Abstract
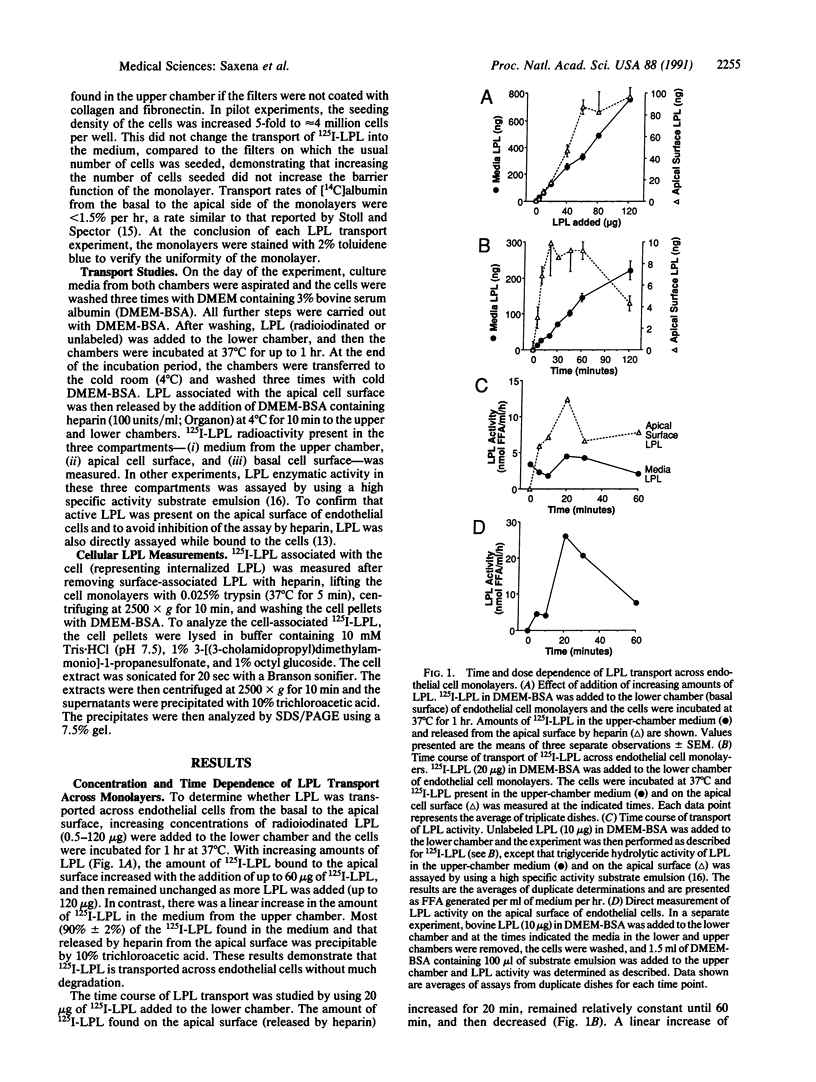
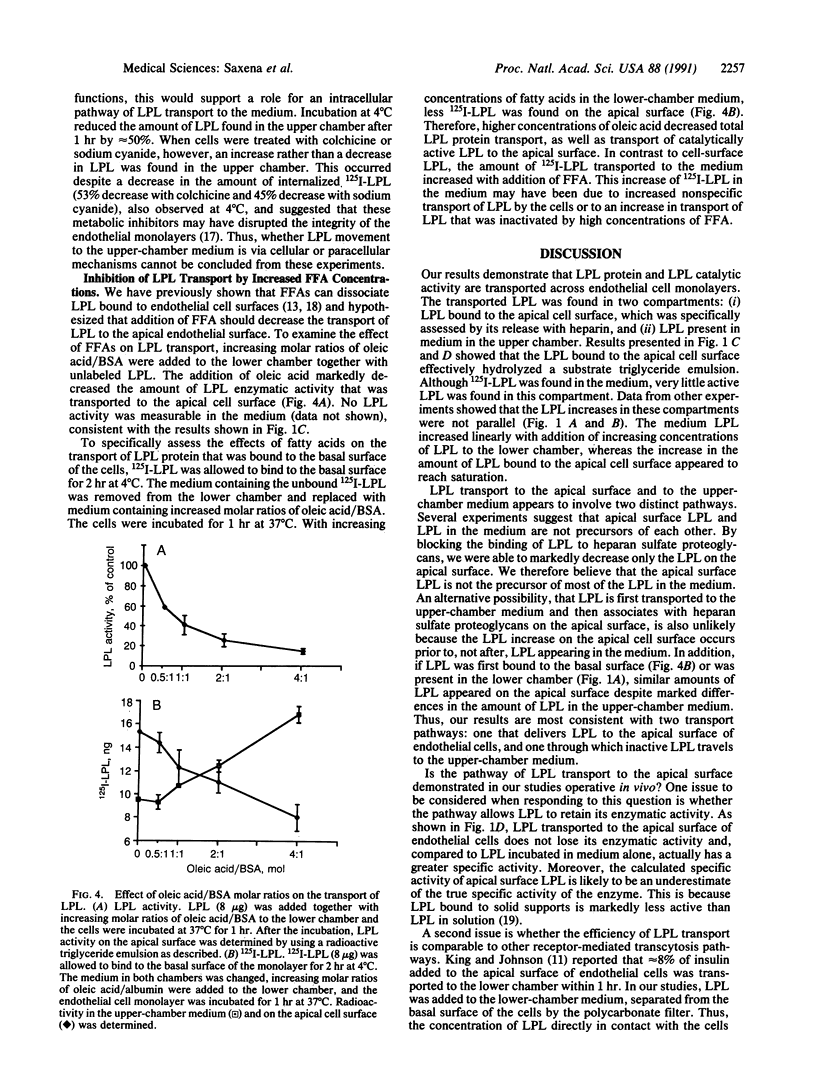
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL), synthesized in muscle and fat, hydrolyzes plasma triglycerides primarily while bound to luminal endothelial cell surfaces. To obtain information about the movement of LPL from the basal to the luminal endothelial cell surface, we studied the transport of purified bovine milk LPL across bovine aortic endothelial cell monolayers. 125I-labeled LPL (125I-LPL) added to the basal surface of the monolayers was detected on the apical side of the cells in two compartments: (i) in the medium of the upper chamber, and (ii) bound to the apical cell surface. The amount of 125I-LPL on the cell surface, but not in the medium, reached saturation with time and LPL dose. Catalytically active LPL was transported to the apical surface but very little LPL activity appeared in the medium. Heparinase treatment of the basal cell surface and addition of dextran sulfate (0.15 microM) to the lower chamber decreased the amount of 125I-LPL appearing on the apical surface. Similarly, the presence of increasing molar ratios of oleic acid/bovine serum albumin at the basal surface decreased the transport of active LPL across the monolayer. Thus, a saturable transport system, which requires heparan sulfate proteoglycans and is inhibited by high concentrations of free fatty acids on the basal side of the cells, appears to exist for passage of enzymatically active LPL across endothelial cells. We postulate that regulation of LPL transport to the endothelial luminal surface modulates the physiologically active pool of LPL in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beg O. U., Meng M. S., Skarlatos S. I., Previato L., Brunzell J. D., Brewer H. B., Jr, Fojo S. S. Lipoprotein lipaseBethesda: a single amino acid substitution (Ala-176----Thr) leads to abnormal heparin binding and loss of enzymic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3474–3478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette-Mackie E. J., Masuno H., Dwyer N. K., Olivecrona T., Scow R. O. Lipoprotein lipase in myocytes and capillary endothelium of heart: immunocytochemical study. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):E818–E828. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.256.6.E818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng C. F., Oosta G. M., Bensadoun A., Rosenberg R. D. Binding of lipoprotein lipase to endothelial cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12893–12898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Vecchio P. J., Siflinger-Birnboim A., Shepard J. M., Bizios R., Cooper J. A., Malik A. B. Endothelial monolayer permeability to macromolecules. Fed Proc. 1987 Jun;46(8):2511–2515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle M. H., Ben-Zeev O., Elovson J., Martin D., Kirchgessner T. G. The response of lipoprotein lipase to feeding and fasting. Evidence for posttranslational regulation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4570–4577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel R. H., Goldberg I. J., Steiner L., Yost T. J., Paterniti J. R., Jr Plasma lipolytic activity. Relationship to postheparin lipolytic activity and evidence for metabolic regulation. Diabetes. 1988 May;37(5):610–615. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.5.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel R. H. Lipoprotein lipase. A multifunctional enzyme relevant to common metabolic diseases. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 20;320(16):1060–1068. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904203201607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachiya H. L., Halban P. A., King G. L. Intracellular pathways of insulin transport across vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 1):C459–C464. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.4.C459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Johnson S. M. Receptor-mediated transport of insulin across endothelial cells. Science. 1985 Mar 29;227(4694):1583–1586. doi: 10.1126/science.3883490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Ehle P., Garfinkel A. S., Schotz M. C. Lipolytic enzymes and plasma lipoprotein metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:667–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong J. M., Kern P. A. Effect of feeding and obesity on lipoprotein lipase activity, immunoreactive protein, and messenger RNA levels in human adipose tissue. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):305–311. doi: 10.1172/JCI114155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne J. C., Jr, Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Lee N. S., Olivecrona T. Studies on inactivation of lipoprotein lipase: role of the dimer to monomer dissociation. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5606–5611. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner I., Wang C. S., McConathy W. J. The comparative kinetics of soluble and heparin-Sepharose-immobilized bovine lipoprotein lipase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Oct 1;226(1):306–316. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkin E. M. Capillary transport of macromolecules: pores and other endothelial pathways. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Feb;58(2):315–325. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.58.2.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena U., Goldberg I. J. Interaction of lipoprotein lipase with glycosaminoglycans and apolipoprotein C-II: effects of free-fatty-acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 2;1043(2):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena U., Klein M. G., Goldberg I. J. Metabolism of endothelial cell-bound lipoprotein lipase. Evidence for heparan sulfate proteoglycan-mediated internalization and recycling. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12880–12886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena U., Witte L. D., Goldberg I. J. Release of endothelial cell lipoprotein lipase by plasma lipoproteins and free fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4349–4355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneeberger E. E. Proteins and vesicular transport in capillary endothelium. Fed Proc. 1983 May 15;42(8):2419–2424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scow R. O., Blanchette-Mackie E. J. Why fatty acids flow in cell membranes. Prog Lipid Res. 1985;24(3):197–241. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(85)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semb H., Olivecrona T. Two different mechanisms are involved in nutritional regulation of lipoprotein lipase in guinea-pig adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):505–511. doi: 10.1042/bj2620505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Shasby S. S. Active transendothelial transport of albumin. Interstitium to lumen. Circ Res. 1985 Dec;57(6):903–908. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.6.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Shasby S. S., Sullivan J. M., Peach M. J. Role of endothelial cell cytoskeleton in control of endothelial permeability. Circ Res. 1982 Nov;51(5):657–661. doi: 10.1161/01.res.51.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Shasby S. S., Sullivan J. M., Peach M. J. Role of endothelial cell cytoskeleton in control of endothelial permeability. Circ Res. 1982 Nov;51(5):657–661. doi: 10.1161/01.res.51.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siflinger-Birnboim A., Del Vecchio P. J., Cooper J. A., Malik A. B. Transendothelial albumin flux: evidence against asymmetric transport. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Dec;61(6):2035–2039. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.6.2035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simionescu N. Cellular aspects of transcapillary exchange. Physiol Rev. 1983 Oct;63(4):1536–1579. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1983.63.4.1536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll L. L., Spector A. A. Lipid transfer between endothelial and smooth muscle cells in coculture. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Oct;133(1):103–110. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]