Abstract
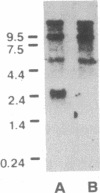
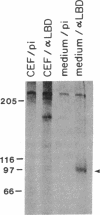
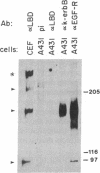
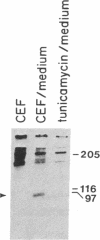
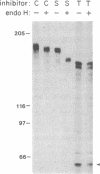
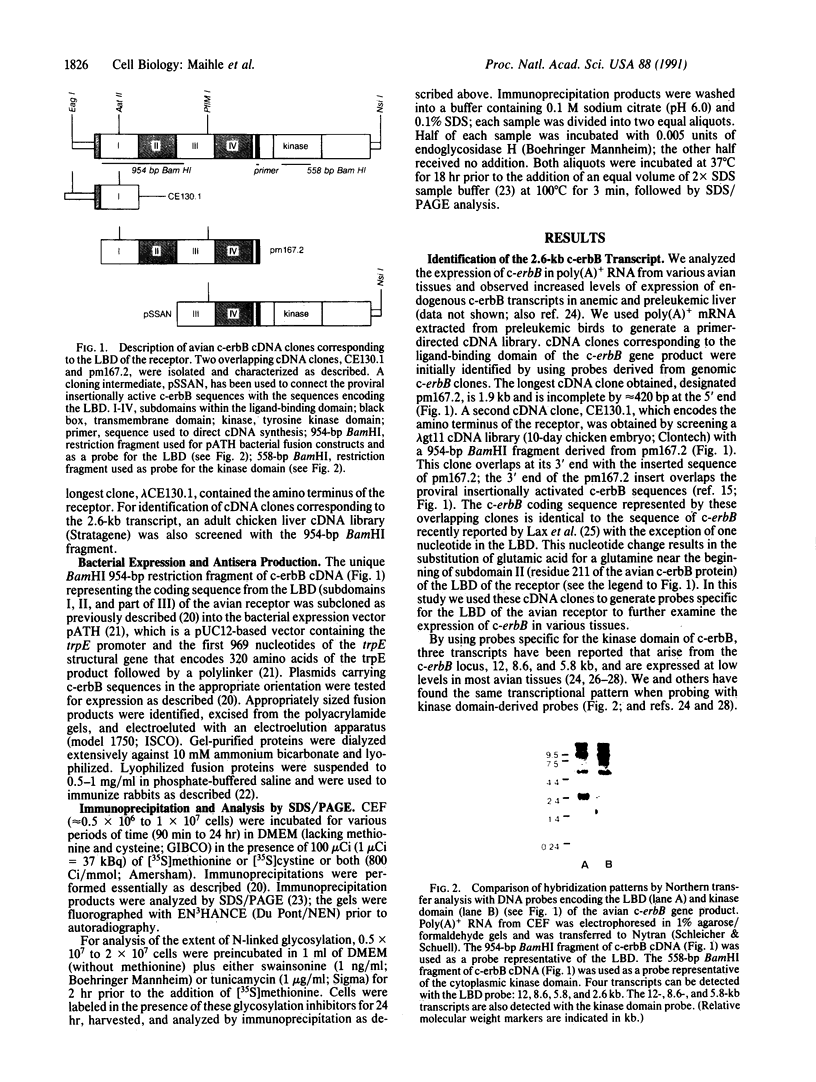
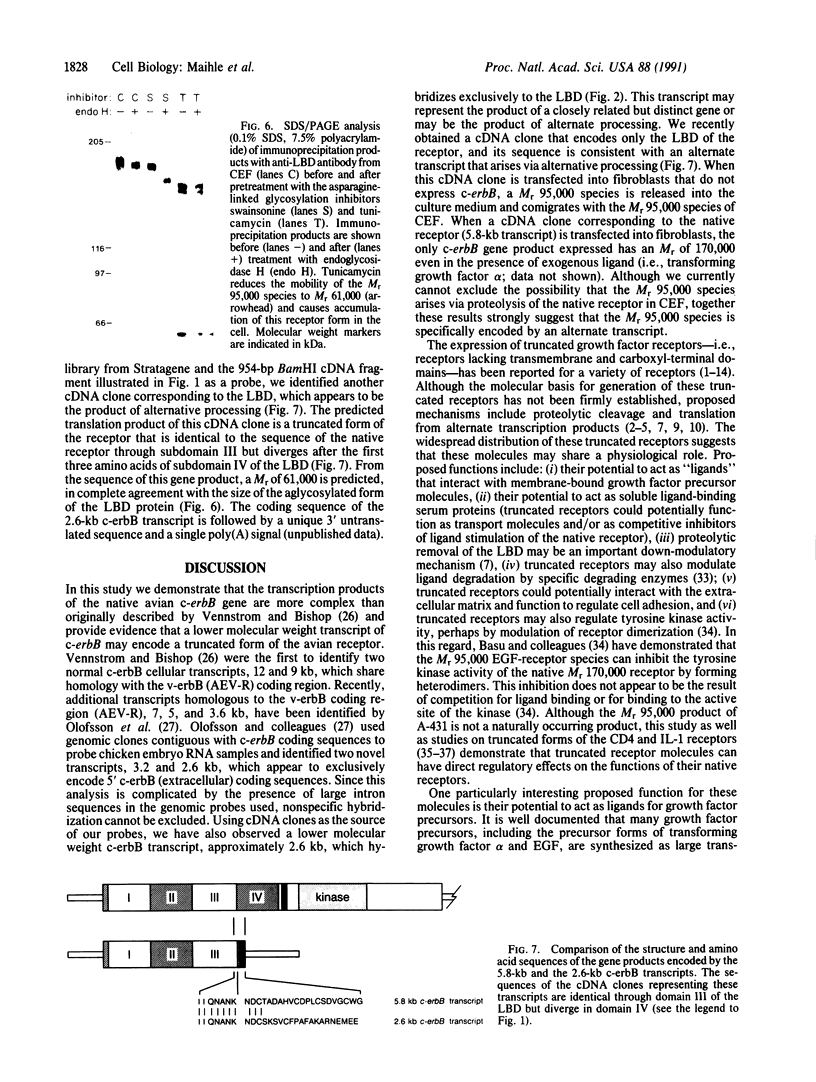
A primer-directed cDNA library was used to obtain cDNA clones corresponding to the 5' end (i.e., the ligand-binding domain) of the avian c-erbB gene. Bacterial c-erbB fusion proteins were synthesized and used to obtain polyclonal antisera specific for the ligand-binding domain of the avian receptor. These antisera and antisera specific for the carboxyl terminal domain of the chicken c-erbB gene product have been used to study the native protein products of the c-erbB locus in primary cell cultures by in vivo labeling and immunoprecipitation. Our studies reveal that three c-erbB gene products of Mr 300,000, Mr 170,000, and Mr 95,000 are synthesized in uninfected chicken embryo fibroblasts. Only the Mr 300,000 and Mr 170,000 species can be precipitated by using antisera specific for the cytoplasmic domain of the c-erbB product. The 95,000 species is not recognized by the antiserum directed against the carboxyl-terminal domain of c-erbB and is specifically released into the culture medium. Northern transfer studies reveal a lower molecular weight transcript of approximately 2.6 kilobases that selectively hybridizes to the ligand-binding domain of the avian c-erbB gene product but does not hybridize with probes specific for the cytoplasmic kinase domain of c-erbB. An additional cDNA clone corresponding to this transcript has been isolated, and its sequence suggests it may arise via alternative processing. Together, these data suggest that a truncated form of this growth factor receptor--i.e., a Mr 95,000 species--is synthesized from a low molecular weight c-erbB transcript that exclusively encodes the ligand-binding domain of the receptor. Secretion of truncated growth factor receptors has been reported recently in several systems, and our results are discussed in the light of these findings.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthos J., Deen K. C., Chaikin M. A., Fornwald J. A., Sathe G., Sattentau Q. J., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., McDougal J. S., Pietropaolo C. Identification of the residues in human CD4 critical for the binding of HIV. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90922-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu A., Raghunath M., Bishayee S., Das M. Inhibition of tyrosine kinase activity of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor by a truncated receptor form that binds to EGF: role for interreceptor interaction in kinase regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):671–677. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumbach W. R., Horner D. L., Logan J. S. The growth hormone-binding protein in rat serum is an alternatively spliced form of the rat growth hormone receptor. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1199–1205. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beguin Y., Huebers H. A., Josephson B., Finch C. A. Transferrin receptors in rat plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):637–640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brachmann R., Lindquist P. B., Nagashima M., Kohr W., Lipari T., Napier M., Derynck R. Transmembrane TGF-alpha precursors activate EGF/TGF-alpha receptors. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):691–700. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90591-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. Purification of denatured epidermal growth factor-receptor from A431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Feb 1;228(2):621–626. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Roberts A. B., Winkler M. E., Chen E. Y., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-alpha: precursor structure and expression in E. coli. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90550-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiAugustine R. P., Petrusz P., Bell G. I., Brown C. F., Korach K. S., McLachlan J. A., Teng C. T. Influence of estrogens on mouse uterine epidermal growth factor precursor protein and messenger ribonucleic acid. Endocrinology. 1988 Jun;122(6):2355–2363. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-6-2355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiStefano P. S., Johnson E. M., Jr Identification of a truncated form of the nerve growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):270–274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieckmann C. L., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. CBP6, a yeast nuclear gene necessary for synthesis of cytochrome b. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1513–1520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing J. R., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Ligand and protein kinase C downmodulate the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor by independent mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2890–2896. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanslow W. C., Sims J. E., Sassenfeld H., Morrissey P. J., Gillis S., Dower S. K., Widmer M. B. Regulation of alloreactivity in vivo by a soluble form of the interleukin-1 receptor. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):739–742. doi: 10.1126/science.2139736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamou S., Hirai M., Rikimaru K., Enomoto S., Shimizu N. Biosynthesis of the epidermal growth factor receptor in human squamous cell carcinoma lines: secretion of the truncated receptor is not common to epidermal growth factor receptor-hyperproducing cells. Cell Struct Funct. 1988 Feb;13(1):25–38. doi: 10.1247/csf.13.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. V., Gehm B. D., Rosner M. R. An evolutionarily conserved enzyme degrades transforming growth factor-alpha as well as insulin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1301–1307. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin R. G., Friend D., Ziegler S. F., Jerzy R., Falk B. A., Gimpel S., Cosman D., Dower S. K., March C. J., Namen A. E. Cloning of the human and murine interleukin-7 receptors: demonstration of a soluble form and homology to a new receptor superfamily. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):941–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90342-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin R. G., Rottman F. M., Callaghan T., Kung H. J., Maroney P. A., Nilsen T. W. c-erbB activation in avian leukosis virus-induced erythroblastosis: multiple epidermal growth factor receptor mRNAs are generated by alternative RNA processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3128–3133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gower H. J., Barton C. H., Elsom V. L., Thompson J., Moore S. E., Dickson G., Walsh F. S. Alternative splicing generates a secreted form of N-CAM in muscle and brain. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):955–964. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90241-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray A., Dull T. J., Ullrich A. Nucleotide sequence of epidermal growth factor cDNA predicts a 128,000-molecular weight protein precursor. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):722–725. doi: 10.1038/303722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Johnson A., Howk R., Sap J., Bellot F., Winkler M., Ullrich A., Vennstrom B., Schlessinger J., Givol D. Chicken epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor: cDNA cloning, expression in mouse cells, and differential binding of EGF and transforming growth factor alpha. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1970–1978. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Spencer S. A., Cachianes G., Hammonds R. G., Collins C., Henzel W. J., Barnard R., Waters M. J., Wood W. I. Growth hormone receptor and serum binding protein: purification, cloning and expression. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):537–543. doi: 10.1038/330537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loosfelt H., Misrahi M., Atger M., Salesse R., Vu Hai-Luu Thi M. T., Jolivet A., Guiochon-Mantel A., Sar S., Jallal B., Garnier J. Cloning and sequencing of porcine LH-hCG receptor cDNA: variants lacking transmembrane domain. Science. 1989 Aug 4;245(4917):525–528. doi: 10.1126/science.2502844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loughnan M. S., Sanderson C. J., Nossal G. J. Soluble interleukin 2 receptors are released from the cell surface of normal murine B lymphocytes stimulated with interleukin 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3115–3119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. G., Tepper M. A., Clairmont K. B., Perregaux S. B., Czech M. P. Serum form of the rat insulin-like growth factor II/mannose 6-phosphate receptor is truncated in the carboxyl-terminal domain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3256–3261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maihle N. J., Raines M. A., Flickinger T. W., Kung H. J. Proviral insertional activation of c-erbB: differential processing of the protein products arising from two alternate transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4868–4876. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maihle N. J., Satir B. H. Identification of a biochemical marker for the secretory pathway in Tetrahymena thermophila. J Cell Biochem. 1986;31(3):195–202. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlino G. T., Ishii S., Whang-Peng J., Knutsen T., Xu Y. H., Clark A. J., Stratton R. H., Wilson R. K., Ma D. P., Roe B. A. Structure and localization of genes encoding aberrant and normal epidermal growth factor receptor RNAs from A431 human carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1722–1734. doi: 10.1128/MCB.5.7.1722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mroczkowski B., Reich M., Chen K., Bell G. I., Cohen S. Recombinant human epidermal growth factor precursor is a glycosylated membrane protein with biological activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2771–2778. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Maroney P. A., Goodwin R. G., Rottman F. M., Crittenden L. B., Raines M. A., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in ALV-induced erythroblastosis: novel RNA processing and promoter insertion result in expression of an amino-truncated EGF receptor. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):719–726. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson B., Pizon V., Zahraoui A., Tavitian A., Therwath A. Structure and expression of the chicken epidermal growth factor receptor gene locus. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):261–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petch L. A., Harris J., Raymond V. W., Blasband A., Lee D. C., Earp H. S. A truncated, secreted form of the epidermal growth factor receptor is encoded by an alternatively spliced transcript in normal rat tissue. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2973–2982. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in avian leukosis virus-induced erythroblastosis: clustered integration sites and the arrangement of provirus in the c-erbB alleles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2287–2291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall L. B., Scott J., Bell G. I., Crawford R. J., Penschow J. D., Niall H. D., Coghlan J. P. Mouse prepro-epidermal growth factor synthesis by the kidney and other tissues. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):228–231. doi: 10.1038/313228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. A., Kurman C. C., Fritz M. E., Biddison W. E., Boutin B., Yarchoan R., Nelson D. L. Soluble interleukin 2 receptors are released from activated human lymphoid cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3172–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall T. J., Lewis M., Koller K. J., Lee A., Rice G. C., Wong G. H., Gatanaga T., Granger G. A., Lentz R., Raab H. Molecular cloning and expression of a receptor for human tumor necrosis factor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90816-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Samelson L. E., Bolen J. B. Signal transduction through the CD4 receptor involves the activation of the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):257–259. doi: 10.1038/338257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Bishop J. M. Isolation and characterization of chicken DNA homologous to the two putative oncogenes of avian erythroblastosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman H. F., Bartow T., Leppo M. K., Marsh H. C., Jr, Carson G. R., Concino M. F., Boyle M. P., Roux K. H., Weisfeldt M. L., Fearon D. T. Soluble human complement receptor type 1: in vivo inhibitor of complement suppressing post-ischemic myocardial inflammation and necrosis. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):146–151. doi: 10.1126/science.2371562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A. Receptor molecule blocks HIV. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):15–15. doi: 10.1038/331015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. T., Winchell L. F., McCune B. K., Earp H. S., Teixidó J., Massagué J., Herman B., Lee D. C. The TGF-alpha precursor expressed on the cell surface binds to the EGF receptor on adjacent cells, leading to signal transduction. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):495–506. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90252-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]