Abstract
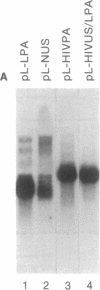
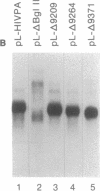
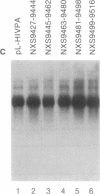
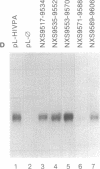
Several polyadenylylation (PA) signals containing elements upstream of the AAUAAA have recently been characterized. Similar to PA elements found downstream of the AAUAAA, the upstream elements function to increase efficiency of AAUAAA use as a signal for cleavage and PA. Using deletion and linker scanning mutations we show that the PA signal of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 contains upstream elements transcribed from the U3 region of the 3' long terminal repeat. The element that has the greatest effect on PA site use lies 77 to 94 nucleotides upstream of the AAUAAA, between the TATA element and the transcriptional initiation site. Mutations in the adjacent region, between 59 and 76 nucleotides upstream of the AAUAAA, have a smaller effect on PA efficiency. Mutations in a region further upstream, between 141 and 176 nucleotides upstream of the AAUAAA, also affected PA modestly. Functional similarity between upstream elements was indicated by the ability of the human immunodeficiency virus upstream region to replace the upstream region of the simian virus 40 late PA signal. The sequence of the major upstream element of human immunodeficiency virus is uracil-rich, analogous to many defined downstream PA elements. This fact may imply that upstream and downstream elements have similar mechanisms of action.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Böhnlein S., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Identification of a U5-specific sequence required for efficient polyadenylation within the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):421–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.421-424.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway L., Wickens M. A sequence downstream of A-A-U-A-A-A is required for formation of simian virus 40 late mRNA 3' termini in frog oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3949–3953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeZazzo J. D., Imperiale M. J. Sequences upstream of AAUAAA influence poly(A) site selection in a complex transcription unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4951–4961. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M. B., Dworkin-Rastl E. Changes in RNA titers and polyadenylation during oogenesis and oocyte maturation in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1985 Dec;112(2):451–457. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falck-Pedersen E., Logan J. Regulation of poly(A) site selection in adenovirus. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):532–541. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.532-541.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falck-Pedersen E., Logan J., Shenk T., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription termination within the E1A gene of adenovirus induced by insertion of the mouse beta-major globin terminator element. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):897–905. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90349-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. A., Sheets M. D., Wickens M. P. Poly(A) addition during maturation of frog oocytes: distinct nuclear and cytoplasmic activities and regulation by the sequence UUUUUAU. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2151–2162. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Guise J. W., McDevitt M. A., Tucker P. W., Nevins J. R. Relative position and strengths of poly(A) sites as well as transcription termination are critical to membrane versus secreted mu-chain expression during B-cell development. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):471–481. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenh C. H., Deng T. L., Li D. W., DeWille J., Johnson L. F. Mouse thymidylate synthase messenger RNA lacks a 3' untranslated region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8482–8486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenh C. H., Geyer P. K., Johnson L. F. Control of thymidylate synthase mRNA content and gene transcription in an overproducing mouse cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2527–2532. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Growth-dependent expression of dihydrofolate reductase mRNA from modular cDNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;3(9):1598–1608. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.9.1598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Analysis of an activatable promoter: sequences in the simian virus 40 late promoter required for T-antigen-mediated trans activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1859–1869. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt N., Briggs D., Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. Definition of an efficient synthetic poly(A) site. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1019–1025. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather E. L., Nelson K. J., Haimovich J., Perry R. P. Mode of regulation of immunoglobulin mu- and delta-chain expression varies during B-lymphocyte maturation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Simpson S., Clements J. B. Herpes simplex virus induces a processing factor that stimulates poly(A) site usage. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1093–1105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90765-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Steps in the processing of Ad2 mRNA: poly(A)+ nuclear sequences are conserved and poly(A) addition precedes splicing. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1477–1493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Wilson M. C. Regulation of adenovirus-2 gene expression at the level of transcriptional termination and RNA processing. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):113–118. doi: 10.1038/290113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. L., Perry R. P. The regulated production of mu m and mu s mRNA is dependent on the relative efficiencies of mu s poly(A) site usage and the c mu 4-to-M1 splice. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):726–738. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju V. S., Reddy P. R. Inhibition of polyadenylation of mRNA by gonadotropin releasing hormone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Sep 15;115(2):451–455. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadofsky M., Connelly S., Manley J. L., Alwine J. C. Identification of a sequence element on the 3' side of AAUAAA which is necessary for simian virus 40 late mRNA 3'-end processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2713–2719. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Huarte J., Belin D., Gubler P., Vassalli A., O'Connell M. L., Parton L. A., Rickles R. J., Strickland S. Regulated polyadenylation controls mRNA translation during meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2163–2171. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen A., Sharp P. A. Processing at immunoglobulin polyadenylation sites in lymphoid cell extracts. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1421–1429. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02959.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J., Feig D. I., Shenk T. The C proteins of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes interact with RNA sequences downstream of polyadenylation cleavage sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4477–4483. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Liu J. K., DiPersio C. M. Site-directed mutagenesis reveals a liver transcription factor essential for the albumin transcriptional enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5469–5473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]