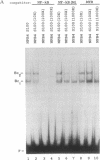
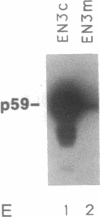
Abstract
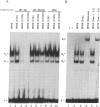
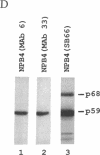
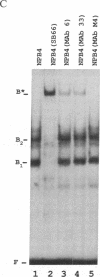
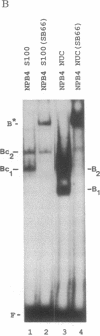
The avian reticuloendotheliosis virus T contains within its genome the oncogene rel. The expression of this gene is responsible for the induction of lymphoid tumors in birds. Recently, the rel gene was shown to be related to the p50 DNA binding subunit of the transcription factor complex NF-kappa B. Binding sites for the NF-kappa B complex are found in the enhancer regions of a number of genes, including the immunoglobulin kappa gene and the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat. In this communication we identify an activity from avian reticuloendotheliosis virus T-transformed avian lymphoid cells that binds in an electrophoretic-mobility-shift assay to an NF-kappa B binding site from the kappa enhancer. This activity contains proteins immunologically related to rel, as detected by polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies directed against v-rel. In a DNA affinity precipitation assay using the NF-kappa B site from the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat, v-rel and several other proteins were identified. These data suggest that oncogenic transformation by v-rel is the result of an altered pattern of gene expression.
Full text
PDF

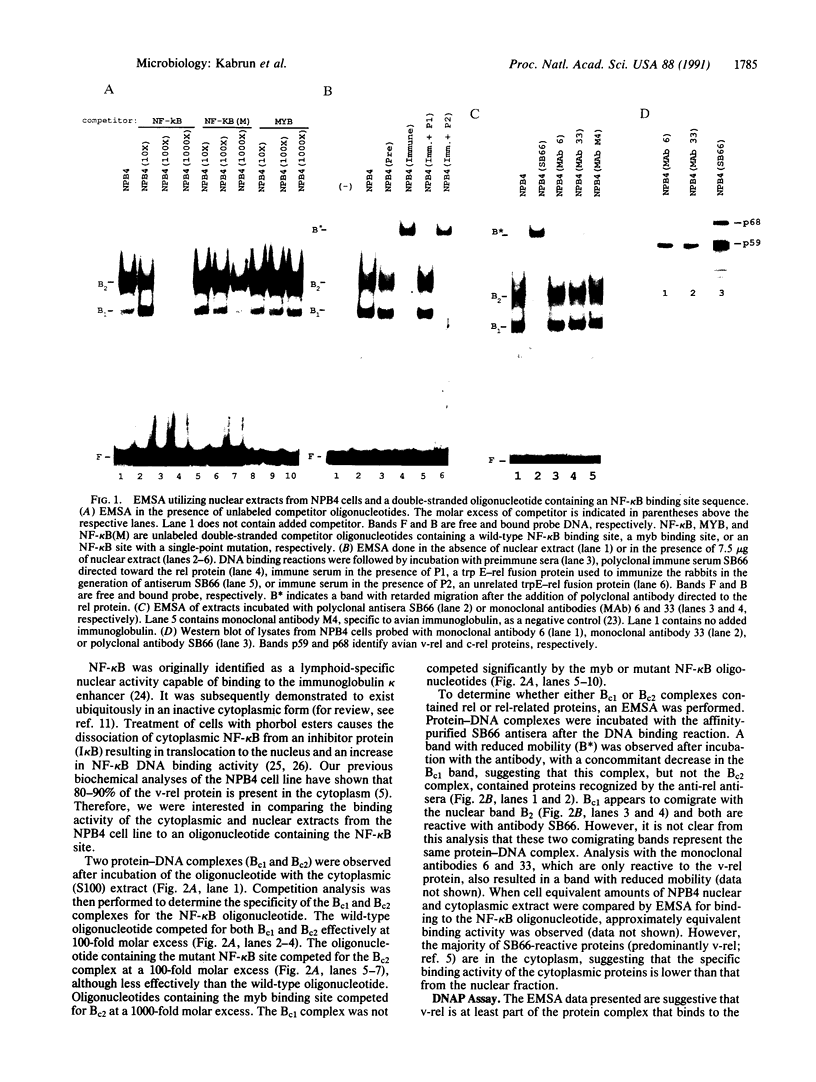
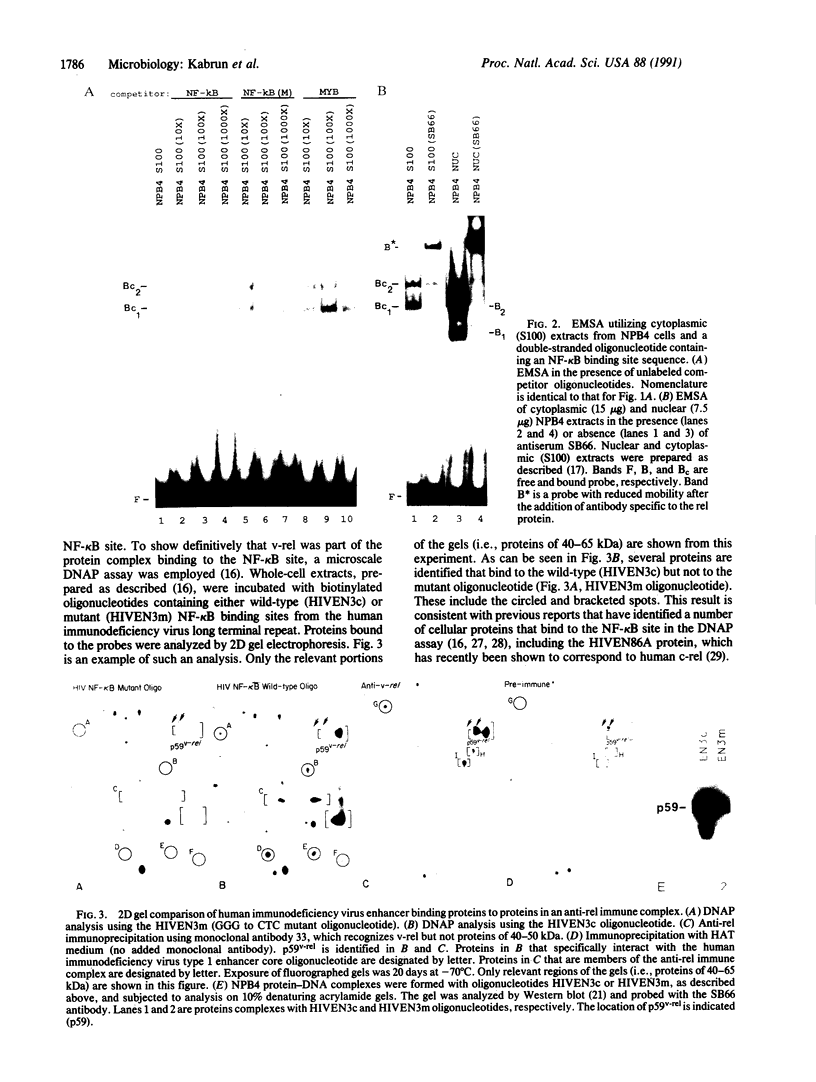

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Müller H., Grieser S., Doederlein G., Graf T. Hematopoietic cells transformed in vitro by REVT avian reticuloendotheliosis virus express characteristics of very immature lymphoid cells. Virology. 1981 Dec;115(2):295–309. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull P., Morley K. L., Hoekstra M. F., Hunter T., Verma I. M. The mouse c-rel protein has an N-terminal regulatory domain and a C-terminal transcriptional transactivation domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5473–5485. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capobianco A. J., Simmons D. L., Gilmore T. D. Cloning and expression of a chicken c-rel cDNA: unlike p59v-rel, p68c-rel is a cytoplasmic protein in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):257–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. L., Lehmeyer J. E., Cooper M. D. Evidence for an IgD homologue on chicken lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2580–2585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I. S., Mak T. W., O'Rear J. J., Temin H. M. Characterization of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T DNA and isolation of a novel variant of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T by molecular cloning. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):800–811. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.800-811.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franza B. R., Jr, Josephs S. F., Gilman M. Z., Ryan W., Clarkson B. Characterization of cellular proteins recognizing the HIV enhancer using a microscale DNA-affinity precipitation assay. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):391–395. doi: 10.1038/330391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gélinas C., Temin H. M. The v-rel oncogene encodes a cell-specific transcriptional activator of certain promoters. Oncogene. 1988 Oct;3(4):349–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannink M., Temin H. M. Transactivation of gene expression by nuclear and cytoplasmic rel proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4323–4336. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamens J., Richardson P., Mosialos G., Brent R., Gilmore T. Oncogenic transformation by vrel requires an amino-terminal activation domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2840–2847. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Scheidereit C., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human immunoglobulin-enhancer-binding protein (NF-kappa B) that activates transcription from a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4700–4704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison L. E., Kabrun N., Mudri S., Hayman M. J., Enrietto P. J. Viral rel and cellular rel associate with cellular proteins in transformed and normal cells. Oncogene. 1989 Jun;4(6):677–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchase H. G., Witter R. L. The reticuloendotheliosis viruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;71:103–124. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66193-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C. A., Han K., Manley J. L., Levine M. The graded distribution of the dorsal morphogen is initiated by selective nuclear transport in Drosophila. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1165–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90772-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. C., Witte O. N. A recombinant murine retrovirus expressing v-rel is cytopathic. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):182–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90671-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simek S., Rice N. R. p59v-rel, the transforming protein of reticuloendotheliosis virus, is complexed with at least four other proteins in transformed chicken lymphoid cells. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4730–4736. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4730-4736.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Dorsal, an embryonic polarity gene in Drosophila, is homologous to the vertebrate proto-oncogene, c-rel. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):692–694. doi: 10.1126/science.3118464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]