Abstract
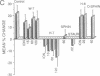
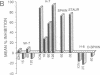
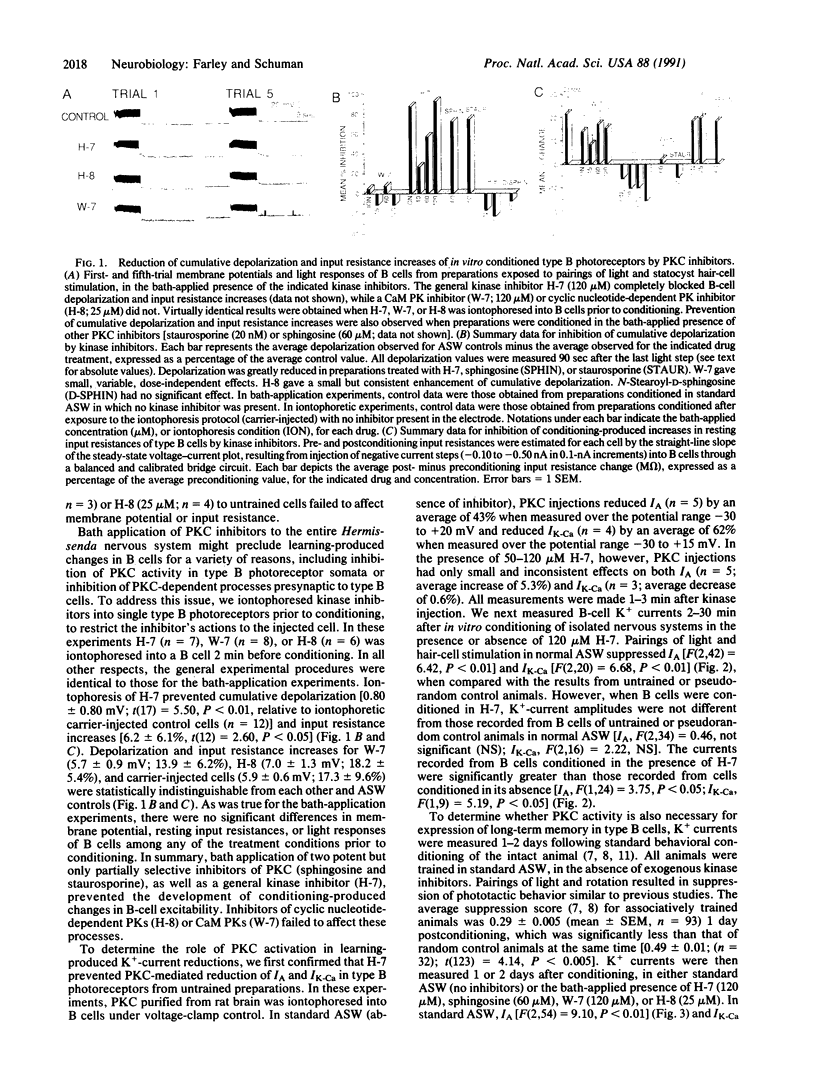
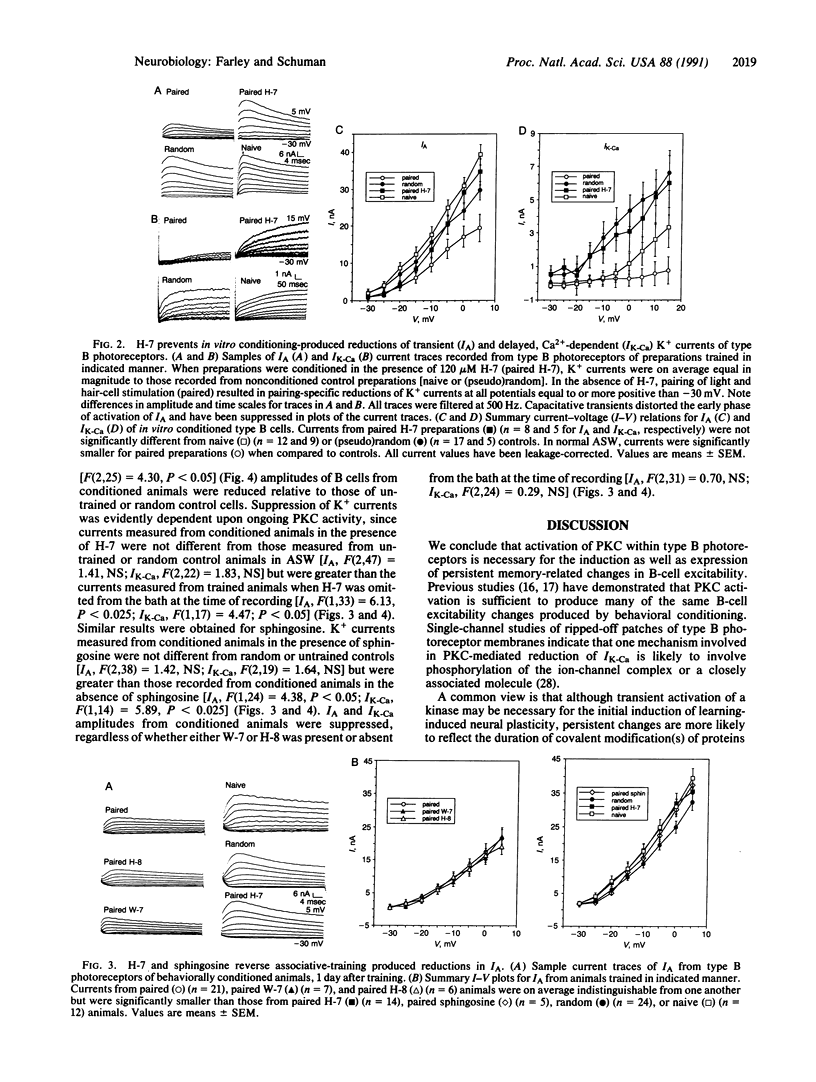
Injections of cAMP-dependent, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent, or Ca2+/phospholipid-dependent protein kinases into Hermissenda crassicornis type B photoreceptors are sufficient to induce many of the changes in B-cell excitability produced by associative conditioning. We report that inhibitors of Ca2+/phospholipid-dependent protein kinases, but not inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide- or Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases, prevent the induction as well as continued expression of learning-produced changes in type-B-cell excitability: reductions of voltage-dependent and Ca2(+)-activated K+ currents. Our results represent a direct demonstration of long-term (days) experientially induced modulation of ion-channel activity that is dependent upon persistent kinase activity.
Full text
PDF

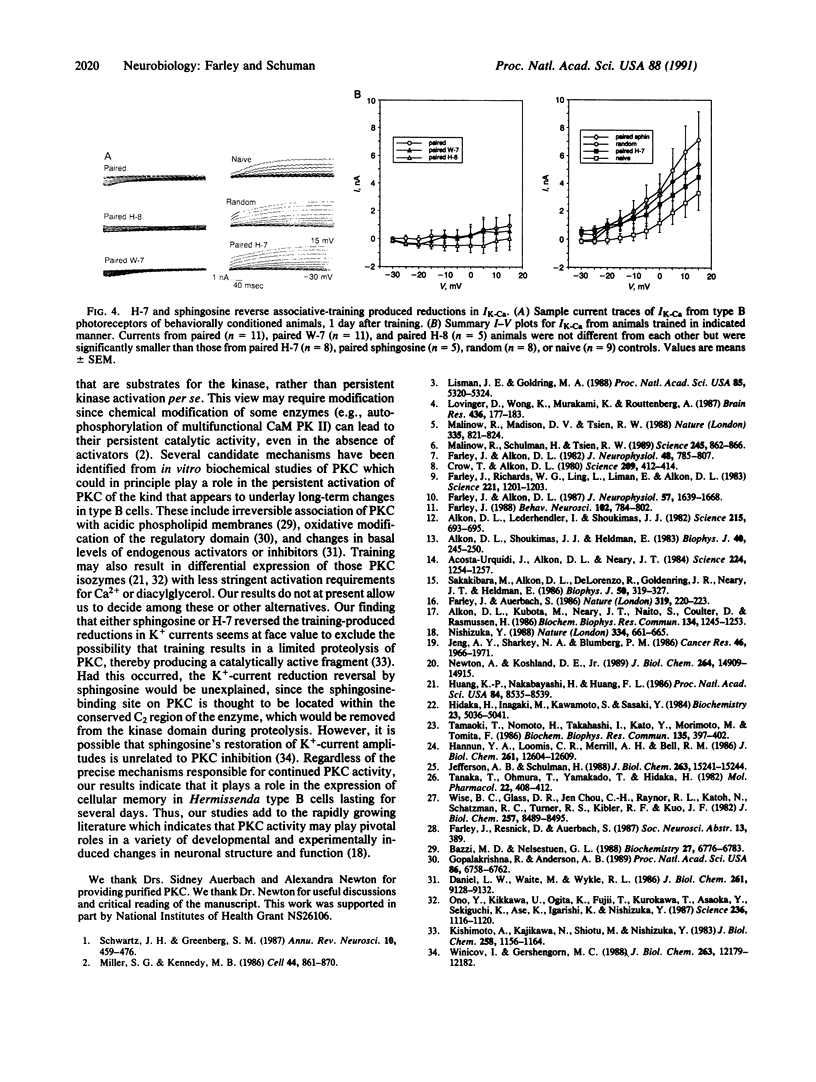
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acosta-Urquidi J., Alkon D. L., Neary J. T. Ca2+-dependent protein kinase injection in a photoreceptor mimics biophysical effects of associative learning. Science. 1984 Jun 15;224(4654):1254–1257. doi: 10.1126/science.6328653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L., Kubota M., Neary J. T., Naito S., Coulter D., Rasmussen H. C-kinase activation prolongs Ca2+-dependent inactivation of K+ currents. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1245–1253. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L., Lederhendler I., Shoukimas J. J. Primary changes of membrane currents during retention of associative learning. Science. 1982 Feb 5;215(4533):693–695. doi: 10.1126/science.7058334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazzi M. D., Nelsestuen G. L. Association of protein kinase C with phospholipid monolayers: two-stage irreversible binding. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):6776–6783. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow T. J., Alkon D. L. Associative behavioral modification in hermissenda: cellular correlates. Science. 1980 Jul 18;209(4454):412–414. doi: 10.1126/science.209.4454.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel L. W., Waite M., Wykle R. L. A novel mechanism of diglyceride formation. 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate stimulates the cyclic breakdown and resynthesis of phosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9128–9132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J., Alkon D. L. Associative neural and behavioral change in Hermissenda: consequences of nervous system orientation for light and pairing specificity. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Sep;48(3):785–807. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.48.3.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J., Alkon D. L. In vitro associative conditioning of Hermissenda: cumulative depolarization of type B photoreceptors and short-term associative behavioral changes. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Jun;57(6):1639–1668. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.57.6.1639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J., Auerbach S. Protein kinase C activation induces conductance changes in Hermissenda photoreceptors like those seen in associative learning. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):220–223. doi: 10.1038/319220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J., Richards W. G., Ling L. J., Liman E., Alkon D. L. Membrane changes in a single photoreceptor cause associative learning in Hermissenda. Science. 1983 Sep 16;221(4616):1201–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.6612335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna R., Anderson W. B. Ca2+- and phospholipid-independent activation of protein kinase C by selective oxidative modification of the regulatory domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6758–6762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Loomis C. R., Merrill A. H., Jr, Bell R. M. Sphingosine inhibition of protein kinase C activity and of phorbol dibutyrate binding in vitro and in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12604–12609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. P., Nakabayashi H., Huang F. L. Isozymic forms of rat brain Ca2+-activated and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8535–8539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson A. B., Schulman H. Sphingosine inhibits calmodulin-dependent enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15241–15244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeng A. Y., Sharkey N. A., Blumberg P. M. Purification of stable protein kinase C from mouse brain cytosol by specific ligand elution using fast protein liquid chromatography. Cancer Res. 1986 Apr;46(4 Pt 2):1966–1971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Kajikawa N., Shiota M., Nishizuka Y. Proteolytic activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by calcium-dependent neutral protease. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1156–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisman J. E., Goldring M. A. Feasibility of long-term storage of graded information by the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase molecules of the postsynaptic density. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5320–5324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovinger D. M., Wong K. L., Murakami K., Routtenberg A. Protein kinase C inhibitors eliminate hippocampal long-term potentiation. Brain Res. 1987 Dec 8;436(1):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91573-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinow R., Madison D. V., Tsien R. W. Persistent protein kinase activity underlying long-term potentiation. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):820–824. doi: 10.1038/335820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinow R., Schulman H., Tsien R. W. Inhibition of postsynaptic PKC or CaMKII blocks induction but not expression of LTP. Science. 1989 Aug 25;245(4920):862–866. doi: 10.1126/science.2549638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. G., Kennedy M. B. Regulation of brain type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase by autophosphorylation: a Ca2+-triggered molecular switch. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):861–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton A. C., Koshland D. E., Jr High cooperativity, specificity, and multiplicity in the protein kinase C-lipid interaction. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14909–14915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Kikkawa U., Ogita K., Fujii T., Kurokawa T., Asaoka Y., Sekiguchi K., Ase K., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. Expression and properties of two types of protein kinase C: alternative splicing from a single gene. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1116–1120. doi: 10.1126/science.3576226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. H., Greenberg S. M. Molecular mechanisms for memory: second-messenger induced modifications of protein kinases in nerve cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1987;10:459–476. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.10.030187.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Ohmura T., Yamakado T., Hidaka H. Two types of calcium-dependent protein phosphorylations modulated by calmodulin antagonists. Naphthalenesulfonamide derivatives. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;22(2):408–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winicov I., Gershengorn M. C. Sphingosine inhibits thyrotropin-releasing hormone binding to pituitary cells by a mechanism independent of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12179–12182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise B. C., Glass D. B., Chou C. H., Raynor R. L., Katoh N., Schatzman R. C., Turner R. S., Kibler R. F., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from heart. II. Substrate specificity and inhibition by various agents. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8489–8495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]