Abstract
Background:
Little is known about the effects of a low energy dense diet on weight maintenance and cardiovascular risks following a recent weight reduction. Therefore, we assessed if weight maintenance, lipid profiles, and glycemic control differ between low energy density (LED) diet and usual diet consumers following a recent weight reduction.
Materials and Methods:
In this randomized controlled clinical trial study in a parallel design, we recruited 70 patients with the history of weight reduction in the recent 1 year. LED diet contained 30% fat, 15% protein, and 55% carbohydrate was administered to the test group, and a usual diet including 35% fat, 15% protein, and 50% carbohydrate was prescribed to the control group for 7 months. Dietary intake was assessed by using 3 days food records. Biochemical markers and anthropometric measures were done according to the standard protocol.
Results:
Weight reduced in LED diet consumers compared to usual diet consumers (−0.3 ± 0.2 vs. 1.3 ± 0.4%, P = 0.002). The results was the same regarding waist circumference (−0.4 ± 0.2 vs. 0.3 ± 0.1%, P = 0.004). Fasting blood sugar also decreased in LED diet group (−9.5 ± 0.8 vs. 0.4 ± 1.0%, P = 0.0001). LED diet group had a drop in percent change of their total cholesterol (−0.4 ± 0.5 vs. 2.05 ± 0.4%, P = 0.04) and low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (4.8 ± 0.9 vs. −0.3 ± 0.9%, P = 0.002).
Conclusion:
Our findings confirmed beneficial effects of LED diet on attenuating weight regain in subjects with history of recent weight reduction. It might be derived from higher consumption of fruits, vegetables, and fiber among LED diet than usual diet consumers.
Keywords: Anthropometric measurements, cardiovascular disease, energy density, weight maintenance
INTRODUCTION
Overweight and obesity are chronic conditions that increase the risk of cardiovascular and different chronic disorders.[1,2] In 2014, more than 1.9 billion adults were overweight, of whom more than 600 million were obese worldwide.[3] Bibbins-Domingo et al. estimated that the prevalence of obesity will increase by 7% among men and by 10% among women in 2020.[4]
Obesity might be treated by utilizing a combination of different lifestyle strategies such as energy intake restriction, increasing physical activity, and providing behavioral modification. Weight is often regained in a short-term period after initial weight loss maintenance. Therefore, long-term weight loss maintenance is usually an important issue. There are limited academic long-term evaluations of weight loss programs.[3,5,6] Making dietary strategies for weight maintenance among the general population and, especially among weight-reduced individuals still needs more careful researches.[3] Previous studies introduced different dietary interventions for weight loss maintenance. Besides the debate on low-fat or low-carbohydrate diets,[6,7] focusing on some food groups including fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairies in the diet may be helpful for weight maintenance according to the recent body of evidence. However, energy intake is the key factor of weight maintenance.[3] Energy intake will decrease by reducing energy density (ED) of a diet without producing short-term calorie restriction or feeling hunger.[8] ED of foods refers to their energy content per unit weight (kcal/g).[6] Low ED (LED) diets refer to the diets that are high in low-fat dairy products, lean meats, as well as fresh vegetables and fruits.[2] There are several studies which showed the beneficial effects of LED diets on weight reduction.[9,10,11,12,13] However, few studies discusses regarding the effects of such diets on weight maintenance.[1,3] Some earlier studies showed that long-term weight control will be facilitated by reducing the ED of the diet, through increasing intake of whole grains, fruits, vegetables,[14] use of artificial sugar,[14,15] and fat substitutes.[16] However, these results for long-term and short-term programs are still controversial.[17] Fruits and vegetables could provide suitable amount of fiber and also a low glycemic index regimen, which might be appropriate for attenuating weight regain.[4] In addition, these items could decrease the ED of the diet. Weight of food that subjects intake every day could be a factor related to their dietary ED.[1,8] Furthermore, long-term effects of this kind of diet on weight maintenance did not clearly state previously.[18] Improvements in cardiovascular risk factors such as hyperglycemia, high blood pressure, elevated serum triglyceride (TG) level, and decreased high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) was relevant to weight management. However, cardiovascular risks status is not clearly stated in weight loss maintenance period under different dietary management in the previously published papers. Many cardiovascular risk factors can be modified by dietary intakes like fiber, which is a key factor in a LED diet.[19] There are few studies which determine the effects of LED diet on biochemical markers related to cardiovascular risk factors including TG, fasting blood sugar (FBS), low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C), HDL-C, total cholesterol, and blood pressure. Hence, we determined the longitudinal effects of LED diet on weight loss maintenance as the primary outcome and cardiovascular risk factors as the secondary outcome among those patients with the history of recently intentional weight reduction.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Subjects
This was a randomized controlled clinical trial study in a parallel design. Participants were recruited from the clinic in Alzahra Hospital, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran, during 2011. The sample size was calculated on the basis of the sample size formula suggested for parallel trials n = 2([Z1−α/2+ Z1−β]2 × S2)/d2.[20,21] In order to reject the H0 hypothesis by α =0.05 and 1−β =80%, a 6.3 mg/dl change in serum LDL-C was considered as the significant level.[20] Hence, 16 patients in each group (32 total) would provide adequate power for this study. However, to increase the power of study and compensating the dropping out within the study, 76 participants were screened, and finally, 70 participants were enrolled in the study. Participants were defined as those who were on usual weight loss diet for general health or medical reasons during the last 1 year, lost 4.6–9.1 kg of their body weight and in addition, they did not want to lose more weight. Hence, they were voluntarily going to maintain their weight following the previous weight loss period. Nonpregnant, nonlactative, and nonsmokers aged 40–70 years included in the present study. We followed up the participant for 7 months. Self-report of any ongoing condition that may contribute to significant weight gain or weight loss (e.g., pregnancy, cancer) was the only exclusion criterion.
The nutritionist enrolled seventy-six patients who were voluntarily agreed to participate in the present study, but six of them did not meet the inclusion criteria. Therefore, just 70 patients participated in the current study (male =35 and female =35). The protocol of the study was explained clearly for all the participants of the present study, and their written informed consent was obtained. The study was approved by the Research Council and Ethical Committee of Food Security Research Centre, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran, and has been registered at randomized clinical trial website (http://www.register.clinicaltrials.gov) with ID number NCT01659450. All subjects were assured about the medical confidentiality by informing that the data will be reported just as a result of research. The study was funded by Isfahan University of Medical Sciences; the funder had no involvement in the design, analysis, and interpretation of the data.
Study design
The subjects were divided randomly by a nutritionist into two groups based on random sequencing generated in SPSS. The first group received a diet appropriate with their weight and the second group also received a diet with the same amount of the calorie in the form of LED diet. The LED diet was mostly contained watery foods such as soup, whole grain, fruits, and vegetables. During the 7 months follow-up, all participants met individually the dietitian each month and were given the new 1-day menu and encouraged to adhere the dietary program. We followed up the participants for 7 months and during all visits, a trained dietician provided dietary advice to the subjects for 15–20 min. Participants in both groups were encouraged to control their energy intake, but in LED group, more attention and emphasizes was done regarding the consumption of low-energy dense foods, such as vegetables, fruits, and soup. All subjects were educated regarding the exchange list during their weight loss period, and they were allowed to change their menu based on exchange list. Two groups were matched one-by-one for confounding variables such as age (age ±2 years), body mass index ([BMI] ±0.5 kg/m2), sex, and chronic diseases. Three days dietary and physical activity records were completed by each participant every month during the study and reviewed by dietitian in each visit. We requested all patients to do a physical activity program for 30 min each day. This physical activity was the same for all participants all over the study period. Blood pressure measurements were performed each month, and biochemical indices were assessed at baseline and end of the study after an overnight fasting (12 h). We had a dietary intervention; so, participants were not blinded.
Diets
In the group with a usual diet, 35% of the energy was provided by fat, 15% by protein and 50% by carbohydrate. While diet of the LED group contained, 30% fat, 15% protein, and 55% carbohydrate. Most of the consumed carbohydrates in the LED diet group were fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. In addition, the group with a LED diet received more servings of vegetable groups daily in the form of liquid diets such as soup and stew or some menus contain more vegetables. Calorie requirements of each subject were estimated based on resting energy expenditure by the use of Harris–Benedict equation[22] and physical activity levels. The amount of energy requirement was calculated based on the current weight of subjects without any more restriction. An exchange list of food groups was given to each person.[23]
Assessment of dietary intake
Dietary intake was estimated from 3-day food records that included 2 week day and 1 weekend day. The participants completed the food records in each month for their follow-up visit. Food records were analyzed using the NUTRITIONIST IV. We used the method of Ledikwe et al.[24] to determine the ED of the diets. This method calculates ED from food only as energy (kcal)/weight of food (g) excluding nonenergetic beverages.
Assessment of anthropometric measures
Anthropometric measurements including weight, height, and waist circumferences (WCs) were carried out on subjects. Calibrated digital scales were used for measuring the weight in minimally clothed of subjects. Height was measured by using an unstretched tape measure while the shoulders were in a normal position. We calculated BMI as weight (kg) divided by height (m2). WC was measured at the lowest rib margin and the iliac crest at the mid-axillary line, using an unscratched tape to the nearest 0.1 cm, respectively.[25]
Assessment of other variables
A questionnaire was used for sociodemographic status. Physical activity level was evaluated using a 3-day physical activity record and expressed as the metabolic equivalent (MET) hour/week. To calculate the MET, the compendium list of physical activity was used[26] as follows: MET × duration of physical activity (minute). At last, the average of 3 days MET was reported for each subject as the total MET.
Assessment of blood pressure
Blood pressure of subjects was measured and recorded monthly by professional staffs that were blinded to the intervention. Participant's blood pressure was measured 3 times with at least 30 s interval in each follow-up session. Finally, the average amount of three measurements was considered as blood pressure.
Assessment of biochemical markers
Blood samples of all the subjects were checked at baseline and end of the study to evaluate changes of the biochemical markers including, FBS, TG, LDL-C, HDL-C, total cholesterol during this 7 months period. Laboratory staffs were blinded.
Statistical analysis
First, normal distribution of variables was tested by using Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, histogram, and p-p plots. All analyses were performed according to the intention-to-treat by using the last-observation-carried-forward method.[27] Participant's data in their groups were analyzed based on random allocation, which was generated by a nurse, regardless of whether or not they actually adhered the dietary intervention. Descriptive statistics were calculated for all study participants using the SPSS statistical program (Version 16.0, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Dietary intake patterns of the participants and percentage of calories from fat, carbohydrate, and protein between two groups were compared using t-tests. To compare the differential changes of cardiovascular risk factors between two intervention groups repeated measures ANOVA was done. The analysis was carried on with and without adjustment for weight loss. The P < 0.05 considered as significant. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
RESULTS
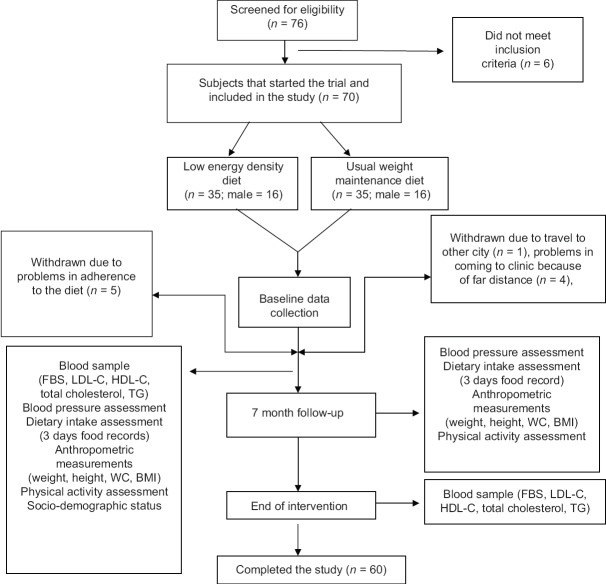
From 70 patients who participated in the present study, sixty patients completed this study. The attrition rate in both groups was 14%. Ten patients did not continue all the follow-up visits due to far distances between their home and clinic (n = 4), travel to another city (n = 1) and did not act according to their diets all over the study (five in low energy dense diet group). Patient's flow diagram is presented in Figure 1. The baseline characteristics of patients are summarized in Table 1. The mean age of participants was 55.0 ± 6.9 years mean ± SEM of BMI in LED and control groups were 24.0 ± 0.40 and 24.4 ± 0.46 kg/m2, respectively.
Figure 1.
Patients flow diagram in the present study
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of participants
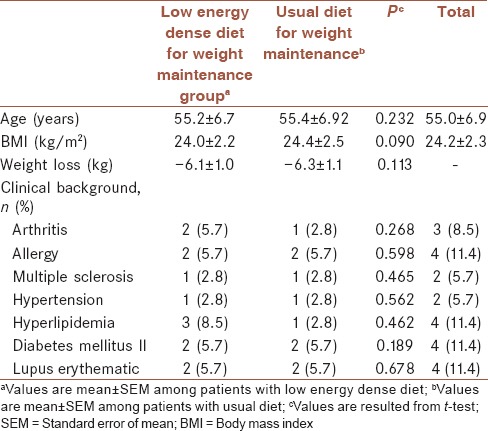
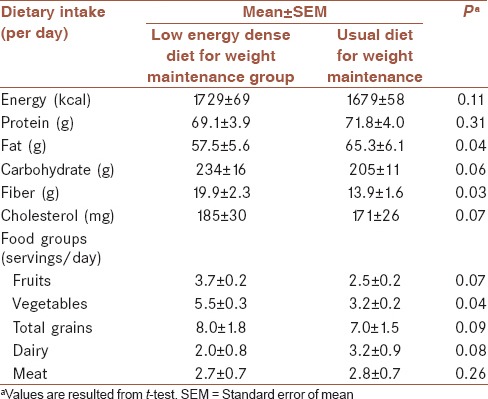
Table 2 shows dietary intakes of patients in LED diet group and usual weight maintenance diet group. According to this table, the LED diet group consumed higher amount of vegetables (5.5 ± 0.3 vs. 3.2 ± 0.2 servings/day, P = 0.04), fiber (19.9 ± 2.3 vs. 13.9 ± 1.6 g/day, P = 0.03), and lower amount of fat (57.5 ± 5.6 vs. 65.3 ± 6.1 g/day, P = 0.04). Amount of energy intake between these two groups was not statistically significant. Physical activity level was not significantly different between two groups (19.7 ± 3.3 MET h/w in usual diet vs. 17.3 ± 3.1 MET h/w in LED diet, P = 0.19).
Table 2.
Dietary intakes of patients in low energy dense diet group for weight maintenance and usual weight maintenance diet group
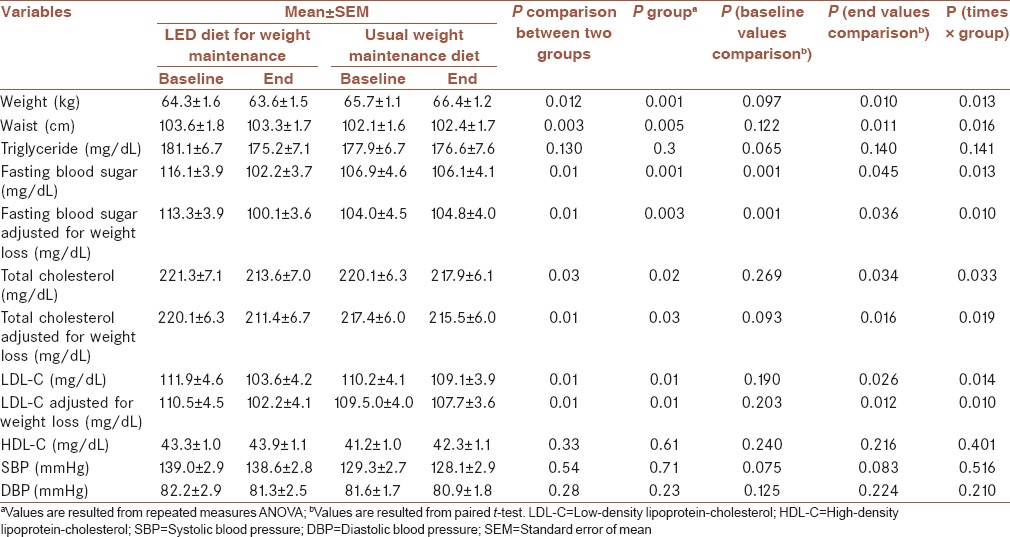
Baseline and end values as well as differences in changes of baseline and end values of cardiovascular risk factors in subjects with a usual weight maintenance diet and a LED diet for weight maintenance are summarized in Table 3. Based on this table, the percentage of weight loss was −1% in low energy dense diet and 1% in usual weight maintenance diet. Besides, there was a significant difference in the changes of FBS (P = 0.001), total cholesterol (0.02), and LDL-C values (P = 0.01) of control group as compared with LED diet group. These differences were still observed after adjusting for weight loss.
Table 3.
Baseline and final values of cardiovascular risk factors among patients with the history of weight reduction in weight maintenance period following a usual weight maintenance diet and a low energy dense diet for weight maintenancea
DISCUSSION
Results of the present study showed −1% weight loss in patients with LED diet while the usual diet consumers had 1% weight gain. Furthermore, LED diet showed more favorable effects on FBS, total cholesterol, and LDL-C. Nowadays, the way of maintaining lost weight is more important than losing weight. Accumulative evidence indicates that different behaviors such as eating breakfast every day, consuming a low-fat diet, and high levels of physical activity can be effective in controlling the weight maintenance.[28,29] However, little is known about the efficacy of different diets on weigh maintenance and cardiovascular risk factors. Present study is the first study which determined the effects of LED diet on both weight maintenance and cardiovascular risk factors among Asian people.
In the present study, a significant difference was observed in fat and fiber intake between two groups. The amount of fat and fiber intake, affect the ED, which consequently might lead to weight management. Previous studies reported that lower carbohydrate intake resulted in a greater weight loss than a low-fat, high carbohydrate diet.[30,31] However, it is not shown that low-carbohydrate intake facilitates weight maintenance after 1 year of follow-up.[31] No significant association between total carbohydrate intake and BMI was reported in earlier studies.[32,33] Accordingly, our findings suggest that the type of carbohydrate might be more effective on body weight and weight maintenance than its amount. We found that higher amount of carbohydrate intake, especially in the form of fiber and complex carbohydrate had more beneficial effects on weight maintenance. The possible underlying mechanism of these effects might be due to the higher contents of fiber and water in complex carbohydrate which increase the food volume without any significant increase in calorie content.[34,35]
Results of the present study showed a significant reduction in weight and WC of subjects in LED diet group, which is in agreement with earlier study.[36] The effects of dietary fiber on reducing the body fat stores might be due to reducing the energy intake and chylomicron concentrations and increasing the fat excretion.[37] Moreover, high fiber intake will increase the blunted postprandial, which consequently improves the insulin sensitivity.[38]
Furthermore, changes of FBS in LED diet group decreased after 7 months follow–up while did not markedly change in the control group. One of the markers which can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) is elevated FBS. McKeown et al.[39] reported an inverse association between complex carbohydrate and FBS concentration. In addition, more consumption of fruits and vegetables lead to better control of glycemia level, which is due to higher amount of fiber, isoflavon, and phytoestrogen.[40] Previous epidemiologic[38] and clinical trial studies[40] indicated the associations between high fiber intake and improved cardiovascular risk factors. Weight loss was not the only beneficial health effects of LED diet. A significant reduction was also observed in the changes of total cholesterol and LDL-C in LED diet group compared with usual diet weight maintenance group after 7 months of follow-up. LED diet in the form of fiber and complex carbohydrate like Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension diet can play an important role in reducing cardiovascular risk factors.[41] Improvement of cardiovascular risk factors might be due to the viscose fiber of fruits and vegetables (such as pectin) in the LED diet.[42,43,44] The possible mechanism of reduced LDL-C by fiber consumption is via the absorption of bile acids and cholesterol. Fiber will decrease the reabsorption of bile. Therefore, liver will convert more cholesterol into bile acids and uptake more LDL-C.[45] Although the control group had a usual weight maintenance diet, the CVD risks between them were much higher than the LED diet group.
Weight and WC significantly reduced in LED diet group while these measurements increased in the group with usual diet. Although there were significant differences in the amount of FBS, total cholesterol, and LDL-C, the extent to which the benefits of LED diet on the mentioned cardiovascular risks were mediated by weight loss was not clear. However, as the significant difference between two groups after adjustment for weight reduction was still observed, it appeared that LED diet exerted beneficial effects independently.
There are some strengths in the present study that should be taken into account. This is the first study which assessed the long-term effects of LED diet on cardiovascular risk factors and weight maintenance at the same time among Asian people. Until recently, all of the studies were limited to the ED effects on weight management. Besides, foods were not prepared for the participants in the present study, and dietary intake was self-reported. By the way, the significant effects of LED diet showed the possible adherence of the patients. One of the limitations of the present research was the duration of the study. The aim of the study was assessing the weight maintenance in LED and usual diet consumers. Therefore, the researchers included all the possible numbers of the subjects and did not focus on the healthy people. Besides, in the present study, we could not measure the psychological factors related to CVD. However, some recent studies showed that psychological factors play an important role in the etiology, progression, and consequences of this disease.[46] Indeed, we need more long-term studies to determine the effects of LED diets on weight maintenance and cardiovascular risk factors among healthy individuals.
CONCLUSION
The present study suggests that individuals with LED diet can maintain their weight loss longer and they are less dispose to the risk of CVD. Generally, reductions in dietary ED are a healthy weight management strategy.
Financial support and sponsorship
The study was funded by Isfahan University of Medical Sciences.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
AUTHOR’S CONTRIBUTION
GK contributed in the conception of the work, literature, writing the manuscript, revising the draft, approval the final version of the manuscript, and agreed for all aspects of the work.
LA contributed in the conception of the work, conducting the study, contributed in revising the draft, approval the final version of the manuscript, and agreed for all aspects of the work.
FH contributed in the revising the draft, approval of the final version of the manuscript, and agreed for all aspects of the work.
AE contributed in conducting study, data and statistical analysis, approval of the final version of the manuscript, and agreed for all aspects of the work.
REFERENCES
- 1.Wulaningsih W, Holmberg L, Ng T, Rohrmann S, Van Hemelrijck M. Serum leptin, C-reactive protein, and cancer mortality in the NHANES III. Cancer Med. 2016;5:120–8. doi: 10.1002/cam4.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Karimi G, Sabran MR, Jamaluddin R, Parvaneh K, Mohtarrudin N, Ahmad Z, et al. The anti-obesity effects of Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota versus orlistat on high fat diet-induced obese rats. Food Nutr Res. 2015;59:29273. doi: 10.3402/fnr.v59.29273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.World Health Organization (2015). Obesity and overweight. Fact sheet N8. 311, Media Centre. [Updated January 2015] [Last cited on 2015 Feb 12]. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/
- 4.Bibbins-Domingo K, Chertow GM, Coxson PG, Moran A, Lightwood JM, Pletcher MJ, et al. Projected effect of dietary salt reductions on future cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:590–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0907355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lowe MR, Butryn ML, Thomas JG, Coletta M. Meal replacements, reduced energy density eating, and weight loss maintenance in primary care patients: A randomized controlled trial. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2014;22:94–100. doi: 10.1002/oby.20582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Golubnitschaja O, Costigliola V. EPMA. General report & recommendations in predictive, preventive and personalised medicine 2012: White paper of the European Association for Predictive, Preventive and Personalised Medicine. EPMA J. 2012;3:14. doi: 10.1186/1878-5085-3-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pem D, Jeewon R. Fruit and vegetable intake: Benefits and progress of nutrition education interventions- narrative review article. Iran J Public Health. 2015;44:1309–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gilbert CA, Slingerland JM. Cytokines, obesity, and cancer: New insights on mechanisms linking obesity to cancer risk and progression. Annu Rev Med. 2013;64:45–57. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-121211-091527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Masheb RM, Grilo CM, Rolls BJ. A randomized controlled trial for obesity and binge eating disorder: Low-energy-density dietary counseling and cognitive-behavioral therapy. Behav Res Ther. 2011;49:821–9. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2011.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Birketvedt GS, Shimshi M, Erling T, Florholmen J. Experiences with three different fiber supplements in weight reduction. Med Sci Monit. 2005;11:PI5–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Maki KC, Beiseigel JM, Jonnalagadda SS, Gugger CK, Reeves MS, Farmer MV, et al. Whole-grain ready-to-eat oat cereal, as part of a dietary program for weight loss, reduces low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in adults with overweight and obesity more than a dietary program including low-fiber control foods. J Am Diet Assoc. 2010;110:205–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2009.10.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Flood A, Mitchell N, Jaeb M, Finch EA, Laqua PS, Welsh EM, et al. Energy density and weight change in a long-term weight-loss trial. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2009;6:57. doi: 10.1186/1479-5868-6-57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lowe M, Annunziato R, Riddell L. Controlled trial of a nutrition-focused treatment for weight loss maintenance. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2002;11:S10. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Raben A, Vasilaras TH, Møller AC, Astrup A. Sucrose compared with artificial sweeteners: Different effects on ad libitum food intake and body weight after 10 wk of supplementation in overweight subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;76:721–9. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/76.4.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Blackburn GL, Kanders BS, Lavin PT, Keller SD, Whatley J. The effect of aspartame as part of a multidisciplinary weight-control program on short- and long-term control of body weight. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997;65:409–18. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/65.2.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Eldridge AL, Cooper DA, Peters JC. A role for olestra in body weight management. Obes Rev. 2002;3:17–25. doi: 10.1046/j.1467-789x.2002.00050.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lowe MR, Tappe KA, Annunziato RA, Riddell LJ, Coletta MC, Crerand CE, et al. The effect of training in reduced energy density eating and food self-monitoring accuracy on weight loss maintenance. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008;16:2016–23. doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wing RR, Lang W, Wadden TA, Safford M, Knowler WC, Bertoni AG, et al. Benefits of modest weight loss in improving cardiovascular risk factors in overweight and obese individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:1481–6. doi: 10.2337/dc10-2415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Manson JE, Ridker PM, Gaziano JM, Hennekens CH. Prevention of myocardial infarction. New York: Oxford University Press; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Azadbakht L, Shakerhosseini R, Atabak S, Jamshidian M, Mehrabi Y, Esmaill-Zadeh A. Beneficiary effect of dietary soy protein on lowering plasma levels of lipid and improving kidney function in type II diabetes with nephropathy. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2003;57:1292–4. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fleiss JL. Design and analysis of clinical experiments. John Wiley & Sons; 2011. doi: 10.1002/9781118032923.fmatter. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Carol S, Ireton-Jones . Kraus's food. In: Mahan LK, Escott Stump S, editors. Nutrition & Diet Therapy. 13th ed. Washington University, USA: WB saunders; 2012. pp. 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mahan LK, Raymond JL, Escott-Stump S. Kraus's Food, Nutrition & Diet Therapy. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2008. Exchange lists for meal planning. Appendix 34; pp. 1251–60. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ledikwe JH, Blanck HM, Khan LK, Serdula MK, Seymour JD, Tohill BC, et al. Dietary energy density determined by eight calculation methods in a nationally representative United States population. J Nutr. 2005;135:273–8. doi: 10.1093/jn/135.2.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Copenhagen: World Health Organization, 1989, Nutrition Unit Document, Eur Icp Nut; 1987. World Health Organization. Measuring Obesity-Classification and Description of Anthropometric Data. Report on a WHO Consultation of the Epidemiology of Obesity. Warsaw 21-23 October, 1987; p. 123. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Whitt MC, Irwin ML, Swartz AM, Strath SJ, et al. Compendium of physical activities: An update of activity codes and MET intensities. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000;32(9 Suppl):S498–504. doi: 10.1097/00005768-200009001-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Streiner D, Geddes J. Intention to treat analysis in clinical trials when there are missing data. Evid Based Ment Health. 2001;4:70–1. doi: 10.1136/ebmh.4.3.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Stunkard AJ, Wadden TA. Obesity: Theory and therapy. New York: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Raven press Ltd; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hill JO, Thompson H, Wyatt H. Weight maintenance: What's missing? J Am Diet Assoc. 2005;105(5 Suppl 1):S63–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2005.02.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tobias DK, Chen M, Manson JE, Ludwig DS, Willett W, Hu FB. Effect of low-fat diet interventions versus other diet interventions on long-term weight change in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3:968–79. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00367-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Stern L, Iqbal N, Seshadri P, Chicano KL, Daily DA, McGrory J, et al. The effects of low-carbohydrate versus conventional weight loss diets in severely obese adults: One-year follow-up of a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:778–85. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-140-10-200405180-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ma Y, Olendzki B, Chiriboga D, Hebert JR, Li Y, Li W, et al. Association between dietary carbohydrates and body weight. Am J Epidemiol. 2005;161:359–67. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwi051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Karl JP, Roberts SB, Schaefer EJ, Gleason JA, Fuss P, Rasmussen H, et al. Effects of carbohydrate quantity and glycemic index on resting metabolic rate and body composition during weight loss. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2015;23:2190–8. doi: 10.1002/oby.21268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Shafaeizadeh S, Jamalian J, Owji AA, Azadbakht L, Ramezani R, Karbalaei N, et al. The effect of consuming oxidized oil supplemented with fiber on lipid profiles in rat model. J Res Med Sci. 2011;16:1541–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Adam CL, Thomson LM, Williams PA, Ross AW. Soluble fermentable dietary fibre (Pectin) decreases caloric intake, adiposity and lipidaemia in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0140392. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Briganti S, Ermetici F, Malavazos AE, Dozio E, Giubbilini P, Rigolini R, et al. Effect of an isocaloric diet containing fiber-enriched flour on anthropometric and biochemical parameters in healthy non-obese non-diabetic subjects. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2015;57:217–22. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.14-133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Bozzetto L, Annuzzi G, Costabile G, Costagliola L, Giorgini M, Alderisio A, et al. A CHO/fibre diet reduces and a MUFA diet increases postprandial lipaemia in type 2 diabetes: No supplementary effects of low-volume physical training. Acta Diabetol. 2014;51:385–93. doi: 10.1007/s00592-013-0522-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ludwig DS, Pereira MA, Kroenke CH, Hilner JE, Van Horn L, Slattery ML, et al. Dietary fiber, weight gain, and cardiovascular disease risk factors in young adults. JAMA. 1999;282:1539–46. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.16.1539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.McKeown NM, Meigs JB, Liu S, Wilson PW, Jacques PF. Whole-grain intake is favorably associated with metabolic risk factors for type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease in the Framingham Offspring Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;76:390–8. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/76.2.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Pereira MA, Jacobs DR, Jr, Pins JJ, Raatz SK, Gross MD, Slavin JL, et al. Effect of whole grains on insulin sensitivity in overweight hyperinsulinemic adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;75:848–55. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/75.5.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Azadbakht L, Fard NR, Karimi M, Baghaei MH, Surkan PJ, Rahimi M, et al. Effects of the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) eating plan on cardiovascular risks among type 2 diabetic patients: A randomized crossover clinical trial. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:55–7. doi: 10.2337/dc10-0676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Babio N, Balanza R, Basulto J, Bulló M, Salas-Salvadó J. Dietary fibre: Influence on body weight, glycemic control and plasma cholesterol profile. Nutr Hosp. 2010;25:327–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sánchez D, Muguerza B, Moulay L, Hernández R, Miguel M, Aleixandre A. Highly methoxylated pectin improves insulin resistance and other cardiometabolic risk factors in Zucker fatty rats. J Agric Food Chem. 2008;56:3574–81. doi: 10.1021/jf703598j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Brufau G, Canela MA, Rafecas M. A high-saturated fat diet enriched with phytosterol and pectin affects the fatty acid profile in guinea pigs. Lipids. 2006;41:159–68. doi: 10.1007/s11745-006-5084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Theuwissen E, Mensink RP. Water-soluble dietary fibers and cardiovascular disease. Physiol Behav. 2008;94:285–92. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2008.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Nekouei ZK, Yousefy A, Doost HT, Manshaee G, Sadeghei M. Structural model of psychological risk and protective factors affecting on quality of life in patients with coronary heart disease: A psychocardiology model. J Res Med Sci. 2014;19:90–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]