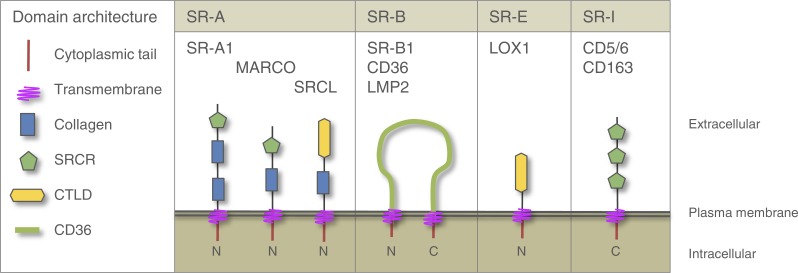
Figure 1. Domain architecture of vertebrate SRs relevant to this study.
All SR sequences are anchored in the membrane with one or two transmembrane domains. All have very short cytoplasmic tails and extensive extracellular ligand-binding domains. SR-As contain a collagen domain(s) and can include an SRCR or a CTLD. SR-Bs have two cytoplasmic tails on either side of a CD36 domain that forms an extracellular loop. SR-Es are defined by the presence of a CTLD. SR-Is have multiple SRCR repeats and no other identifiable extracellular domains. C, carboxy terminus; CTLD, C type lectin domain; LOX1, lectin-like oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor 1; MARCO, macrophage receptor with collagenous structure; N, amino terminus; SRCL, scavenger receptor with C-type lectin; SRCR, scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain.