Abstract
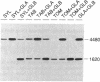
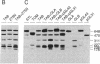
Two genes for prepro glucan endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase (1,3-beta-glucanase; 1,3-beta-D-glucan glucanohydrolase, EC 3.2.1.39) of tobacco were cloned and their sequences were compared with cDNA clones. Southern analysis indicates that the genomic clones represent genes derived from ancestral parents of tobacco similar to the present day species Nicotiana sylvestris and Nicotiana tomentosiformis, whereas the genes represented by two of the cDNA clones appear to be unique to tobacco. The coding sequences of the genomic clones and cDNA clones differed at less than 2.2% of the positions, indicating that the tobacco 1,3-beta-glucanase gene family is highly conserved. Alternating blocks of sequence in the cDNA clones were identical to the coding sequence of the two genomic clones. These results and an analysis of evolutionary distances for nucleotide substitution are consistent with the hypothesis that the evolution of the tobacco 1,3-beta-glucanase gene family has involved exchange of DNA between members of the tomentosiformis and sylvestris subgenomes by recombination or gene conversion.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W. A catalogue of splice junction and putative branch point sequences from plant introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9549–9559. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron D R. Inheritance in Nicotiana Tabacum. Xxiv. Intraspecific Differences in Chromosome Structure. Genetics. 1952 May;37(3):288–296. doi: 10.1093/genetics/37.3.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Loose M., Alliotte T., Gheysen G., Genetello C., Gielen J., Soetaert P., Van Montagu M., Inzé D. Primary structure of a hormonally regulated beta-glucanase of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluhr Robert, Moses Phyllis, Morelli Giorgio, Coruzzi Gloria, Chua Nam-Hai. Expression dynamics of the pea rbcS multigene family and organ distribution of the transcripts. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2063–2071. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerstel D U. Segregation in New Allopolyploids of Nicotiana. I. Comparison of 6x (N. Tabacum x Tomentosiformis) and 6x (N. Tabacum x Otophora). Genetics. 1960 Dec;45(12):1723–1734. doi: 10.1093/genetics/45.12.1723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerstel D U. Segregation in New Allopolyploids of Nicotiana. II. Discordant Ratios from Individual Loci in 6x (N. Tabacum x N. Sylvestris). Genetics. 1963 May;48(5):677–689. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.5.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. C., Kung S. D., Wildman S. G. Origin of Nicotiana tabacum L. detected by polypeptide composition of Fraction I protein. Nature. 1974 Nov 15;252(5480):226–227. doi: 10.1038/252226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høj P. B., Hartman D. J., Morrice N. A., Doan D. N., Fincher G. B. Purification of (1-->3)-beta-glucan endohydrolase isoenzyme II from germinated barley and determination of its primary structure from a cDNA clone. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Jul;13(1):31–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00027333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamet E., Durr A., Fleck J. Absence of some truncated genes in the amphidiploid Nicotiana tabacum. Gene. 1987;59(2-3):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90329-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi C. P. An inspection of the domain between putative TATA box and translation start site in 79 plant genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6643–6653. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi C. P. Putative polyadenylation signals in nuclear genes of higher plants: a compilation and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9627–9640. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol. 1980 Dec;16(2):111–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01731581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütcke H. A., Chow K. C., Mickel F. S., Moss K. A., Kern H. F., Scheele G. A. Selection of AUG initiation codons differs in plants and animals. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):43–48. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Smithies O. The evolution of multigene families: human haptoglobin genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:81–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metraux J. P., Burkhart W., Moyer M., Dincher S., Middlesteadt W., Williams S., Payne G., Carnes M., Ryals J. Isolation of a complementary DNA encoding a chitinase with structural homology to a bifunctional lysozyme/chitinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):896–900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohnen D., Shinshi H., Felix G., Meins F. Hormonal regulation of beta1,3-glucanase messenger RNA levels in cultured tobacco tissues. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1631–1635. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03830.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G., Thompson W. F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4321–4325. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichersky E., Bernatzky R., Tanksley S. D., Cashmore A. R. Evidence for selection as a mechanism in the concerted evolution of Lycopersicon esculentum (tomato) genes encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3880–3884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinshi H., Neuhas J. M., Ryals J., Meins F., Jr Structure of a tobacco endochitinase gene: evidence that different chitinase genes can arise by transposition of sequences encoding a cysteine-rich domain. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Mar;14(3):357–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00028772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinshi H., Wenzler H., Neuhaus J. M., Felix G., Hofsteenge J., Meins F. Evidence for N- and C-terminal processing of a plant defense-related enzyme: Primary structure of tobacco prepro-beta-1,3-glucanase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5541–5545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita M., Manzara T., Pichersky E., Cashmore A., Gruissem W. Genomic organization, sequence analysis and expression of all five genes encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from tomato. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):247–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00329650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]