Abstract
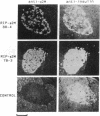
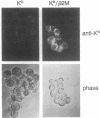
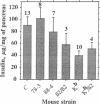
Overexpression of heavy chains of the class I major histocompatibility complex in islet beta cells of transgenic mice is known to induce nonimmune diabetes. We have now overexpressed the secretory protein beta 2-microglobulin in beta cells. Transgenic mice of one lineage had normal islets. Mice of another lineage did not become overtly diabetic but showed significant depletion of beta-cell insulin. When mice were made homozygous for the transgene locus, they developed diabetes. Introduction of the beta 2-microglobulin chain into class I heavy chain transgenic mice resulted in a significant improvement in their islet morphology and insulin content, and the female mice remained normoglycemic. These results suggest that different transgene molecules overexpressed in beta cells can cause islet dysfunction, though not necessarily overt diabetes, and that this effect is mediated by the level of transgene expression. Evidence is provided to show that beta-cell disruption by transgene overexpression occurs at the level of protein and involves a defect in insulin secretion.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J., Campbell I. L., Morahan G., Mandel T. E., Harrison L. C., Miller J. F. Diabetes in transgenic mice resulting from over-expression of class I histocompatibility molecules in pancreatic beta cells. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):529–533. doi: 10.1038/333529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison J., Harrison L. C., Campbell I. L., Miller J. F. Major histocompatibility complex molecules and the beta cell: inferences from transgenic models. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;156:121–135. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75239-1_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhme J., Haskins K., Stecha P., van Ewijk W., LeMeur M., Gerlinger P., Benoist C., Mathis D. Transgenic mice with I-A on islet cells are normoglycemic but immunologically intolerant. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1179–1183. doi: 10.1126/science.2499048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. J., Hammer R. E., Chan S. J., Swift H. H., Rubenstein A. H., Steiner D. F. A mutant human proinsulin is secreted from islets of Langerhans in increased amounts via an unregulated pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8943–8947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culvenor J. G., Crewther P. E. S-antigen localization in the erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium falciparum. J Protozool. 1990 Jan-Feb;37(1):59–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1990.tb01117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Fleischer N., Hanahan D. Diabetes induced in male transgenic mice by expression of human H-ras oncoprotein in pancreatic beta cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1779–1783. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P. N., Overbeek P. A., Means A. R. Calmodulin-induced early-onset diabetes in transgenic mice. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1067–1073. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90505-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Heritable formation of pancreatic beta-cell tumours in transgenic mice expressing recombinant insulin/simian virus 40 oncogenes. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):115–122. doi: 10.1038/315115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo D., Burkly L. C., Widera G., Cowing C., Flavell R. A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Diabetes and tolerance in transgenic mice expressing class II MHC molecules in pancreatic beta cells. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):159–168. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90497-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies D. H., Parnes J. R., Johnson N. A., Seidman J. G. Linkage of beta 2-microglobulin and ly-m11 by molecular cloning and DNA-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2328–2331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuuchi L., Buckley K. M., Lowe A. W., Kelly R. B. Targeting of secretory vesicles to cytoplasmic domains in AtT-20 and PC-12 cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):239–251. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Daitch L., Rath S., Selsing E. Tissue-specific expression of allogeneic class II MHC molecules induces neither tissue rejection nor clonal inactivation of alloreactive T cells. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):334–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Gumbiner B., Kelly R. B. Chloroquine diverts ACTH from a regulated to a constitutive secretory pathway in AtT-20 cells. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):434–436. doi: 10.1038/302434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morahan G., Allison J., Miller J. F. Tolerance of class I histocompatibility antigens expressed extrathymically. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):622–624. doi: 10.1038/339622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Ravazzola M., Amherdt M., Perrelet A., Powell S. K., Quinn D. L., Moore H. P. The trans-most cisternae of the Golgi complex: a compartment for sorting of secretory and plasma membrane proteins. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1039–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90590-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Seidman J. G. Structure of wild-type and mutant mouse beta 2-microglobulin genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):661–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Cannon L. E., Strominger J. L. Cell-free translation of the mRNAs for the heavy and light chains of HLA-A and HLA-B antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2273–2277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P., Weiss U., Pepperkok R., Ansorge W., Niehrs C., Stelzer E. H., Huttner W. B. An antibody against secretogranin I (chromogranin B) is packaged into secretory granules. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):17–34. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvetnick N., Liggitt D., Pitts S. L., Hansen S. E., Stewart T. A. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus induced in transgenic mice by ectopic expression of class II MHC and interferon-gamma. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):773–782. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90414-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinsson L., Peterson P. A. Beta 2-microglobulin induces intracellular transport of human class I transplantation antigen heavy chains in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):226–232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada N., Kimura S., Hatzfeld A., Hämmerling U. Ly-m11: the H-3 region of mouse chromosome 2 controls a new surface alloantigen. Immunogenetics. 1980;11(5):441–449. doi: 10.1007/BF01567813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]