Abstract
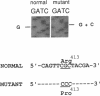
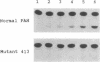
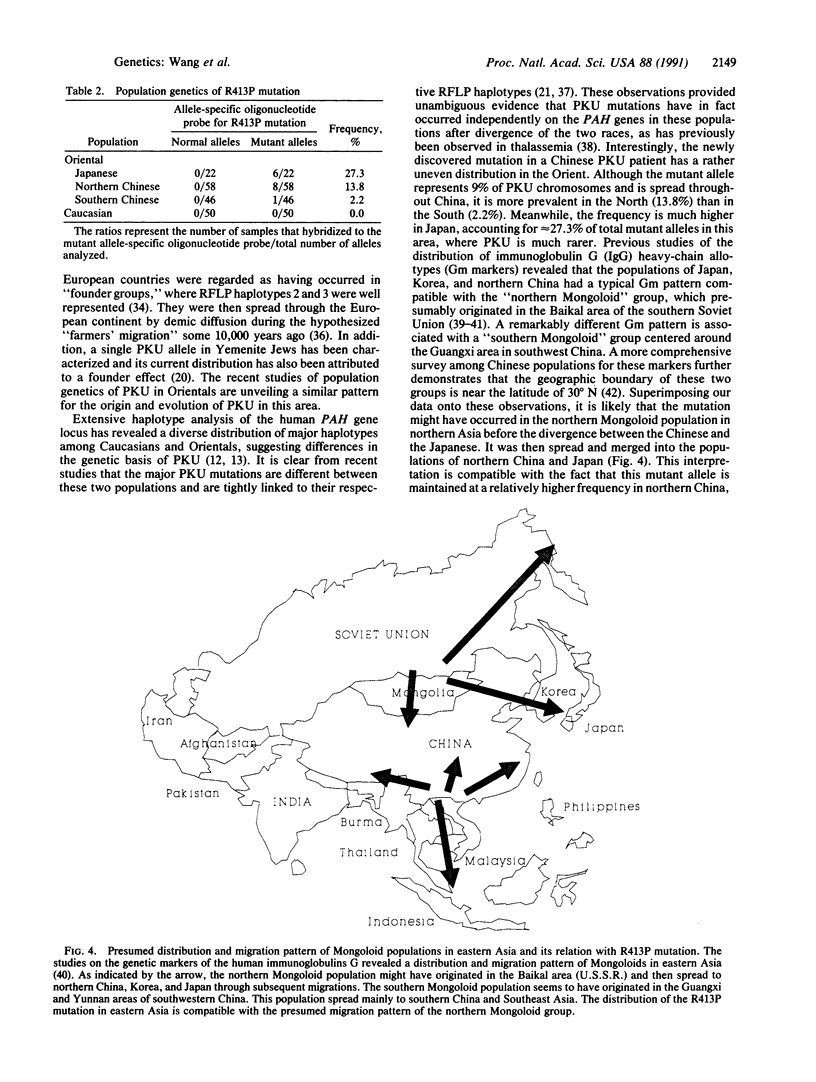
A missense mutation has been identified in the human phenylalanine hydroxylase [PAH; phenylalanine 4-monooxygenase; L-phenylalanine, tetrahydrobiopterin:oxygen oxidoreductase (4-hydroxylating), EC 1.14.16.1] gene in a Chinese patient with classic phenylketonuria (PKU). A G-to-C transition at the second base of codon 413 in exon 12 of the gene results in the substitution of Pro413 for Arg413 in the mutant protein. This mutation (R413P) results in negligible enzymatic activity when expressed in heterologous mammalian cells and is compatible with a classic PKU phenotype in the patient. Population genetic studies reveal that this mutation is tightly linked to restriction fragment length polymorphism haplotype 4, which is the predominant haplotype of the PAH locus in the Oriental population. It accounts for 13.8% of northern Chinese and 27% of Japanese PKU alleles, but it is rare in southern Chinese (2.2%) and is absent in the Caucasian population. The data demonstrate unambiguously that the mutation occurred after racial divergence of Orientals and Caucasians and suggest that the allele has spread throughout the Orient by a founder effect. Previous protein polymorphism studies in eastern Asia have led to the hypothesis that "northern Mongoloids" represented a founding population in Asia. Our results are compatible with this hypothesis in that the PKU mutation might have occurred in northern Mongoloids and subsequently spread to the Chinese and Japanese populations.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abadie V., Lyonnet S., Maurin N., Berthelon M., Caillaud C., Giraud F., Mattei J. F., Rey J., Rey F., Munnich A. CpG dinucleotides are mutation hot spots in phenylketonuria. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):936–939. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avigad S., Cohen B. E., Bauer S., Schwartz G., Frydman M., Woo S. L., Niny Y., Shiloh Y. A single origin of phenylketonuria in Yemenite Jews. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):168–170. doi: 10.1038/344168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BICKEL H., GERRARD J., HICKMANS E. M. The influence of phenylalanine intake on the chemistry and behaviour of a phenyl-ketonuric child. Acta Paediatr. 1954 Jan;43(1):64–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1954.tb04000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty R., Lidsky A. S., Daiger S. P., Güttler F., Sullivan S., Dilella A. G., Woo S. L. Polymorphic DNA haplotypes at the human phenylalanine hydroxylase locus and their relationship with phenylketonuria. Hum Genet. 1987 May;76(1):40–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00283048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Hsiao K. J., Lin L. H., Liu T. T., Tang R. B., Su T. S. Study of restriction fragment length polymorphisms at the human phenylalanine hydroxylase locus and evaluation of its potential application in prenatal diagnosis of phenylketonuria in Chinese. Hum Genet. 1989 Feb;81(3):226–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00278993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daiger S. P., Chakraborty R., Reed L., Fekete G., Schuler D., Berenssi G., Nasz I., Brdicka R., Kamarýt J., Pijácková A. Polymorphic DNA haplotypes at the phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) locus in European families with phenylketonuria (PKU). Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Aug;45(2):310–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daiger S. P., Reed L., Huang S. S., Zeng Y. T., Wang T., Lo W. H., Okano Y., Hase Y., Fukuda Y., Oura T. Polymorphic DNA haplotypes at the phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) locus in Asian families with phenylketonuria (PKU). Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Aug;45(2):319–324. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Huang W. M., Woo S. L. Screening for phenylketonuria mutations by DNA amplification with the polymerase chain reaction. Lancet. 1988 Mar 5;1(8584):497–499. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91295-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Marvit J., Brayton K., Woo S. L. An amino-acid substitution involved in phenylketonuria is in linkage disequilibrium with DNA haplotype 2. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):333–336. doi: 10.1038/327333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Marvit J., Lidsky A. S., Güttler F., Woo S. L. Tight linkage between a splicing mutation and a specific DNA haplotype in phenylketonuria. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):799–803. doi: 10.1038/322799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güttler F. Hyperphenylalaninemia: diagnosis and classification of the various types of phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency in childhood. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl. 1980;280:1–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JERVIS G. A. Phenylpyruvic oligophrenia deficiency of phenylalanine-oxidizing system. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Mar;82(3):514–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John S. W., Rozen R., Laframboise R., Laberge C., Scriver C. R. Novel PKU mutation on haplotype 2 in French-Canadians. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Dec;45(6):905–909. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd K. K. Phenylketonuria. Population genetics of a disease. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):282–283. doi: 10.1038/327282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S. C., Ledley F. D., DiLella A. G., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length complementary DNA clone and amino acid sequence of human phenylalanine hydroxylase. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):556–561. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledley F. D., Grenett H. E., DiLella A. G., Kwok S. C., Woo S. L. Gene transfer and expression of human phenylalanine hydroxylase. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.3856322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy H. L. Molecular genetics of phenylketonuria and its implications. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Nov;45(5):667–670. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter-Konecki U., Konecki D. S., DiLella A. G., Brayton K., Marvit J., Hahn T. M., Trefz F. K., Woo S. L. Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency caused by a single base substitution in an exon of the human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2881–2885. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidsky A. S., Ledley F. D., DiLella A. G., Kwok S. C., Daiger S. P., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. Extensive restriction site polymorphism at the human phenylalanine hydroxylase locus and application in prenatal diagnosis of phenylketonuria. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jul;37(4):619–634. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyonnet S., Caillaud C., Rey F., Berthelon M., Frézal J., Rey J., Munnich A. Molecular genetics of phenylketonuria in Mediterranean countries: a mutation associated with partial phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;44(4):511–517. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H. Characteristics of Mongoloid and neighboring populations based on the genetic markers of human immunoglobulins. Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;80(3):207–218. doi: 10.1007/BF01790088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H. Characteristics of Mongoloid populations based on the human immunoglobulin allotypes. Anthropol Anz. 1988 Jun;46(2):119–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Miyazaki T., Xu X., Watanabe H., Kawai N., Suzuki K. Distribution of Gm and Km allotypes among five populations in China. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1986 Jun;70(2):161–165. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330700203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menozzi P., Piazza A., Cavalli-Sforza L. Synthetic maps of human gene frequencies in Europeans. Science. 1978 Sep 1;201(4358):786–792. doi: 10.1126/science.356262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano Y., Wang T., Eisensmith R. C., Steinmann B., Gitzelmann R., Woo S. L. Missense mutations associated with RFLP haplotypes 1 and 4 of the human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jan;46(1):18–25. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr The mutation and polymorphism of the human beta-globin gene and its surrounding DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:131–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson K. J., Chandra T., MacGillivray R. T., Woo S. L. Polysome immunoprecipitation of phenylalanine hydroxylase mRNA from rat liver and cloning of its cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4701–4705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scriver C. R., Clow C. L. Phenylketonuria and other phenylalanine hydroxylation mutants in man. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:179–202. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoflet E. S., Koeberl D. D., Sarkar G., Sommer S. S. Genomic amplification with transcript sequencing. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):491–494. doi: 10.1126/science.3340835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T., Okano Y., Eisensmith R. C., Fekete G., Schuler D., Berencsi G., Nasz I., Woo S. L. Molecular genetics of PKU in eastern Europe: a nonsense mutation associated with haplotype 4 of the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1990 Jan;16(1):85–90. doi: 10.1007/BF01650483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T., Okano Y., Eisensmith R., Huang S. Z., Zeng Y. T., Lo W. H., Woo S. L. Molecular genetics of phenylketonuria in Orientals: linkage disequilibrium between a termination mutation and haplotype 4 of the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Nov;45(5):675–680. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo S. L. Collation of RFLP haplotypes at the human phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):781–783. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo S. L. Molecular basis and population genetics of phenylketonuria. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):1–7. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao T. M., Lee T. D. Gm and Km allotypes in 74 Chinese populations: a hypothesis of the origin of the Chinese nation. Hum Genet. 1989 Sep;83(2):101–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00286699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]