IB, Hoving JL, van Tulder MW, et al. Cost effectiveness of physiotherapy, manual therapy, and general practitioner care for neck pain: economic evaluation alongside a randomised controlled trial. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 2003;326(7395):911. doi: 10.1136/bmj.326.7395.911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Lewis M, James M, Stokes E, et al. An economic evaluation of three physiotherapy treatments for non-specific neck disorders alongside a randomized trial. Rheumatology. 2007;46(11):1701–8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kem245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bosmans JE, Pool JJ, de Vet HC, van Tulder MW, Ostelo RW. Is behavioral graded activity cost-effective in comparison with manual therapy for patients with subacute neck pain? An economic evaluation alongside a randomized clinical trial. Spine. 2011;36(18):E1179–86. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31820644ed. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Manca A, Epstein DM, Torgerson DJ, et al. Randomized trial of a brief physiotherapy intervention compared with usual physiotherapy for neck pain patients: cost-effectiveness analysis. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2006;22(1):67–75. doi: 10.1017/s0266462306050859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Klaber Moffett JA, Jackson DA, Richmond S, et al. Randomised trial of a brief physiotherapy intervention compared with usual physiotherapy for neck pain patients: outcomes and patients' preference. BMJ. 2005;330(7482):75. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38286.493206.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Krol M, Brouwer W. How to estimate productivity costs in economic evaluations. PharmacoEconomics. 2014;32(4):335–44. doi: 10.1007/s40273-014-0132-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Hollingworth W, McKell-Redwood D, Hampson L, Metcalfe C. Cost-utility analysis conducted alongside randomized controlled trials: are economic end points considered in sample size calculations and does it matter? Clin Trials. 2013;10(1):43–53. doi: 10.1177/1740774512465358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Fritz JM, Hunter SJ, Tracy DM, Brennan GP. Utilization and clinical outcomes of outpatient physical therapy for medicare beneficiaries with musculoskeletal conditions. Phys Ther. 2011;91(3):330–45. doi: 10.2522/ptj.20090290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Jarvik JG, Comstock BA, Heagerty PJ, et al. Back pain in seniors: the Back pain Outcomes using Longitudinal Data (BOLD) cohort baseline data. BMC musculoskeletal disorders. 2014;15:134. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-15-134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]