Abstract
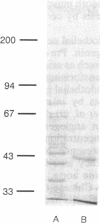
A 42-kDa bovine protein that binds bovine angiogenin [angiogenin binding protein (AngBP)] has been identified as a dissociable cell-surface component of calf pulmonary artery endothelial cells and a transformed bovine endothelial cell line, GM7373. Binding of 125I-labeled bovine angiogenin (125I-Ang) to AngBP occurs with an apparent Kd approximately 5 x 10(-10) M and is specific, saturable, and inhibited by excess unlabeled angiogenin. 125I-Ang can be crosslinked efficiently to AngBP by a water-soluble carbodiimide, 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbo-diimide. Bovine ribonuclease A competes with the binding of 125I-Ang to AngBP, but lysozyme does not. Direct binding to AngBP of 125I-labeled bovine ribonuclease A is, however, much weaker than that of 125I-Ang. Two enzymatically active derivatives of angiogenin cleaved at residues 60-61 and 67-68, respectively, fail to induce angiogenesis and also bind to AngBP only weakly. AngBP has been isolated by treatment of cells with heparan sulfate, affinity chromatography on angiogenin-Sepharose of the material dissociated from the cell surface, and gel filtration HPLC. The results suggest that AngBP has the characteristics of a receptor that may likely function in angiogenesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres J. L., Stanley K., Cheifetz S., Massagué J. Membrane-anchored and soluble forms of betaglycan, a polymorphic proteoglycan that binds transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3137–3145. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badet J., Soncin F., Guitton J. D., Lamare O., Cartwright T., Barritault D. Specific binding of angiogenin to calf pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8427–8431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknell R., Vallee B. L. Angiogenin activates endothelial cell phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5961–5965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknell R., Vallee B. L. Angiogenin stimulates endothelial cell prostacyclin secretion by activation of phospholipase A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1573–1577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blood C. H., Zetter B. R. Tumor interactions with the vasculature: angiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 1;1032(1):89–118. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(90)90014-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond M. D., Vallee B. L. Isolation of bovine angiogenin using a placental ribonuclease inhibitor binding assay. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6282–6287. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett J. W., Strydom D. J., Lobb R. R., Alderman E. M., Bethune J. L., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Isolation and characterization of angiogenin, an angiogenic protein from human carcinoma cells. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5480–5486. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto J., Stewart S. J., Levy R. Immunochemical analysis of the released Leu-2 (T8) molecule. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):116–124. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Buell D. N., Roth J. Water-soluble insulin receptors from human lymphocytes. Science. 1972 Oct 13;178(4057):168–169. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4057.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinspan J. B., Mueller S. N., Levine E. M. Bovine endothelial cells transformed in vitro by benzo(a)pyrene. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Mar;114(3):328–338. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041140312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallahan T. W., Shapiro R., Vallee B. L. Dual site model for the organogenic activity of angiogenin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2222–2226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Vallee B. L. A covalent angiogenin/ribonuclease hybrid with a fourth disulfide bond generated by regional mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1875–1884. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath W. F., Jr, Moore F., Bicknell R., Vallee B. L. Modulation of mitogenic stimuli by angiogenin correlates with in vitro phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2718–2722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hök M., Kjellén L., Johansson S. Cell-surface glycosaminoglycans. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:847–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.004215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen S., Jalkanen M., Bargatze R., Tammi M., Butcher E. C. Biochemical properties of glycoproteins involved in lymphocyte recognition of high endothelial venules in man. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1615–1623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krangel M. S. Secretion of HLA-A and -B antigens via an alternative RNA splicing pathway. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1173–1190. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. S., Shapiro R., Vallee B. L. Tight-binding inhibition of angiogenin and ribonuclease A by placental ribonuclease inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):225–230. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maes P., Damart D., Rommens C., Montreuil J., Spik G., Tartar A. The complete amino acid sequence of bovine milk angiogenin. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 5;241(1-2):41–45. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena U., Klein M. G., Goldberg I. J. Metabolism of endothelial cell-bound lipoprotein lipase. Evidence for heparan sulfate proteoglycan-mediated internalization and recycling. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12880–12886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Characteristic ribonucleolytic activity of human angiogenin. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3527–3532. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Strydom D. J., Olson K. A., Vallee B. L. Isolation of angiogenin from normal human plasma. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 11;26(16):5141–5146. doi: 10.1021/bi00390a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Vallee B. L. Site-directed mutagenesis of histidine-13 and histidine-114 of human angiogenin. Alanine derivatives inhibit angiogenin-induced angiogenesis. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7401–7408. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair D. K., Rybak S. M., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Angiogenin abolishes cell-free protein synthesis by specific ribonucleolytic inactivation of ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8330–8334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaisman N., Gospodarowicz D., Neufeld G. Characterization of the receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19461–19466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber W., Gill G. N., Spiess J. Production of an epidermal growth factor receptor-related protein. Science. 1984 Apr 20;224(4646):294–297. doi: 10.1126/science.6324343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]