Abstract
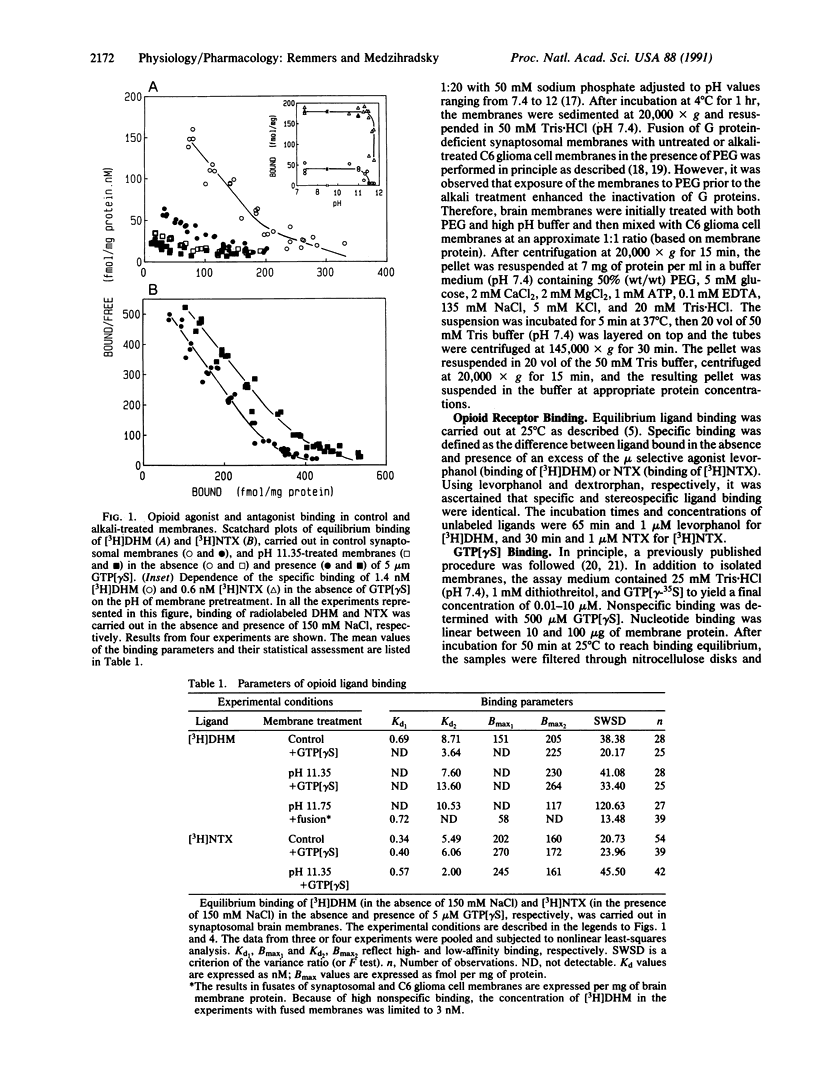
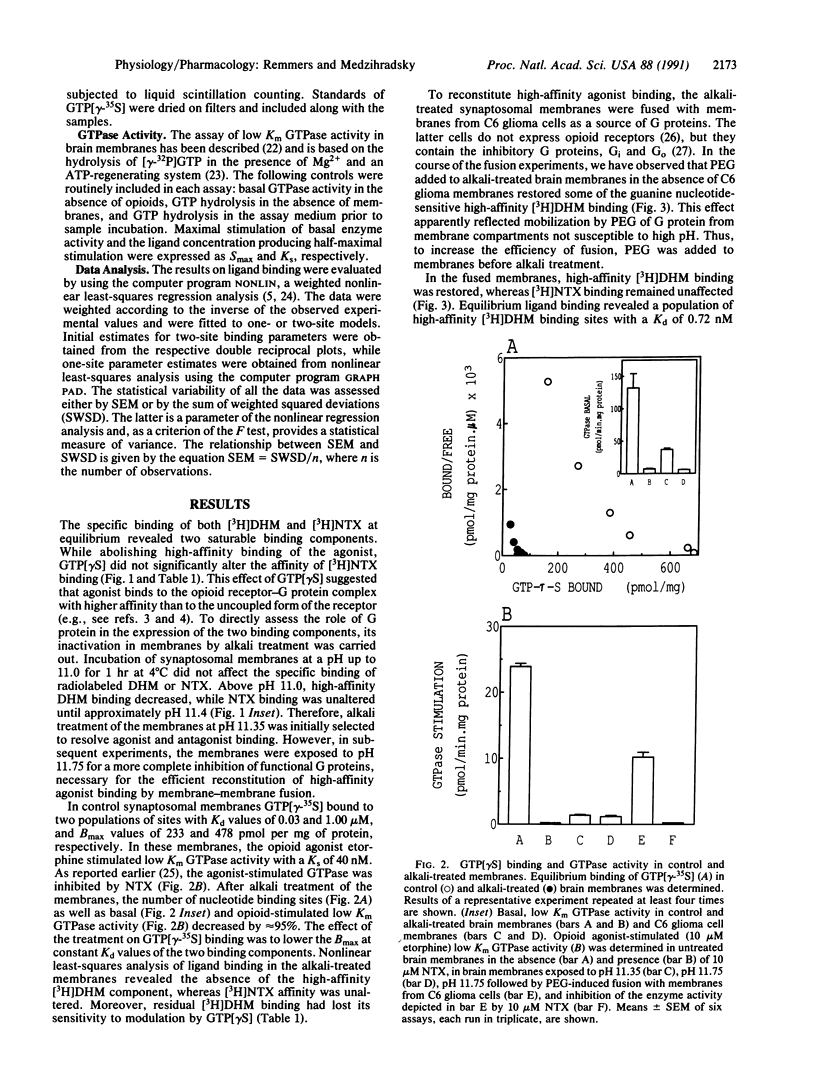
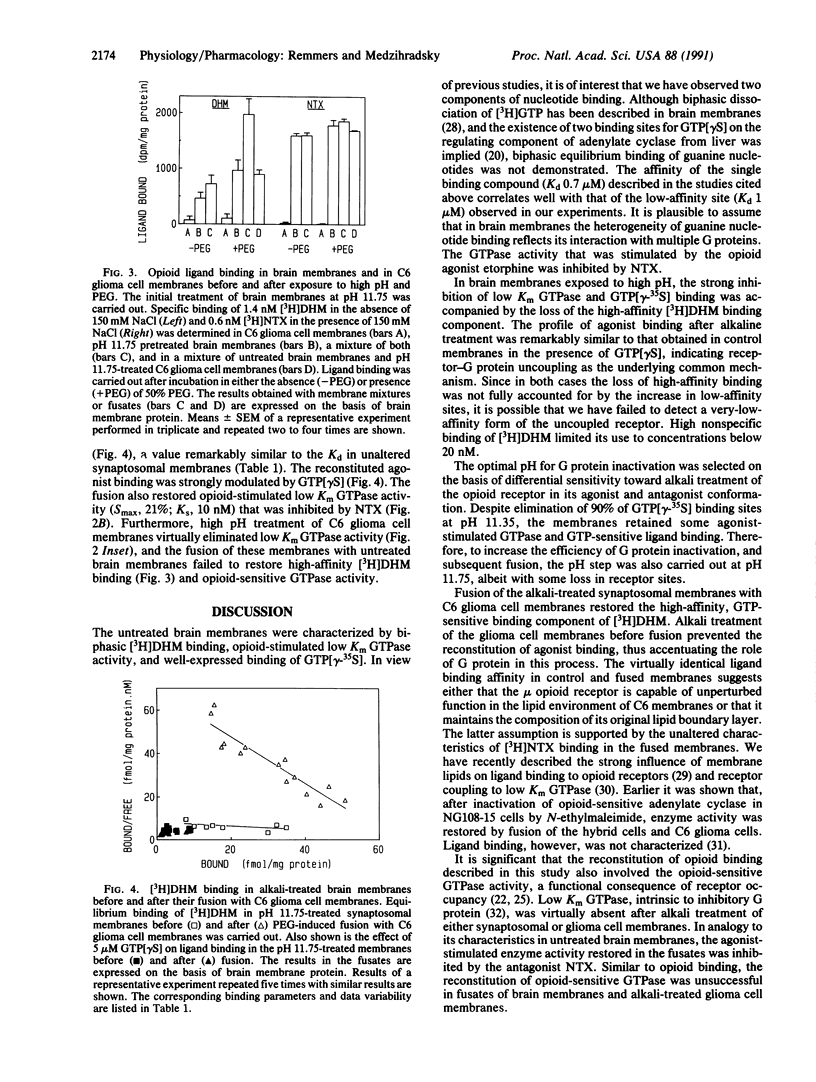
In synaptosomal membranes from rat brain cortex, the mu selective agonist [3H]dihydromorphine in the absence of sodium, and the nonselective antagonist [3H]naltrexone in the presence of sodium, bound to two populations of opioid receptor sites with Kd values of 0.69 and 8.7 nM for dihydromorphine, and 0.34 and 5.5 nM for naltrexone. The addition of 5 microM guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[gamma S]) strongly reduced high-affinity agonist but not antagonist binding. Exposure of the membranes to high pH reduced the number of GTP[gamma-35S] binding sites by 90% and low Km, opioid-sensitive GTPase activity by 95%. In these membranes, high-affinity agonist binding was abolished and modulation of residual binding by GTP[gamma S] was diminished. High-affinity (Kd, 0.72 nM), guanine nucleotide-sensitive agonist binding was reconstituted by polyethylene glycol-induced fusion of the alkali-treated membranes with (opioid receptor devoid) C6 glioma cell membranes. Also restored was opioid agonist-stimulated, naltrexone-inhibited GTPase activity. In contrast, antagonist binding in the fused membranes was unaltered. Alkali treatment of the glioma cell membranes prior to fusion inhibited most of the low Km GTPase activity and prevented the reconstitution of agonist binding. The results show that high-affinity opioid agonist binding reflects the ligand-occupied receptor-guanine nucleotide binding protein complex.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abood M. E., Lee N. M., Loh H. H. Modification of opioid agonist binding by pertussis toxin. Brain Res. 1987 Aug 4;417(1):70–74. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchfeld C. C., Medzihradsky F. Receptor-mediated stimulation of brain GTPase by opiates in normal and dependent rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 15;121(2):641–648. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume A. J. Interaction of ligands with the opiate receptors of brain membranes: regulation by ions and nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1713–1717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill A. L., Medzihradsky F. Interaction of central nervous system drugs with synaptosomal transport processes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Oct 15;25(20):2257–2264. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Catecholamine-stimulated GTPase activity in turkey erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 8;452(2):538–551. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90206-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Blanchard S. G., Cuatrecasas P. Unmasking of magnesium-dependent high-affinity binding sites for [dAla2, dLeu5]enkephalin after pretreatment of brain membranes with guanine nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):940–944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childers S. R., Snyder S. H. Characterization of [3H]guanine nucleotide binding sites in brain membranes. J Neurochem. 1980 Jul;35(1):183–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb12505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childers S. R., Snyder S. H. Differential regulation by guanine nucleotides or opiate agonist and antagonist receptor interactions. J Neurochem. 1980 Mar;34(3):583–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb11184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. J., Carter B. D., Medzihradsky F. Selectivity of ligand binding to opioid receptors in brain membranes from the rat, monkey and guinea pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 13;148(3):343–351. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. J., Medzihradsky F. Coupling of multiple opioid receptors to GTPase following selective receptor alkylation in brain membranes. Neuropharmacology. 1987 Dec;26(12):1763–1770. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(87)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. J., Nordby G. L., Medzihradsky F. Relationship between opioid-receptor occupancy and stimulation of low-Km GTPase in brain membranes. J Neurochem. 1989 Apr;52(4):1162–1169. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb01862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischel S. V., Medzihradsky F. Interaction between [3H]ethylketocyclazocine and [3H]etorphine and opioid receptors in membranes from rat brain. A kinetic analysis. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Apr;25(4):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90229-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischel S. V., Medzihradsky F. Scatchard analysis of opiate receptor binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;20(2):269–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillan M. G., Kosterlitz H. W., Paterson S. J. Comparison of the binding characteristics of tritiated opiates and opioid peptides. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;70(3):481–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb08727.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., James I. F. Site-directed alkylation of multiple opioid receptors. II. Pharmacological selectivity. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 May;25(3):343–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Lowney L. I., Pal B. K. Stereospecific and nonspecific interactions of the morphine congener levorphanol in subcellular fractions of mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1742–1747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsia J. A., Moss J., Hewlett E. L., Vaughan M. ADP-ribosylation of adenylate cyclase by pertussis toxin. Effects on inhibitory agonist binding. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1086–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nagata S., Nakamura S., Katada T., Ui M., Iwai S., Ohtsuka E., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of cDNAs for alpha subunits of the guanine nucleotide-binding proteins Gs, Gi, and Go from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3776–3780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James I. F., Goldstein A. Site-directed alkylation of multiple opioid receptors. I. Binding selectivity. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 May;25(3):337–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M. H., Neubig R. R. Membrane reconstitution of high-affinity alpha 2 adrenergic agonist binding with guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3664–3672. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M. H., Neubig R. R. Parallel inactivation of alpha 2-adrenergic agonist binding and Ni by alkaline treatment. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 18;192(2):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee W. A., Nirenberg M. A neuroblastoma times glioma hybrid cell line with morphine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3474–3477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski G., Klee W. A. Opiates inhibit adenylate cyclase by stimulating GTP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4185–4189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar D. F., Medzihradsky F. Differential inhibition of delta-opiate binding and low-Km GTPase stimulation by phospholipase A2 treatment. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;328:113–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Klee W. A. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding protein (Ni) purified from bovine brain is a high affinity GTPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2057–2063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The guanine nucleotide activating site of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Identification by ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11416–11423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Snyder S. H. Identification of novel high affinity opiate receptor binding in rat brain. Nature. 1975 Feb 13;253(5492):563–565. doi: 10.1038/253563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remmers A. E., Nordby G. L., Medzihradsky F. Modulation of opioid receptor binding by cis and trans fatty acids. J Neurochem. 1990 Dec;55(6):1993–2000. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb05787.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm M. Transfer of glucagon receptor from liver membranes to a foreign adenylate cyclase by a membrane fusion procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1174–1178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tocqué B., Pfeiffer A., Klee A. Transfer of functional opiate receptors from membranes to recipient cells by polyethylene glycol-induced fusion. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 5;222(2):327–331. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80395-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Harada H., Nozaki M., Katada T., Ui M., Satoh M., Takagi H. Reconstitution of rat brain mu opioid receptors with purified guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins, Gi and Go. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):7013–7017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.7013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werling L. L., Puttfarcken P. S., Cox B. M. Multiple agonist-affinity states of opioid receptors: regulation of binding by guanyl nucleotides in guinea pig cortical, NG108-15, and 7315c cell membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;33(4):423–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



