Abstract
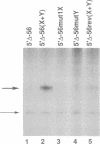
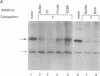
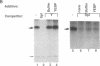
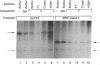
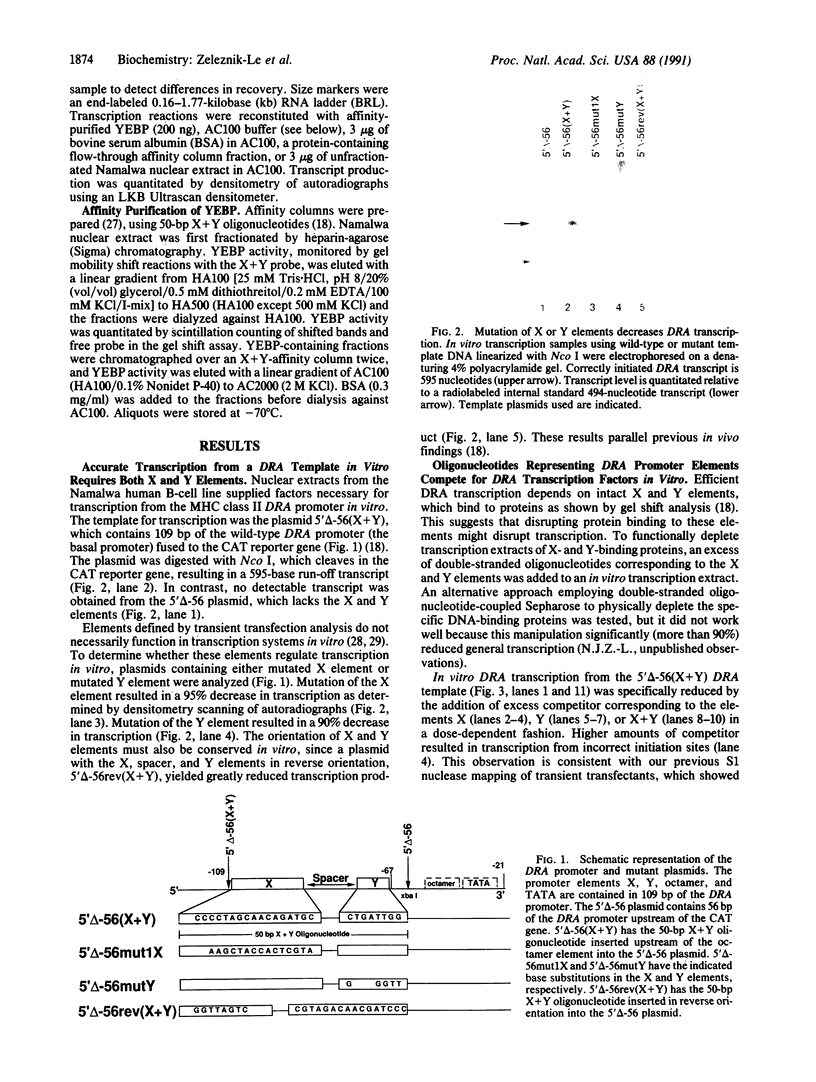
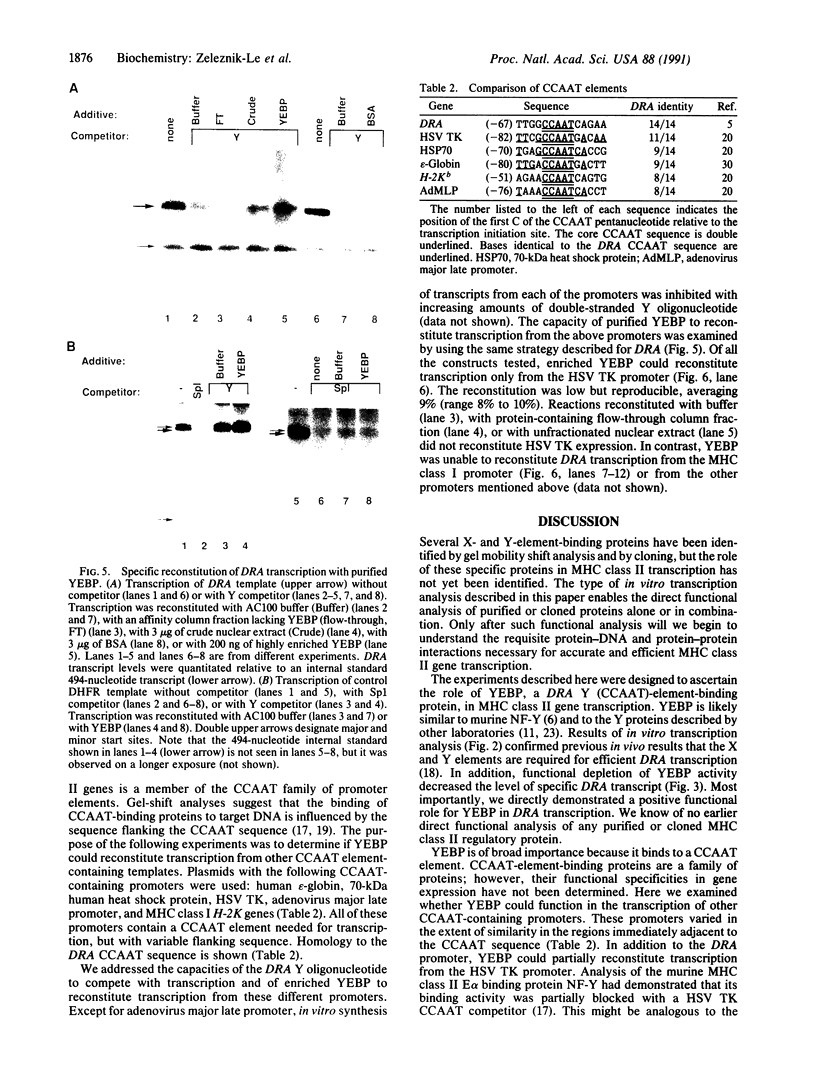
Efficient major histocompatibility complex class II gene expression requires conserved protein-binding promoter elements, including X and Y elements. We affinity purified an HLA-DRA Y-element (CCAAT)-binding protein (YEBP) and used it to reconstitute Y-depleted HLA-DRA in vitro transcription. This directly demonstrates a positive functional role for YEBP in HLA-DRA transcription. The ability of YEBP to regulate divergent CCAAT elements was also assessed; YEBP was found to partially activate the thymidine kinase promoter. This functional analysis of YEBP shows that this protein plays an important role in the regulation of multiple genes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baralle F. E., Shoulders C. C., Proudfoot N. J. The primary structure of the human epsilon-globin gene. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):621–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celada A., Maki R. A. DNA binding of the mouse class II major histocompatibility CCAAT factor depends on two components. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3097–3100. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celada A., Maki R. Evidence for multiple major histocompatibility class II X-box binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5219–5222. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogswell J. P., Basta P. V., Ting J. P. X-box-binding proteins positively and negatively regulate transcription of the HLA-DRA gene through interaction with discrete upstream W and V elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7703–7707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedrick R. L., Jones P. P. Sequence elements required for activity of a murine major histocompatibility complex class II promoter bind common and cell-type-specific nuclear factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):593–604. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didier D. K., Schiffenbauer J., Woulfe S. L., Zacheis M., Schwartz B. D. Characterization of the cDNA encoding a protein binding to the major histocompatibility complex class II Y box. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7322–7326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Cochran M. D., Dobkin C., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Three regions upstream from the cap site are required for efficient and accurate transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse 3T6 cells. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Durand B., Marfing C., Le Meur M., Benoist C., Mathis D. Conserved major histocompatibility complex class II boxes--X and Y--are transcriptional control elements and specifically bind nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6249–6253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., Shewmaker C. K., Jat P., Flavell R. A. Localization of DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vitro. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90246-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Steinmetz M., Malissen B. Genes of the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:529–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooft van Huijsduijnen R. A., Bollekens J., Dorn A., Benoist C., Mathis D. Properties of a CCAAT box-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7265–7282. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Rao L. G., Muench A. J. Regulation of thymidine kinase enzyme level in serum-stimulated mouse 3T6 fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Mar;138(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. F., Auffray C., Korman A. J., Shackelford D. A., Strominger J. The class II molecules of the human and murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou H. C., Boothby M. R., Finn P. W., Davidon R., Nabavi N., Zeleznik-Le N. J., Ting J. P., Glimcher L. H. A new member of the leucine zipper class of proteins that binds to the HLA DR alpha promoter. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1581–1584. doi: 10.1126/science.2321018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa K., Doyle C., Strominger J. L. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with conserved sequences of human class II major histocompatibility complex genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4939–4943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima-Sugano J., Roeder R. G. Cell-type-specific transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa light chain gene in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8511–8515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith W., Barras E., Satola S., Kobr M., Reinhart D., Sanchez C. H., Mach B. Cloning of the major histocompatibility complex class II promoter binding protein affected in a hereditary defect in class II gene regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4200–4204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith W., Satola S., Sanchez C. H., Amaldi I., Lisowska-Grospierre B., Griscelli C., Hadam M. R., Mach B. Congenital immunodeficiency with a regulatory defect in MHC class II gene expression lacks a specific HLA-DR promoter binding protein, RF-X. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):897–906. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90389-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai M., Strominger J. L. B-cell-specific enhancer activity of conserved upstream elements of the class II major histocompatibility complex DQB gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6909–6913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Glassy M. C., Ferrone S., Jones O. W. Cell cycle and the differential expression of HLA-A,B and HLA-DR antigens on human B lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7297–7301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servenius B., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Class II genes of the human major histocompatibility complex. The DO beta gene is a divergent member of the class II beta gene family. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8759–8766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherley J. L., Kelly T. J. Regulation of human thymidine kinase during the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8350–8358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Basta P. V., Heguy A., Wloch M. K., Roeder R. G., Ting J. P. The octamer motif is a B-lymphocyte-specific regulatory element of the HLA-DR alpha gene promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6739–6743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Basta P. V., Moore T. L., Brown A. M., Ting J. P. Class II box consensus sequences in the HLA-DR alpha gene: transcriptional function and interaction with nuclear proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):50–56. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Basta P. V., Ting J. P. Upstream DNA sequences required for tissue-specific expression of the HLA-DR alpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4254–4258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swick A. G., Blake M. C., Kahn J. W., Azizkhan J. C. Functional analysis of GC element binding and transcription in the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9291–9304. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang S. Y., Nakanishi M., Peterlin B. M. Mutational analysis of the DRA promoter: cis-acting sequences and trans-acting factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):711–719. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]