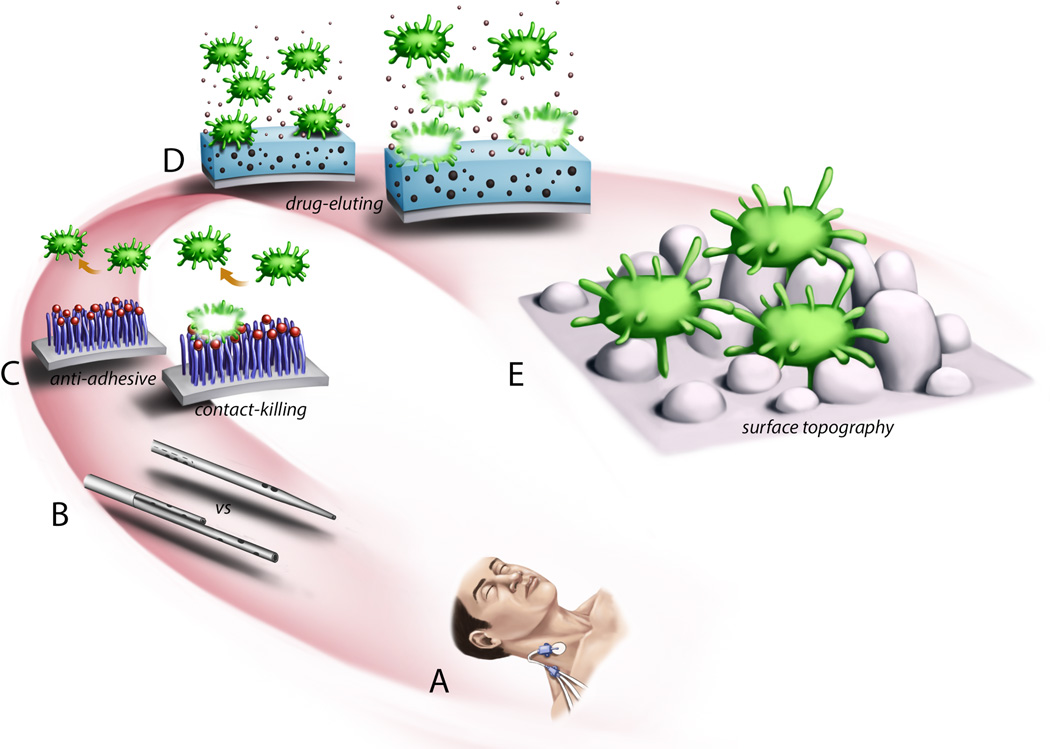
Figure 4.
Demonstration of specific preventative anti-infective strategies mapped onto the length-scale conceptualization of implantable device related infection. (A) Chlorhexidine sponge at the insertion site of a triple lumen central venous catheter to reduce transport of skin bacteria along the catheter to the bloodstream. (B) Dialysis catheters with different geometries can altered blood flow patterns which results in altered transport of cells or other materials to the catheter surface. (C) Polymer coatings with specific chemical end groups that prevent adhesion or have antibacterial properties upon contact. (D) Devices can be impregnated with antimicrobial substances that are eluted to kill bacteria in proximity to the device surface. (E) Nano-scale patterning of a surface can alter bacterial adhesion and proliferation.