Abstract
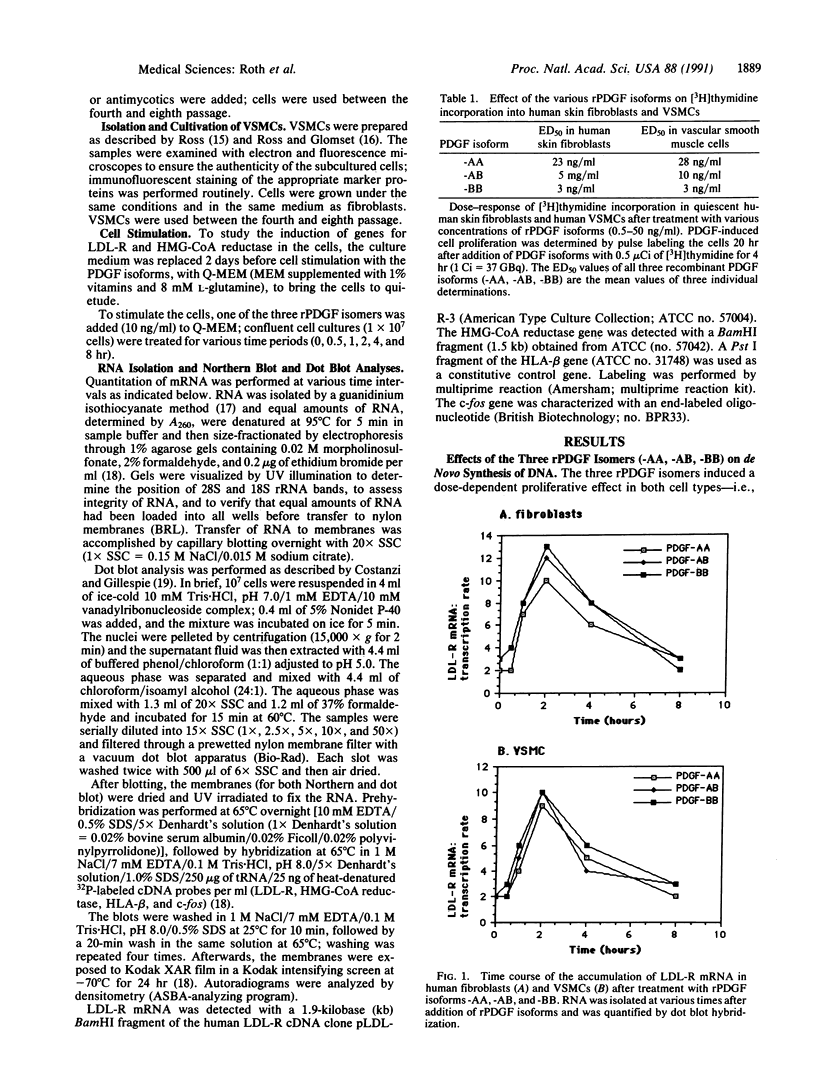
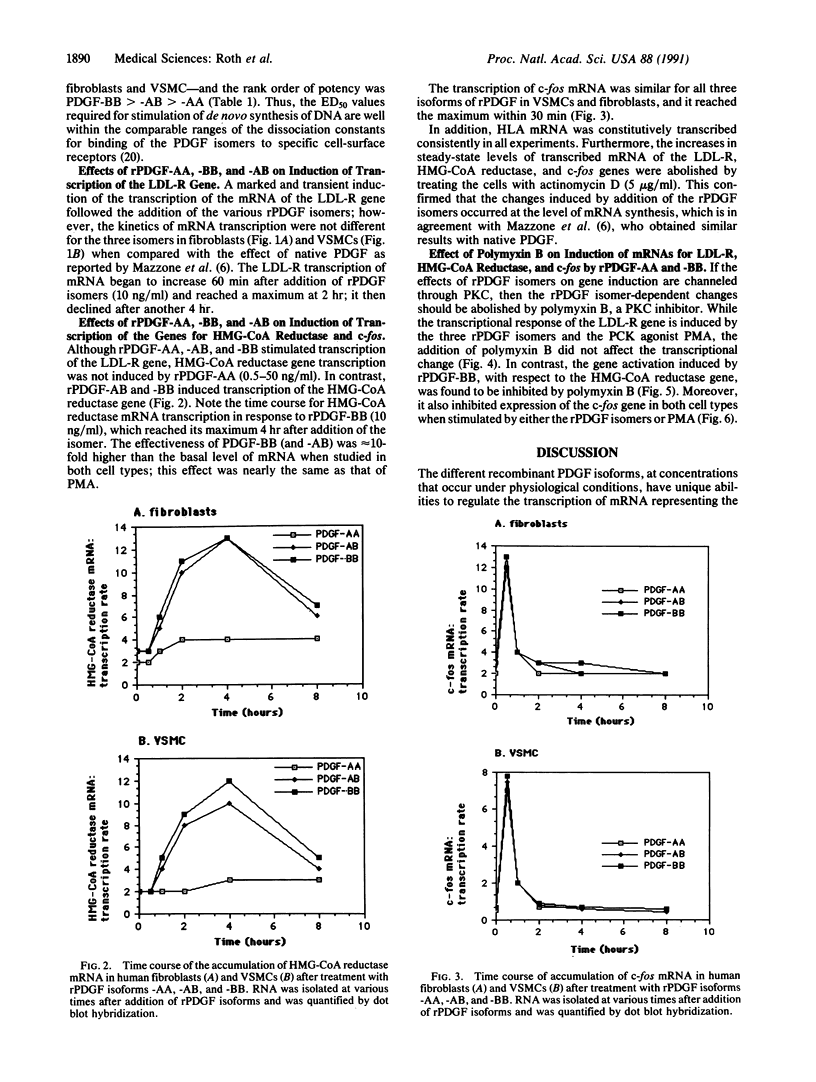
The plausible role that platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) has in the localized pathophysiological changes that occur in the arterial wall during development of atherosclerotic lesions led us to investigate the influence of recombinant (r)PDGF isomers -AA, -AB, and -BB on the expression of low density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R) and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase [(S)-mevalonate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (CoA-acylating), EC 1.1.1.88] genes. In addition, we clarified the role of protein kinase C (PKC) in expression of the two genes in human skin fibroblasts and vascular smooth muscle cells. The various rPDGF isoforms are distinct in their ability to activate transcription of both genes: (i) Both rPDGF-AA and -BB stimulate transcription of the LDL-R gene; in contrast, rPDGF-BB, but not -AA, activates transcription of the HMG-CoA reductase gene. (ii) All recombinant isoforms of PDGF activate transcription of the c-fos gene. (iii) While rPDGF-dependent transcription of the LDL-R gene occurs independently of PKC, transcription of the HMG-CoA reductase gene appears to involve the action of that enzyme.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auwerx J. H., Chait A., Deeb S. S. Regulation of the low density lipoprotein receptor and hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase genes by protein kinase C and a putative negative regulatory protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1133–1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block L. H., Emmons L. R., Vogt E., Sachinidis A., Vetter W., Hoppe J. Ca2+-channel blockers inhibit the action of recombinant platelet-derived growth factor in vascular smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2388–2392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Lipoprotein metabolism in the macrophage: implications for cholesterol deposition in atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:223–261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carew T. E., Schwenke D. C., Steinberg D. Antiatherogenic effect of probucol unrelated to its hypocholesterolemic effect: evidence that antioxidants in vivo can selectively inhibit low density lipoprotein degradation in macrophage-rich fatty streaks and slow the progression of atherosclerosis in the Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7725–7729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesterman C. N., Walker T., Grego B., Chamberlain K., Hearn M. T., Morgan F. J. Comparison of platelet-derived growth factor prepared from release products of fresh platelets and from outdated platelet concentrates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 15;116(3):809–816. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzi C., Gillespie D. Fast blots: immobilization of DNA and RNA from cells. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:582–587. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Lee W. M., Williams P. W., Giels G. M., Williams L. T. c-myc gene expression is stimulated by agents that activate protein kinase C and does not account for the mitogenic effect of PDGF. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreher M. L., Hanley M. R. Multiple modes of protein kinase C regulation and their significance in signalling. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Apr;9(4):114–115. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Progress in understanding the LDL receptor and HMG-CoA reductase, two membrane proteins that regulate the plasma cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 15;25(13):1450–1461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall D. J., Stiles C. D. Platelet-derived growth factor-inducible genes respond differentially to at least two distinct intracellular second messengers. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15302–15308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Zilberstein A., Franks C., Felder S., Kremer S., Ullrich A., Rhee S. G., Skorecki K., Schlessinger J. Effect of phospholipase C-gamma overexpression on PDGF-induced second messengers and mitogenesis. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):607–610. doi: 10.1126/science.2333512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzone T., Basheeruddin K., Ping L., Frazer S., Getz G. S. Mechanism of the growth-related activation of the low density lipoprotein receptor pathway. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1787–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Bierman A. J., Tilly B. C., Verlaan I., Defize L. H., Honegger A. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. A point mutation at the ATP-binding site of the EGF-receptor abolishes signal transduction. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):707–710. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02866.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olashaw N. E., Pledger W. J. Association of platelet-derived growth factor-induced protein with nuclear material. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):272–274. doi: 10.1038/306272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J. A. Atherosclerosis and the arterial smooth muscle cell: Proliferation of smooth muscle is a key event in the genesis of the lesions of atherosclerosis. Science. 1973 Jun 29;180(4093):1332–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4093.1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Masuda J., Raines E. W., Gown A. M., Katsuda S., Sasahara M., Malden L. T., Masuko H., Sato H. Localization of PDGF-B protein in macrophages in all phases of atherogenesis. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1009–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.2343305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. Platelet-derived growth factor. Lancet. 1989 May 27;1(8648):1179–1182. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92760-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The smooth muscle cell. II. Growth of smooth muscle in culture and formation of elastic fibers. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jul;50(1):172–186. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachinidis A., Locher R., Vetter W., Tatje D., Hoppe J. Different effects of platelet-derived growth factor isoforms on rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10238–10243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetton A. D., Monk P. N., Consalvey S. D., Huang S. J., Dexter T. M., Downes C. P. Interleukin 3 stimulates proliferation via protein kinase C activation without increasing inositol lipid turnover. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3284–3288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox J. N., Smith K. M., Williams L. T., Schwartz S. M., Gordon D. Platelet-derived growth factor mRNA detection in human atherosclerotic plaques by in situ hybridization. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):1134–1143. doi: 10.1172/JCI113671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T. Signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1564–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.2538922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









