Abstract
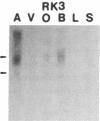
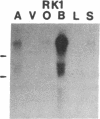
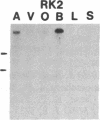
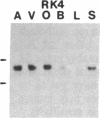
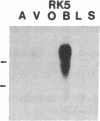
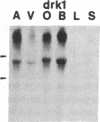
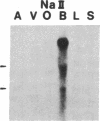
Five distinct K+ channel cDNA molecules (RK1 to RK5) were cloned from either rat heart or rat aorta cDNA libraries. Four of the channels, RK1 to RK4, are similar or identical to Shaker-like K+ channels previously identified in rat brain cDNA libraries. Major differences among RK1 to RK4 exist in the amino- and carboxyl-terminal regions and in amino acids representing potential extracellular sequence between the S1 and S2 hydrophobic domains. RK5 encodes a unique channel of 490 amino acids having six hydrophobic domains but only five basic residues in the putative voltage-sensing domain. Unlike RK1 to RK4, RK5 is a rat homologue of the Drosophila Shal family of K+ channels, which have not been previously described in mammals. Although RK5 mRNA is present in cardiac atrium and ventricle, it is most abundant in brain. RK1, RK2, and RK3 transcripts are predominantly found in brain but are present also at lower levels in other tissues, such as heart and aorta. RK2 is absent from skeletal muscle whereas RK1 and RK3 are present in this tissue. RK4 mRNA is ubiquitous in electrically excitable tissue, being present at comparable levels in atrium, ventricle, aorta, brain, and skeletal muscle. The cloning of RK5 confirms the presence in mammals of all four Drosophila K+ channel families: Shaker, Shab, Shaw, and Shal.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann A., Grupe A., Ackermann A., Pongs O. Structure of the voltage-dependent potassium channel is highly conserved from Drosophila to vertebrate central nervous systems. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2457–2463. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03092.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckh S., Pongs O. Members of the RCK potassium channel family are differentially expressed in the rat nervous system. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):777–782. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08173.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandy K. G., Williams C. B., Spencer R. H., Aguilar B. A., Ghanshani S., Tempel B. L., Gutman G. A. A family of three mouse potassium channel genes with intronless coding regions. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):973–975. doi: 10.1126/science.2305265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. J., Adelman J. P., Douglass J., North R. A. Expression of a cloned rat brain potassium channel in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):221–224. doi: 10.1126/science.2539643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass J., Osborne P. B., Cai Y. C., Wilkinson M., Christie M. J., Adelman J. P. Characterization and functional expression of a rat genomic DNA clone encoding a lymphocyte potassium channel. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4841–4850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folander K., Smith J. S., Antanavage J., Bennett C., Stein R. B., Swanson R. Cloning and expression of the delayed-rectifier IsK channel from neonatal rat heart and diethylstilbestrol-primed rat uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2975–2979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frech G. C., VanDongen A. M., Schuster G., Brown A. M., Joho R. H. A novel potassium channel with delayed rectifier properties isolated from rat brain by expression cloning. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):642–645. doi: 10.1038/340642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grupe A., Schröter K. H., Ruppersberg J. P., Stocker M., Drewes T., Beckh S., Pongs O. Cloning and expression of a human voltage-gated potassium channel. A novel member of the RCK potassium channel family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1749–1756. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08299.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R., Conti F. Pursuing the structure and function of voltage-gated channels. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jun;13(6):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90160-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. C., Ivatt R. J. Synthesis and processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:555–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack T., Vega-Saenz de Miera E. C., Rudy B. Molecular cloning of a member of a third class of Shaker-family K+ channel genes in mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5227–5231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinnon D. Isolation of a cDNA clone coding for a putative second potassium channel indicates the existence of a gene family. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8230–8236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai T., Kakizuka A., Takumi T., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of human genomic DNA encoding a novel membrane protein which exhibits a slowly activating potassium channel activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 30;161(1):176–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91577-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Ikeda T., Kayano T., Suzuki H., Takeshima H., Kurasaki M., Takahashi H., Numa S. Existence of distinct sodium channel messenger RNAs in rat brain. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):188–192. doi: 10.1038/320188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papazian D. M., Schwarz T. L., Tempel B. L., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Cloning of genomic and complementary DNA from Shaker, a putative potassium channel gene from Drosophila. Science. 1987 Aug 14;237(4816):749–753. doi: 10.1126/science.2441470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Ruppersberg J. P., Schröter K. H., Sakmann B., Stocker M., Giese K. P., Perschke A., Baumann A., Pongs O. Molecular basis of functional diversity of voltage-gated potassium channels in mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3235–3244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R., Marshall J., Smith J. S., Williams J. B., Boyle M. B., Folander K., Luneau C. J., Antanavage J., Oliva C., Buhrow S. A. Cloning and expression of cDNA and genomic clones encoding three delayed rectifier potassium channels in rat brain. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):929–939. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90146-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempel B. L., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Cloning of a probable potassium channel gene from mouse brain. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):837–839. doi: 10.1038/332837a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng-Crank J. C., Tseng G. N., Schwartz A., Tanouye M. A. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a potassium channel cDNA isolated from a rat cardiac library. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jul 30;268(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80973-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei A., Covarrubias M., Butler A., Baker K., Pak M., Salkoff L. K+ current diversity is produced by an extended gene family conserved in Drosophila and mouse. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):599–603. doi: 10.1126/science.2333511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama S., Imoto K., Kawamura T., Higashida H., Iwabe N., Miyata T., Numa S. Potassium channels from NG108-15 neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells. Primary structure and functional expression from cDNAs. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81488-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetterqvist O., Ragnarsson U. The structural requirements of substrates of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1982 Mar 22;139(2):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80872-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]