Abstract
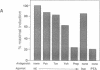
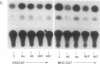
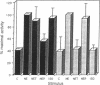
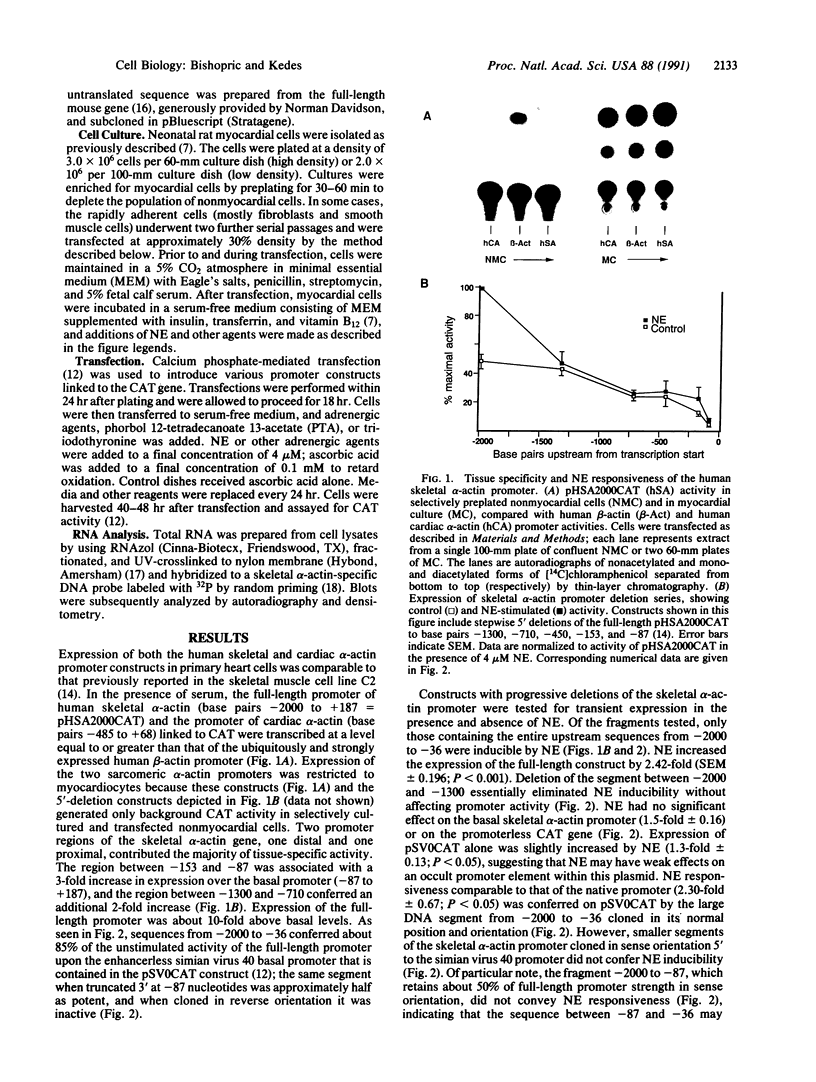
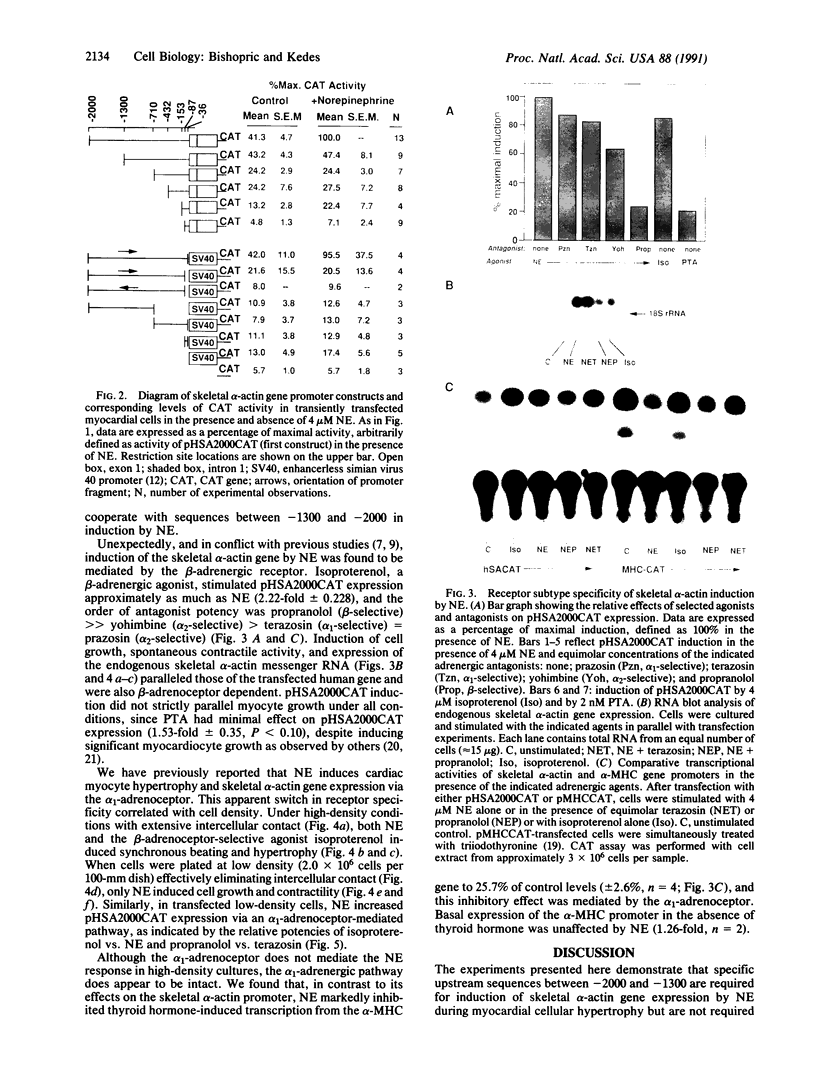
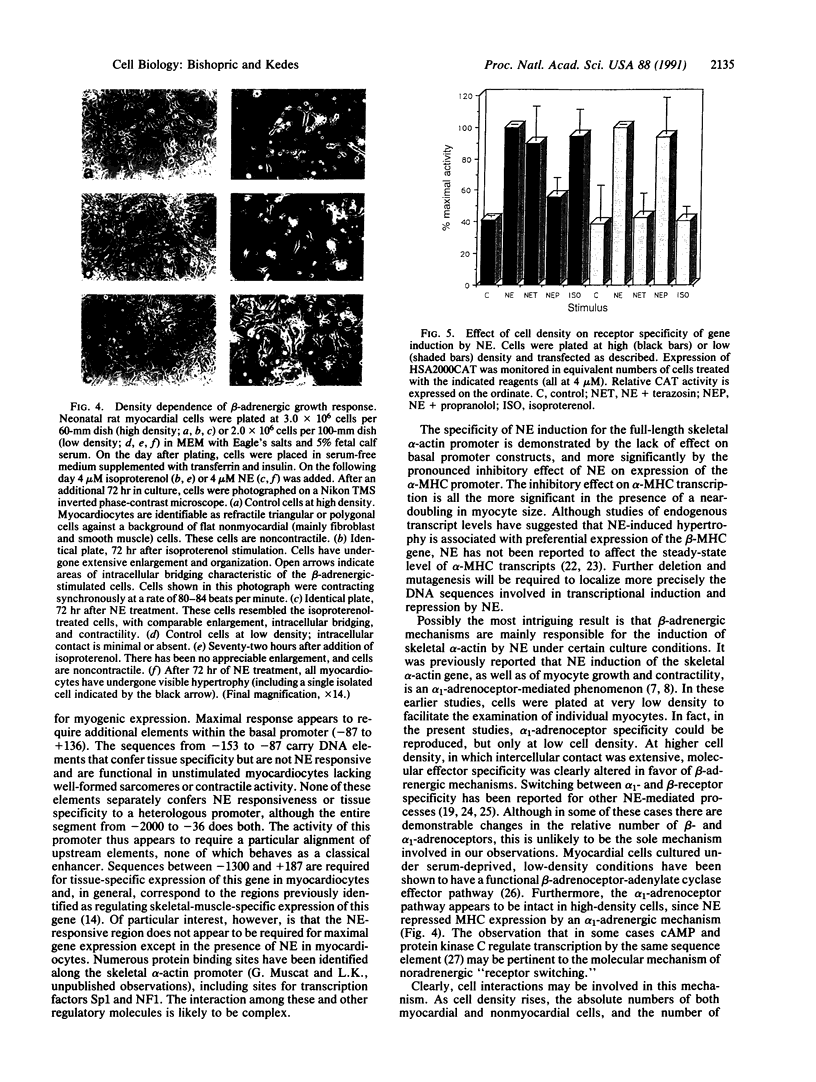
The skeletal alpha-actin gene is expressed in fetal rat heart and is induced during norepinephrine (NE)-stimulated hypertrophy in cultures of neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Here we report that NE positively regulates the human skeletal alpha-actin gene promoter in transiently transfected neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. NE increased expression from the full-length promoter by 2.4-fold. A DNA region required for NE responsiveness but not for tissue-specific expression was located between base pair -2000 and base pair -1300. Distinct regions required for cardiac myocyte expression were located between -1300 to -710 and -153 to -87. None of these elements separately conferred tissue specificity or adrenergic responsiveness on a heterologous promoter, although the intact promoter from -2000 to -36 conferred both when cloned in its correct position and orientation. Additional elements in the basal promoter (-87 to +187) were required for maximal NE responsiveness. The NE induction was mediated by the beta-adrenergic receptor in high-density cultures (3-4 x 10(6) cells per 60-mm dish), as was induction of hypertrophy, contractility, and endogenous skeletal alpha-actin gene expression. The beta-adrenergic agonist isoproterenol was as potent as NE in inducing expression. Furthermore, beta-adrenergic antagonists inhibited the effects on skeletal alpha-actin gene expression but alpha 1-adrenergic antagonists did not. The alpha 1-adrenergic system was intact in these high-density cultures, since the effects of NE on the expression of another contractile protein gene, alpha-myosin heavy chain, were blocked by alpha 1- but not by beta-adrenergic antagonists. In these high-density cultures, cell contact and intermyocardiocyte bridging were prevalent. When cardiac myocytes were plated at a low density, minimizing cell contact, NE induction of skeletal alpha-actin gene expression and hypertrophy was mediated by the alpha 1-adrenoceptor. Factors related to cell communication may influence the pathways mediating NE-regulated gene transcription during cardiac myocyte hypertrophy.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishopric N. H., Simpson P. C., Ordahl C. P. Induction of the skeletal alpha-actin gene in alpha 1-adrenoceptor-mediated hypertrophy of rat cardiac myocytes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1194–1199. doi: 10.1172/JCI113179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugaisky L. B., Zak R. Differentiation of adult rat cardiac myocytes in cell culture. Circ Res. 1989 Mar;64(3):493–500. doi: 10.1161/01.res.64.3.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claycomb W. C. Biochemical aspects of cardiac muscle differentiation. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and nuclear and cytoplasmic deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase activity. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3229–3235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocks T. M., Angus J. A. Endothelium-dependent relaxation of coronary arteries by noradrenaline and serotonin. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):627–630. doi: 10.1038/305627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Bahl J. J., Markham B. E., Roeske W. R., Morkin E. Hormonal regulation of myosin heavy chain and alpha-actin gene expression in cultured fetal rat heart myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13316–13322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Markham B. E., Bahl J. J., Morkin E. Thyroid hormone regulates expression of a transfected alpha-myosin heavy-chain fusion gene in fetal heart cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3122–3126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Sharp S. B., Davidson N. The complete sequence of the mouse skeletal alpha-actin gene reveals several conserved and inverted repeat sequences outside of the protein-coding region. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):15–25. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M. Complexities of gene regulation by cAMP. Trends Genet. 1989 Mar;5(3):65–67. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karliner J. S., Simpson P. C. Beta-adrenoceptor and adenylate cyclase regulation in cardiac myocyte growth. Basic Res Cardiol. 1988 Nov-Dec;83(6):655–663. doi: 10.1007/BF01906960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karliner J. S., Simpson P. C., Taylor J. E., Honbo N., Woloszyn W. Adrenergic receptor characteristics of cardiac myocytes cultured in serum-free medium: comparison with serum-supplemented medium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 16;128(1):376–382. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91689-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen K. A., McElwee S. A., Myers L. A role for the neural cell adhesion molecule, NCAM, in myoblast interaction during myogenesis. Dev Biol. 1990 Mar;138(1):159–168. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90185-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G., Ishac E. J. Mechanism of inverse regulation of alpha 1- and beta-adrenergic receptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 15;36(8):1185–1191. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G., Mucci L., O'Regan S. The influence of hormonal and neuronal factors on rat heart adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(2):371–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann S. M., Walter U. Regulation of the cellular and subcellular concentrations and distribution of cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;18:63–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C. S., Ordahl C. P., Simpson P. C. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor stimulation of sarcomeric actin isogene transcription in hypertrophy of cultured rat heart muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):1078–1082. doi: 10.1172/JCI113951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motz W. H., Strauer B. E. Differential therapy of hypertensive heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 1990 Apr 3;65(14):60G–64G. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(90)90962-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscat G. E., Kedes L. Multiple 5'-flanking regions of the human alpha-skeletal actin gene synergistically modulate muscle-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4089–4099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel E. G., Selwyn A. P., Ganz P. Large coronary arteries in humans are responsive to changing blood flow: an endothelium-dependent mechanism that fails in patients with atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990 Aug;16(2):349–356. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(90)90584-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostman-Smith I. Cardiac sympathetic nerves as the final common pathway in the induction of adaptive cardiac hypertrophy. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Sep;61(3):265–272. doi: 10.1042/cs0610265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ran W., Dean M., Levine R. A., Henkle C., Campisi J. Induction of c-fos and c-myc mRNA by epidermal growth factor or calcium ionophore is cAMP dependent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8216–8220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiaffino S., Samuel J. L., Sassoon D., Lompré A. M., Garner I., Marotte F., Buckingham M., Rappaport L., Schwartz K. Nonsynchronous accumulation of alpha-skeletal actin and beta-myosin heavy chain mRNAs during early stages of pressure-overload--induced cardiac hypertrophy demonstrated by in situ hybridization. Circ Res. 1989 May;64(5):937–948. doi: 10.1161/01.res.64.5.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz K., Lecarpentier Y., Martin J. L., Lompré A. M., Mercadier J. J., Swynghedauw B. Myosin isoenzymic distribution correlates with speed of myocardial contraction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1981 Dec;13(12):1071–1075. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(81)90297-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz K., de la Bastie D., Bouveret P., Oliviéro P., Alonso S., Buckingham M. Alpha-skeletal muscle actin mRNA's accumulate in hypertrophied adult rat hearts. Circ Res. 1986 Nov;59(5):551–555. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.5.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. W., Rodgers R. L., McNeill J. H. Cardiac responsiveness to alpha and beta adrenergic amines: effects of carbachol and hypothyroidism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Oct;219(1):231–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swynghedauw B. Developmental and functional adaptation of contractile proteins in cardiac and skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev. 1986 Jul;66(3):710–771. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1986.66.3.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sáez J. C., Connor J. A., Spray D. C., Bennett M. V. Hepatocyte gap junctions are permeable to the second messenger, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, and to calcium ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2708–2712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veomett G., Kuszynski C., Kazakoff P., Rizzino A. Cell density regulates the number of cell surface receptors for fibroblast growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):694–700. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalin R. J., Montague W. Changes in adenylate cyclase, cyclic AMP, and protein kinase levels in chick myoblasts, and their relationship to differentiation. Cell. 1974 Jun;2(2):103–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]