Abstract
The genus Marinomonas comprises Gram negative bacteria which are widespread in the marine environment and there is no report on the genomic analysis of SXT/R391 ICEs derived from this group of bacteria. This study describes the genomic features of three new SXT/R391 integrating conjugating elements (ICEs) identified in the genome of Marinomonas fungiae JCM 18476T (ICEMfuInd1a and ICEMfuInd1b) and in Marinomonas profundimaris strain D104 (ICEMprChn1). Structural organizations of the three ICEs were similar to the typical SXT/R391 family of ICEs and showed high degree of conservation in the core genes. Sequence analysis revealed ICEMfuInd1b and ICEMprChn1 were inserted into the genome at 5′-end of an typical host prfC gene, while ICEMfuInd1a was inserted at 5′-end of an atypical hipA-like gene. Despite their coexistence, the ICEMfuInd1a and ICEMfuInd1b were not present in a tandem fashion in the genome of M. fungiae. Phylogenetic analyses revealed the three ICEs either evolved independently or high degrees of recombination events had masked their evolution from a common SXT ancestor. Further, we found that the typical entry exclusion mechanism mediated by the TraG/EeX protein pair was likely defective in preventing the conjugative transfer of a second copy of the same S (SXT) group ICE into the M. fungiae genome due to mutations. Our analysis showed the presence of 16, 25, and 27 variable genes in the hotspots of ICEMfuInd1a, ICEMfuInd1b, and ICEMprChn1, respectively, many of which were not reported earlier for SXT/R391 ICEs. Sequence analysis predicted these hotspot regions were shaped by acquisition of genes through homologous recombination between the SXT and R391 related ICEs or mobile genetic elements present in disparate marine bacteria. Multidrug resistance genes which are hallmark feature of SXT/R391 ICEs were not present in either of the two ICEs from M. fungiae but were present within a transposon cassette in the HS-1 of the ICEMprChn1 from M. profundimaris. Finally, our data provided information on the genetic diversity and predicted functions encoded by variable genes present in the hotspot regions of these new ICEs.
Keywords: SXT/R391 ICEs, mobile genetic elements, Marinomonas, genomic analysis, hotspots
Introduction
Integrating conjugative elements (ICEs) are self-transmissible mobile genetic elements (MGEs) that are widely distributed in bacterial genomes and play a major role in bacterial adaptation, genome dynamics, and evolution (Beaber et al., 2004; Burrus and Waldor, 2004a; Bi et al., 2012; Carraro and Burrus, 2014; Johnson and Grossman, 2015). The ICEs of the SXT/R391 family are major drivers in the dissemination of heavy metals and multidrug resistance among environmental and pathogenic clinical strains of diverse bacterial groups within the Gammaproteobacteria (Burrus et al., 2006; Wozniak et al., 2009; Bi et al., 2012; Johnson and Grossman, 2015). To date, SXT/R391 ICEs have been found in several species of Vibrio, Shewanella, Photobacterium, Providencia, and Proteus (Hochhut et al., 2001; Ahmed et al., 2005; Pembroke and Piterina, 2006; Osorio et al., 2008; Wozniak et al., 2009; Harada et al., 2010; Rodríguez-Blanco et al., 2012; Spagnoletti et al., 2014). The prototypical elements of this family of ICEs i.e., SXT and R391 were derived from Vibrio cholerae O139 in India and Providencia rettgeri in South Africa, respectively (Coetzee et al., 1972; Waldor et al., 1996). All the SXT/R391 ICEs are chromosomal MGEs sharing a conserved integrase that mediates site-specific integration into the 5′ end of prfC or t-RNA-ser in the absence of a prfC site (Hochhut and Waldor, 1999; Hochhut et al., 2001; Burrus and Waldor, 2003; Burrus et al., 2006; Taviani et al., 2012; Carraro and Burrus, 2014; Luo et al., 2016). Members of this ICE family contain 52 conserved core genes, many of which are involved in integration/excision, conjugative transfer and regulation of the ICEs (Beaber et al., 2002; Burrus et al., 2006; Wozniak et al., 2009; Bi et al., 2012; Spagnoletti et al., 2014; Carraro et al., 2015; Poulin-Laprade and Burrus, 2015; Poulin-Laprade et al., 2015). In addition, five hotspots (HS1—5) and five variable (VRI—V) regions have also been identified (Lei et al., 2016), which contain variable genes conferring element-specific properties and providing beneficial phenotypes to their hosts (Osorio et al., 2008; Wozniak et al., 2009; Rodríguez-Blanco et al., 2012; Balado et al., 2013; Poulin-Laprade et al., 2015). It has been demonstrated that genes encoding for resistance to multiple antibiotics and heavy metals, aromatic compound degradation pathways, DNA repair and recombination systems, virulence factors, toxin-antitoxin system, regulation of motility, and biofilm formation are found to be present within the hotspots and variable regions in the ICEs of many bacteria (Boltner et al., 2002; Wozniak et al., 2009; Rodríguez-Blanco et al., 2012; Balado et al., 2013). However, information on the dissemination and ecology of ICEs in marine environment is limited. Apart from SXT/R391, the other families of ICEs that are present widespread in Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria and studied extensively to understand their biology and evolution are ICEBs1 from Bacillus subtilis, ICESt1/ICESt3 from Streptococcus thermophilus, ICEclc from Pseudomonas putida, ICEHin1056 from Haemophilus influenza, ICELm1 from Listeria monocytogenes, etc. (Carraro and Burrus, 2014; Johnson and Grossman, 2015).
Previously, laboratory experiments with E. coli and V. cholerae have demonstrated the transfer of SXT and R391 ICEs often results in the formation of exconjugants harboring multiple copies of SXT integrated within the 5′ end of prfC gene in tandem arrays (Hochhut et al., 2001; Burrus and Waldor, 2004b). Further, Marrero and Waldor (2005, 2007) in their studies have shown that the SXT/R391 family of ICEs is divided into two exclusion groups: the S (SXT) and R (R391). It has been demonstrated that cells containing SXT, exclude transfer of a second copy of SXT but not R391 and vice versa which is mediated by variants of the two cognate inner membrane proteins, TraG and Eex, in donor and recipient cells, respectively. Moreover, these ICE tandem arrays do not persist in the recA+ strains and are quickly brought down to a singleton state after a few generations by homologous recombination mediated by host RecA and ICE Bet/Exo (Garriss et al., 2009, 2013).
The coexistence of two ICEs of the same exclusion group either S (SXT) or R (R391) in a genome is very rare (Marrero and Waldor, 2007) and limited information is available on natural isolates harboring such SXT/R391 ICEs arrays (Luo et al., 2016). Moreover, there is no report on the genomic analysis of SXT/R391 ICEs derived from the members of the genus Marinomonas. Thus, in the present study we described and compared the genetic features of three new SXT ICEs. Among them two were identified in the genome of M. fungiae JCM 18476T and one in the previously sequenced genome of M. profundimaris strain D104 (Dong et al., 2014).
Materials and methods
Bacterial strain and media
Marinomonas fungiae JCM 18476T positive for SXT/R391 family related ICEs was used for genomic analysis (Badhai et al., 2013). The bacterium was routinely grown in marine agar 2216 (MA; Difco) at 28°C (Kumari et al., 2014).
Genomic DNA preparation, sequencing, and assembly
The genomic DNA of Marinomonas fungiae JCM 18476T was isolated using standard methods (Sambrook et al., 1989). The draft genome of Marinomonas fungiae JCM 18476T was generated at the DOE Joint Genome Institute (JGI, USA) using the Illumina HiSeq 2000 platform (Bennett, 2004). The genome was annotated using the JGI Microbial Genome Annotation Pipeline (Mavromatis et al., 2009). The methods for the genomic DNA preparation, sequencing, assembly and annotation of M. profundimaris strain D104 was described by Dong et al. (2014).
Comparative analysis of ICEs
The genetic organizations of the three ICEs derived from M. fungiae JCM 18476T (ICEMfuInd1a and ICEMfuInd1b) and M. profundimaris strain D104 (ICEMprChn1) were determined by comparison with the core backbone structures of 11 reference SXT/R391 ICEs from Providencia rettgeri, Vibrio cholerae O139 and O1 strains, Shewanella putrefaciens, Vibrio fluvialis, Photobacterium damselae, Providencia alcalifaciens, and Proteus mirabilis (Wozniak et al., 2009; Lei et al., 2016). We considered only 11 reference SXT/R391 ICEs for comparative analysis as their complete genomic information were available and well characterized from the ICEberg database as on 24th August, 2011 and NCBI-RefSeq database as on 29th May, 2016. Sequence conservation at nucleotide and amino acid levels, as well as presence or absence of genes/ORFs with respect to reference SXT/R391 ICEs was determined using BLAST (Altschul et al., 1997) locally (standalone BLAST−2.2.29+ package; Camacho et al., 2009). In addition, identification of the genes/ORFs present in the hotspot regions was carried out using BLASTX against the NCBI-RefSeq and ICEberg (http://db-mml.sjtu.edu.cn/ICEberg/; Bi et al., 2012) databases. Clustal omega was used for sequence alignments (the program is available at http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/). DNAPlotter was used to generate images of the linear DNA maps (Carver et al., 2009).
Analysis of the excision abilities of the ICEs
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed targeting the reconstituted attP sites of the circular extra chromosomal form of the ICEs using forward 5′-TGCTGTCATCTGCATTCTCCTG-3′ and reverse 5′-GCCAATTACGATTAACACGACGG-3′ primers (Hochhut and Waldor, 1999) to verify the excision abilities of the two ICEs of M. fungiae JCM 18476T.
Phylogenetic analysis of core ICE genes
Phylogenetic analysis was performed based on the concatenated amino acid sequences of 25 core genes encoded proteins: Int, SrpR, SrpM, RumA, S024, TraE, TraK, TraV, TraA, S054, TraC, TrhF, TraU, TraN, S063, Ssb, Bet, Exo, TraF, TraH, TraG, EeX, SetC, SetD, and SetR. In addition, individual phylogenetic analysis was performed for the proteins: Int, TraI, TraG, Eex, Bet, and Exo. Phylogenetic trees were constructed by maximum-likelihood method based on the Poisson correction model (Zuckerkandl and Pauling, 1965) using the MEGA6 (Tamura et al., 2013). Bootstrap analysis with 1000 replications was performed to test the reliability of the tree. Reference ICEs sequences were retrieved from GenBank: SXTMO10 (V. cholerae O139; accession: AY055428), ICEVchInd4 (V. cholera O139; accession: GQ463141), ICEVchInd5 (V. cholera O1; accession: GQ463142), ICEVchBan5 (V. cholera O1; accession: GQ463140), ICEVchMex1 (V. cholerae non O139; accession: GQ463143), R391 (Providencia rettgeri; accession: AY090559), ICEPalBan1 (Providencia alcalifaciens; accession: GQ463139), ICEVflInd1 (V. fluvialis; accession: GQ463144), ICEPdaSpa1 (Photobacterium damselae; accession: AJ870986), ICESpuPO1 (Shewanella putrefaciens; accession: CP000503), and ICEPmiChn1 (Proteus mirabilis; accession: KT962845).
Nucleotide sequence accession number
The draft genome sequence of M. fungiae JCM 18476T and M. profundimaris strain D104 (Dong et al., 2014) are available at NCBI GenBank under the accession no.'s: LIQF00000000 and AYOZ00000000, respectively. The versions described in this paper are version LIQF01000000 and AYOZ01000000, respectively.
Results and discussion
Assembly of the ICEs
Genomic analysis revealed co-existence of two ICEs in the genome of M. fungiae and one ICE in the genome of M. profundimaris. The three ICEs were assembled based on sequence similarity and structural comparison with the backbone of core genes in SXT/R391 ICEs. The two ICEs of M. fungiae were designated as ICEMfuInd1a and ICEMfuInd1b, and the M. profundimaris was designated as ICEMprChn1. The ICEMfuInd1a and ICEMfuInd1b were encoded by three (GenBank accession: LIQF01000019.1, LIQF01000033.1, and LIQF01000014.1) and four (GenBank accession: LIQF01000022.1, LIQF01000023.1, LIQF01000030.1, and LIQF01000009.1) DNA scaffolds of total length 65.5 and 74.7 kb, respectively, whereas the ICEMprChn1 was encoded by four (GenBank accession: AYOZ01000034.1, AYOZ01000017.1, AYOZ01000022.1, and AYOZ01000004.1) DNA scaffolds of total length 86.4 kb. BLAST search showed a homolog of the chromosomal prfC gene was present adjacent to the attR sequence, consistent with the SXT/R391 ICE insertion site (Hochhut and Waldor, 1999; Hochhut et al., 2001; Burrus and Waldor, 2003) at the extreme 3′-end of the ICEMfuInd1b and ICEMprChn1, but it was absent in ICEMfuInd1a. Instead, the ICEMfuInd1a was inserted at the 5′-end of a putative hipA-like toxin gene. Further, the two ICEs of M. fungiae were not arranged in a tandem fashion in the genome, there were several non-ICE genes that immediately followed the predicted setR and the setR-prfC locus at the extreme 3′-end of ICEMfuInd1a and ICEMfuInd1b, respectively.
Structural organization and general features of the core ICE backbones
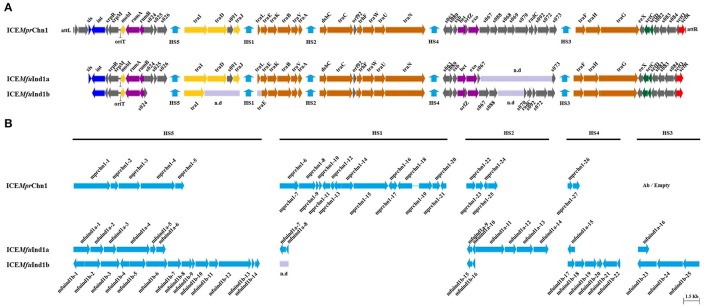
The three elements were not identical; they exhibited variability in the degree of sequence conservation when compared with other SXT/R391 ICEs. Moreover, G+C content was 44.8, 47.2, and 46.9% for ICEMfuInd1a, ICEMfuInd1b, and ICEMprChn1, respectively. Most of the core genes of SXT/R391 ICEs (Beaber et al., 2002; Wozniak et al., 2009; Spagnoletti et al., 2014; Carraro et al., 2015; Poulin-Laprade and Burrus, 2015; Poulin-Laprade et al., 2015) were found to be preserved and were arranged in the same syntenic order in the three elements (Figure 1A, Supplementary Table 1) and showed 60–99% sequence identity at the level of amino acid to the corresponding proteins encoded by SXT/R391 ICEs (Supplementary Table 2).
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the (A), core SXT-like ICE backbones and (B), the five hotspot regions of the three ICEs: ICEMfuInd1a, ICEMfuInd1b, and ICEMprChn1. Genes/ORFs in the five hotspots are designated as a1–a16 and b1–b25 in ICEMfuInd1a and ICEMfuInd1b, respectively (see Table 2). ICEMfuInd1a was encoded by the scaffolds: LIQF01000019.1, LIQF01000033.1, and LIQF01000014.1; ICEMfuInd1b by LIQF01000022.1, LIQF01000023.1, LIQF01000030.1, and LIQF01000009.1; and ICEMprChn1 by: AYOZ01000034.1, AYOZ01000017.1, AYOZ01000022.1, and AYOZ01000004.1. Genes/ORFs are color coded: blue, integration, and excision; yellow, DNA processing; orange, conjugative transfer system; purple, RecA-independent homologous recombination, and Umu-like mutagenic repair; green, transcriptional activator; red, transcriptional repressor; gray, other or hypothetical functions; cyan, hotspot genes; violet, gap regions; n.d, sequence not determined.
Among the conserved core genes, the homologs of genes encoding the excision and integration functions (xis and int at the extreme 5′ end), plasmid-like partition system (srpRMC), a Umu-like mutagenic DNA repair system (rumAB), a RecA-independent λ Red-like homologous recombination system (bet/exo), five conjugative DNA processing and transfer clusters (mobI, traIDJ, traLEKBVA, dsbC/traC/trhF/traWUN, and traFHG), regulators of the excision and conjugative transfer (setCD, croS, and setR) were present in all the three ICEs analyzed (Figure 1A, Supplementary Table 1). However, the sequences of the genes xis, traD, s091, traJ, and traL were not determined in the case of ICEMfuInd1b. Further, PCR assay showed the amplification of a 785 bp DNA fragment containing the reconstituted attP sites of the circular extrachromosomal form of the ICE (Hochhut and Waldor, 1999) suggesting the ICEs are excised from the genome of M. fungiae JCM 18476T (data not shown). In addition, sequence analysis showed all the three ICEs carried an intact rumB gene; lacked the antibiotic resistance gene clusters inserted into the rumB gene, a characteristics typical to many ICEs belonging to the SXT/R391 family. Analysis of the intergenic region between srpM and mobI in all the three ICEs showed a high degree of sequence conservation with the other eleven ICEs used for comparison (Supplementary Figure 1). This region presumably encoded the 299 bp long putative origin of transfer (oriT), where the conjugative DNA transfer is typically initiated following the excision of the ICE from the chromosome (Ceccarelli et al., 2008).
We found low identity of the predicted amino acid sequence of the 3′ regulatory module (consisting of the eight genes setCD, s082, s083, s084, croS, and setR) in ICEMfuInd1a in comparison with those encoded by the conserved core genes of other SXT/R391 ICEs. Therefore, it could be predicted that this newly identified ICE was generated as a result of homologous recombination between two different SXT/R391 ICEs as demonstrated by Garriss et al. (2009, 2013).
Structural variations were also observed in the three ICEs, including in the core backbones and in the five variable DNA regions, termed hotspots (Wozniak et al., 2009; Figure 1). The highly conserved orfZ gene found between bet and exo in SXT/R391 ICEs was absent in ICEMfuInd1a, whereas there was disruption in the 3′-end of the gene s024 and deletion of the entire genes s025 and s026 in ICEMfuInd1b. However, functions of these genes in the conjugative ICE transfer are unknown (Beaber et al., 2002; Wozniak et al., 2009). In ICEMprChn1, the typical hotspot-3 was empty/without variable DNA.
Exclusion system
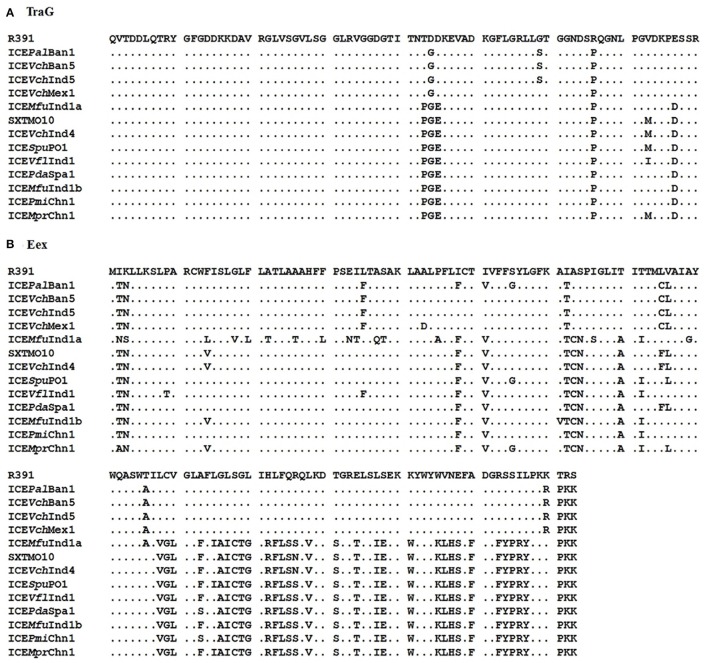
Marrero and Waldor (2005, 2007) have shown that the ICE entry exclusion specificity is determined by the carboxyl terminal residues in the Eex exclusion proteins, but the exclusion potency varied to a large extent on the basis of change in a single amino acid (i.e., 43rd residue) at the amino terminal of this protein. In the present study, all the three ICEs were found to be from the S entry exclusion group. Amino acid sequence alignment of the TraG proteins showed that the predicted S exclusion determinant residues were P-G-E in all the three ICEs (Figure 2A). Similarly, the alignment of Eex exclusion proteins predicted that the three ICEs encoded proteins that belonged to the S exclusion group (Figure 2B). However, we found variations in 16 amino acid residues at the amino terminal region of Eex exclusion protein encoded by ICEMfuInd1a which may have reduced the exclusion potency to a very large extent, thereby allowing the acquisition of a second copy of the SXT-like ICE (ICEMfuInd1b) into the M. fungiae genome.
Figure 2.
Clustal Omega alignment of the (A), TraG and (B), Eex protein sequences obtained from the three ICEs: ICEMfuInd1a, ICEMfuInd1b, and ICEMprChn1, with the corresponding sequences from the 11 reference SXT/R391 ICEs retrieved from the GenBank, showing the predicted SXT-like exclusion amino acids in TraG (P-G-E) and Eex proteins.
Phylogenetic analysis of the core ICE genes
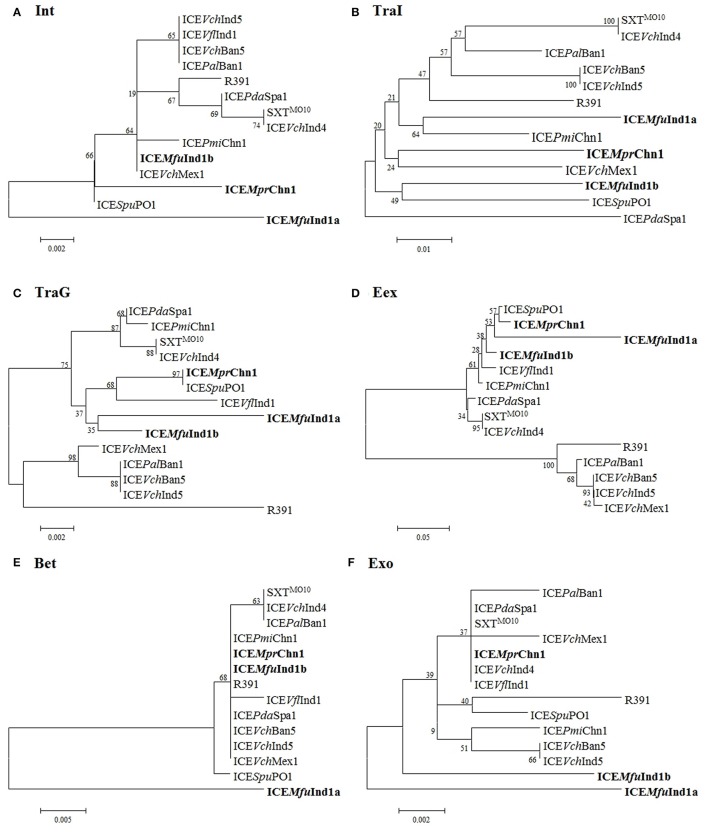
A phylogenetic tree was constructed based on the concatenated amino acid sequences of 25 core proteins: Int, SrpR, SrpM, RumA, S024, TraE, TraK, TraV, TraA, S054, TraC, TrhF, TraU, TraN, S063, Ssb, Bet, Exo, TraF, TraH, TraG, EeX, SetC, SetD, and SetR encoded by ICEMfuInd1a and ICEMfuInd1b derived from M. fungiae JCM 18476T, ICEMprChn1 from M. profundimaris strain D104 and the other 11 reference SXT/R391 ICEs to trace the evolution of these ICEs. Our analysis showed the three ICEs were clustering into two branches; while ICEMfuInd1b and ICEMprChn1 were very closely related and clustered with the SXT ICEs, the ICEMfuInd1a was distantly related to either SXT or R391 ICEs and formed a separate branch (Figure 3, Supplementary Figure 2). To further explore the evolutionary relationship between the ICEs and infer their ancestral root, we created phylogenetic trees for six proteins (Figure 4) involved in most important ICE functions, such as integration (Int), transfer (TraI), exclusion determination (TraG and Eex), and recombination (Bet and Exo). The different clustering of branches in the phylogenetic trees corroborated that most likely these ICEs have evolved independently or high degrees of recombination events have masked their evolution from a common SXT ancestor (Garriss et al., 2009, 2013; Wozniak et al., 2009).
Figure 3.
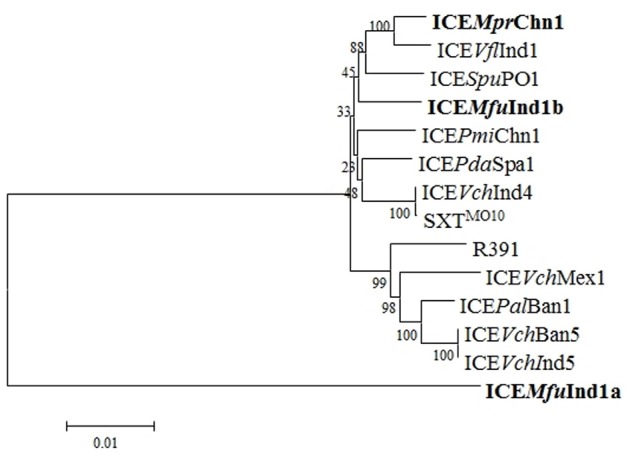
Phylogenetic analysis of core ICE genes encoded proteins. The tree was constructed by applying the Maximum Likelihood method based on the Poisson correction model using the MEGA6. Bootstrap analysis with 1000 replications was performed to test the reliability of the tree.
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic analysis of (A) Int, (B) TraI, (C) TraG, (D) Eex, (E) Bet, and (F) Exo protein. The trees were constructed by applying the Maximum Likelihood method based on the Poisson correction model using MEGA6. Bootstrap analysis with 1000 replications was performed to test the reliability of each tree.
Genetic analysis of the hotspot regions
Despite showing similarity with the conserve core backbones, all the three ICEs derived from the two bacteria of the genus Marinomonas carried variable genes clustered in the five conserved insertion hotspots (Wozniak et al., 2009; Figure 1). The boundaries of the five hotspots were located between s026 and traI (HS-5), traJ, and traL (HS-1, sequence not determined in case of ICEMfuInd1b), traA and s054 (HS-2), s073 and traF (HS-4), and traN and s063 (HS-3) in both the ICEs, except the HS-5 in ICEMfuInd1b (Tables 1–3). The left boundary of the HS-5 of ICEMfuInd1b was within s024 instead of being located downstream to s026 at the 3′ end. These hotspots varied in size from 902 to 9784, 1173 to 19,100, and 1348 to 15,615 bp in ICEMfuInd1a, in ICEMfuInd1a, and ICEMprChn1, respectively.
Table 1.
Descriptions of genes or ORFs present in the hotspot regions of ICEMfuInd1a.
| Hotspot region | ICEMfuInd1a gene/ORF id | Gene name | Length (bp) | Hotspot gene product name | GenBank accession no. of protein homolog | % Similarity with homolog |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HS-5 (s026-traI) | Ga0061065_11938 | mfuind1a-1 | 1560 | Type-I restriction enzyme M subunit | Psychromonas arctica; WP_028870232.1 | 99 |
| Ga0061065_11937 | mfuind1a-2 | 1245 | Type-I restriction enzyme S subunit | Psychromonas arctica; WP_028870233.1 | 70 | |
| Ga0061065_11936 | mfuind1a-3 | 1176 | Hypothetical protein | Photobacterium aquae; WP_047879742.1 | 95 | |
| Ga0061065_11935 | mfuind1a-4 | 3117 | Type-I restriction enzyme R subunit | Psychromonas arctica; WP_028870235.1 | 99 | |
| Ga0061065_11934 | mfuind1a-5 | 564 | Hypothetical protein | Vibrio cholerae; WP_054104207.1 | 99 | |
| Ga0061065_11933 | mfuind1a-6 | 912 | Protein of unknown function | Vibrio cholerae; WP_054104208.1 | 99 | |
| HS-1 (traJ-traL) | Ga0061065_11928 | mfuind1a-7 | 588 | Hypothetical protein | Shewanella decolorationis; WP_023266690.1 | 98 |
| Ga0061065_11927 | mfuind1a-8 | 240 | Hypothetical protein | Vibrio parahaemolyticus; WP_025611035.1 | 96 | |
| HS-2 (traA-s054) | Ga0061065_11920 | mfuind1a-9 | 507 | Acetyltransferase domain containing protein | Vibrio parahaemolyticus; WP_023584043.1 | 95 |
| Ga0061065_11919 | mfuind1a-10 | 267 | Uncharacterized conserved protein, DUF1778 family | Vibrio cholerae; WP_032481064.1 | 95 | |
| Ga0061065_11918 | mfuind1a-11 | 2730 | Heavy metal transporter CzcA | Vibrio cholerae; WP_001901413.1 | 99 | |
| Ga0061065_11917 | mfuind1a-12 | 1110 | Hypothetical protein | Vibrio parahaemolyticus; WP_029855131.1 | 99 | |
| Ga0061065_11916 | mfuind1a-13 | 1533 | Phosphatydylserin/phophatydylglycero-phosphate/cardiolipin synthase | Vibrio cholera; WP_001910860.1 | 99 | |
| Ga0061065_11915 | mfuind1a-14 | 1446 | Transcriptional regulator containing AAA-type ATPase and DNA binding domains | Vibrio cholerae; WP_000369162.1 | 99 | |
| HS-4 (s073-traF) | Ga0061065_1197 | mfuind1a-15 | 693 | Deoxyribonuclease-1 | Vibrio parahaemolyticus; WP_025441436.1 | 83 |
| HS-3 (traN-s063) | Ga0061065_1332 | mfuind1a-16 | 1065 | Hypothetical protein | Shewanella decolorationis; WP_023266664.1 | 99 |
With few exceptions, many of the proteins encoded by the genes in the hotspot regions of the three ICEs did not showed significant sequence identity with the corresponding proteins encoded by genes present in the five hotspots of the 11 reference SXT/R391 ICEs analyzed (Supplementary Table 2). However, a mosAT-like toxin-antitoxin (TA) system was present in the HS-2 of both ICEMfuInd1a and ICEMfuInd1b; but it was absent in ICEMprChn1, instead a hipAB-like TA system was present between the attL and xis, a feature also present in R391 and ICEVchMex1 (Wozniak et al., 2009; Carraro et al., 2015). Additionally, BLASTX search against the NCBI-RefSeq and the ICEberg (Bi et al., 2012) databases showed that most of the genes in these hotspots encoded proteins similar to those found in other marine Gammaproteobacteria (Tables 1–3, Supplementary Tables 3–5). The variable genes present in the hotspots of ICEMfuInd1a and ICEMprChn1 showed high sequence identity with known proteins from marine bacteria, whereas those in ICEMfuInd1b mostly showed relative low sequence identities or were distantly related to known proteins.
Our analysis with the contents of hotspots in ICEMfuInd1a predicts recombination of genes between the SXT- and R391- related ICEs, while those in ICEMfuInd1b predict acquisition of genes from unrelated donor cells. More specifically, the HS-2 in ICEMfuInd1a was composed of genes that encoded proteins with >95% identity with those encoded by ICEs of the SXT group (mfuind1a-11 to mfuind1a-14) and R391-related ICEs (mfuind1a-9 and mfuind1a-10), whereas the HS-2 in ICEMfuIn1b was composed of genes that encoded proteins with >92% identity with those encoded by R391 and ICEVchMex1 (belonging to the R391 group). This suggests the HS-2 of ICEMfuInd1a is shaped by recombination between SXT- and R391-related ICEs in ICEMfuInd1a which was also observed by Osorio et al. (2008), whereas the HS-2 of ICEMfuInd1b was shaped by direct acquisition from a R391-related ancestor. However, the nature and functional attributes of most of these variable hotspot genes are not clear; either they confer element-specific properties or encode functions that have not been described in any known SXT/R391 ICEs. The genes in the hotspots of ICEMfuInd1a (Table 1) encode proteins which likely protect the host cell from heavy metals toxicity (mfuind1a-11), invasion by foreign DNA (mfuind1a-1 to mfuind1a-4) and/or promote integrity of the ICE genome (mfuind1a-9, mfuind1a-10 and mfuind1a-15). Further, the hotspot gene clusters mfuind1a-1 to mfuind1a-4 and mfuind1a-11 to mfuind1a-14 in ICEMfuInd1a showed very high similarity to such clusters in the genomes of Psychromonas arctica DSM 14288 and Vibrio cholerae O1 Inaba G4222 (Table 1). On the other hand, genes present in the hotspots of ICEMfuInd1b encoded distantly related proteins. The HS-5 of ICEMfuInd1b (Table 2) contains genes which likely encode proteins related to the functions of aromatic aldehyde oxidation (mfuind1b-2), cholesterol degradation (mfuind1b-3), histidine degradation by the Hut pathway (mfuind1b-5 to mfuind1b-8), a type-III restriction and modification system (mfuind1b-11 and mfuind1b-12). In addition, genes in HS-3 of ICEMfuInd1b encoded a HipAB-like toxin-antitoxin system (mfuind1b-21 and mfuind1b-22) involved in either ICE maintenance by killing or severely inhibiting the growth of cells that have lost the element (Wozniak and Waldor, 2009) or persister cells formation (Germain et al., 2013), and a predicted novel chemotaxis signal transduction system (mfuind1b-23 to mfuind1b-25). Although ICEs of the SXT/R391 family are well known for fostering dissemination of multidrug resistance genes in both environmental and clinical isolates (Wozniak et al., 2009; Carraro and Burrus, 2014; Spagnoletti et al., 2014; Johnson and Grossman, 2015), interestingly no such genes are found in either ICEMfuInd1a or ICEMfuInd1b of the M. fungiae JCM 18476T. However, analysis of the hotspot regions of ICEMprChn1 (Table 3) revealed the HS-1 contained a putative transposon cassette with genes conferring possible multidrug resistance phenotype to the host M. profundimaris (mprchn1-6 to mprchn1-18). Additionally, the HS-2 also bear a gene predicted to confer heavy metal resistance (mprchn1-24), whereas the HS-5 bear a putative helicase and a type-III restriction and modification system (mprchn1-3 to mprchn1-5). Overall, these hotspot variable genes likely encode functional traits that are advantageous to the host in changing environments and/or for stable maintenance of the ICEs.
Table 2.
Descriptions of genes or ORFs present in the hotspot regions of ICEMfuInd1b.
| Hotspot region | ICEMfuInd1b gene/ORF id | Gene name | Length (bp) | Hotspot gene product name | GenBank accession no. of protein homolog | % Similarity with homolog |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HS-5 (s024-traI) | Ga0061065_12215 | mfuind1b-1 | 1038 | AraC-type DNA-binding protein | Acinetobacter tandoii; WP_016166436.1 | 49 |
| Ga0061065_12214 | mfuind1b-2 | 1485 | Coniferyl-aldehyde dehydrogenase | Vibrio litoralis; WP_027695211.1 | 75 | |
| Ga0061065_12213 | mfuind1b-3 | 1779 | Cholesterol oxidase | Vibrio litoralis; WP_027695212.1 | 69 | |
| Ga0061065_12212 | mfuind1b-4 | 900 | DNA-binding transcriptional regulator, LysR | Colwellia piezophila; WP_019026485.1 | 75 | |
| Ga0061065_12211 | mfuind1b-5 | 1512 | Histidine ammonia lyase | Pseudoalteromonas tunicate; WP_009838609.1 | 84 | |
| Ga0061065_12210 | mfuind1b-6 | 2013 | Urocanate hydratase | Pseudoalteromonas luteoviolacea; WP_023399981.1 | 92 | |
| Ga0061065_1229 | mfuind1b-7 | 1272 | Imidazolonepropionase | Oceanospirillum beijerinckii; WP_028302424.1 | 86 | |
| Ga0061065_1228 | mfuind1b-8 | 1050 | Formiminoglutamase | Oceanospirillum beijerinckii; WP_028302423.1 | 68 | |
| Ga0061065_1227 | mfuind1b-9 | 240 | Hypothetical protein | No homology | – | |
| Ga0061065_1226 | mfuind1b-10 | 1254 | Hypothetical protein | Oceanospirillum beijerinckii; WP_028301959.1 | 47 | |
| Ga0061065_1225 | mfuind1b-11 | 885 | DNA methylase | Vibrio parahaemolyticus; WP_023584030.1 | 77 | |
| Ga0061065_1224 | mfuind1b-12 | 3078 | Type-III restriction enzyme | Vibrio parahaemolyticus; WP_023584031.1 | 99 | |
| Ga0061065_1223 | mfuind1b-13 | 282 | NMD3 family protein | Vibrio parahaemolyticus; WP_023584032.1 | 98 | |
| Ga0061065_1222 | mfuind1b-14 | 474 | Hypothetical protein | Vibrio cholerae; WP_001218616.1 | 100 | |
| HS-1 (traJ-traL) | Sequence not known | – | – | – | – | |
| HS-2 (traA-s054) | Ga0061065_1236 | mfuind1b-15 | 507 | Acetyltransferase (GNAT) domain containing protein | Vibrio parahaemolyticus; WP_025586955.1 | 98 |
| Ga0061065_1237 | mfuind1b-16 | 267 | Uncharacterized conserved protein DUF1778 family | Vibrio; WP_000212004.1 | 100 | |
| HS-4 (s073-traF) | Ga0061065_12315 | mfuind1b-17 | 684 | Hypothetical protein | Escherichia coli; WP_001375061.1 | 52 |
| Ga0061065_12316 | mfuind1b-18 | 897 | Protein of unknown function DUF4433 | Pseudomonas syringae; WP_024639153.1 | 41 | |
| Ga0061065_12317 | mfuind1b-19 | 1131 | TPR repeat containing protein | Denitrovibrio acetiphilus; WP_013010018.1 | 26 | |
| Ga0061065_12318 | mfuind1b-20 | 531 | Hypothetical protein | Acinetobacter baumannii; WP_004742094.1 | 35 | |
| Ga0061065_12319 | mfuind1b-21 | 1317 | Serine/threonine protein kinase HipA | Vibrio vulnificus; WP_011080066.1 | 95 | |
| Ga0061065_12320 | mfuind1b-22 | 324 | Cro/C1-type transcriptional regulator | Vibrio vulnificus; WP_017790219.1 | 92 | |
| HS-3 (traN-s063) | Ga0061065_1306 | mfuind1b-23 | 1782 | PAS domain S-box containing protein | Nitrosomonas sp.; WP_013965400.1 | 35 |
| Ga0061065_1305 | mfuind1b-24 | 2400 | PAS domain S-box containing protein | Rheinheimera nanhaiensis; WP_008221817.1 | 44 | |
| Ga0061065_1304 | mfuind1b-25 | 1557 | Methyl accepting chamotaxis sensory transducer with Pas/Pac sensor | Vibrio furnissii; WP_004729586.1 | 59 |
Table 3.
Descriptions of genes or ORFs present in the hotspot regions of ICEMprChn1.
| Hotspot region | ICEMprChn1 gene/ORF id | Gene name | Length (bp) | Hotspot gene product name | GenBank accession no. of protein homolog | % Similarity with homolog |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HS-5 (s026-traI) | D104_09935 | mprchn1-1 | 3333 | DNA or RNA helicase | Salmonella enterica; WP_060636796.1 | 100 |
| D104_09940 | mprchn1-2 | 687 | Hypothetical protein | Salinivibrio socompensis; WP_025674120.1 | 99 | |
| D104_09945 | mprchn1-3 | 1947 | DNA methyltransferase | Pseudomonas aeruginosa; WP_034019474.1 | 99 | |
| D104_09950 | mprchn1-4 | 3078 | Type III restriction enzyme R subunit | Shewanella decolorationis; WP_023266696.1 | 99 | |
| D104_09955 | mprchn1-5 | 855 | Restriction endonuclease | Vibrio fluvialis; WP_052075075.1 | 98 | |
| HS-1 (traJ-traL) | D104_09980 | mprchn1-6 | 1557 | Transposase | Gammaproteobacteria; WP_000850406.1 | 100 |
| D104_09985 | mprchn1-7 | 96 | Hypothetical protein | – | N.h | |
| D104_09995 | mprchn1-8 | 219 | Hypothetical protein | Gammaproteobacteria; WP_013785946.1 | 99 | |
| D104_10000 | mprchn1-9 | 243 | Hypothetical protein | Nitrincola sp. A-D6; WP_036520787.1 | 98 | |
| D104_10005 | mprchn1-10 | 708 | RES domain-containing protein | Nitrincola nitratireducens; WP_036513282.1 | 67 | |
| D104_10010 | mprchn1-11 | 372 | Hypothetical protein | Neptunomonas Antarctica; WP_054341548.1 | 79 | |
| D104_10015 | mprchn1-12 | 693 | TetR family transcriptional regulator | Alteromonas sp. SN2; WP_013785950.1 | 99 | |
| D104_10020 | mprchn1-13 | 1047 | RND transporter | Marinobacter sp. CP1; WP_053115257.1 | 54 | |
| D104_10025 | mprchn1-14 | 3042 | Multidrug transporter | Alteromonas sp. SN2; WP_013785952.1 | 99 | |
| D104_10030 | mprchn1-15 | 615 | SAM-dependent methyltransferase | Nitrincola sp. A-D6; WP_036520790.1 | 72 | |
| D104_10035 | mprchn1-16 | 234 | Hypothetical protein | Nitrincola sp. A-D6; WP_052063520.1 | 88 | |
| D104_10040 | mprchn1-17 | 1305 | Transposase | Shewanella putrefaciens; WP_014611283.1 | 74 | |
| D104_10445 | mprchn1-18 | 1173 | Transposase | Alteromonas sp. SN2; WP_041452603.1 | 98 | |
| D104_10450 | mprchn1-19 | 696 | ATPase AAA | Vibrio cholerae; WP_000796550.1 | 99 | |
| D104_10455 | mprchn1-20 | 573 | Plasmid-related protein | Alteromonas macleodii; WP_061094531.1 | 96 | |
| HS-2 (traA-s054) | D104_10490 | mprchn1-21 | 834 | Hypothetical protein | Vibrio nigripulchritudo; WP_022609808.1 | 99 |
| D104_10495 | mprchn1-22 | 702 | Hypothetical protein | Vibrio cholerae; WP_053044234.1 | 99 | |
| D104_10500 | mprchn1-23 | 408 | MerR family transcriptional regulator | Serratia marcescens; YP_003602521.1 | 100 | |
| D104_10505 | mprchn1-24 | 885 | Sodium: proton antiporter, CzcD | Pseudoalteromonas shioyasakiensis; WP_063529117.1 | 99 | |
| HS-4 (s073-traF) | D104_04195 | mprchn1-25 | 434 | Hypothetical protein | Vibrio alginolyticus; WP_005396849.1 | 97 |
| D104_04190 | mprchn1-26 | 663 | Hypothetical protein | Vibrio alginolyticus; WP_005396850.1 | 100 |
N.h, No homology.
Conclusions
Our analysis showed all the three ICEs shared a similar genetic organization with SXT/R391-like ICEs. In the backbone most of the syntenic core genes are conserved. Further, the two ICEs of M. fungiae were inserted at two different sites in the genome. Our analysis suggested the conjugative transfer of a second copy of SXT ICE in the same cell is not always impeded by the typical TraG/Eex mediated entry exclusion mechanism. Hotspots regions of all the three ICEs showed presence of large numbers of unique variable genes which were not found in the previously described ICEs. Further, absence of multidrug resistance genes in the hotspots suggested ICEs of M. fungiae have probably evolved through homologous recombination; in contrast the ICEMprChn1 of M. profundimaris strain D104 harbored a typical transposon cassette with multidrug transporter genes in the HS-1. The existence of such ICEs in marine bacteria warrants their rapid identification and functional analysis to understand the dissemination of multidrug resistance genes and their impact in natural populations.
Author contributions
SD conceived the idea of the work. JB designed the experiments and performed the experiments. JB and SD analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Ministry of Environment and Forest, Wild life Division, Government of India, and The Chief Conservator of Forests (Wild life), Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Port Blair officially allowing us to collect coral samples from the Andaman Sea. This work was supported in part by the funding received from Department of Biotechnology, Government of India (D.O. No. BT/PR7661/AAQ/3/629/2013) to SD. The author JB acknowledges the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India for providing the research fellowship. We acknowledge the Distributed Information Sub- Center (DISC) at Institute of Life Sciences, Bhubaneswar for the computational facility. The sequence data used in the study was produced by the US Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute http://www.jgi.doe.gov/.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01896/full#supplementary-material
References
- Ahmed A. M., Shinoda S., Shimamoto T. (2005). A variant type of Vibrio cholerae SXT element in a multidrug-resistant strain of Vibrio fluvialis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 242, 241–247. 10.1016/j.femsle.2004.11.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Madden T. L., Schäffer A. A., Zhang J., Zhang Z., Miller W., et al. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 3389–3402. 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badhai J., Kumari P., Krishnan P., Ramamurthy T., Das S. K. (2013). Presence of SXT integrating conjugative element in marine bacteria isolated from the mucus of the coral Fungia echinata from Andaman Sea. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 338, 118–123. 10.1111/1574-6968.12033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balado M., Lemos M. L., Osorio C. R. (2013). Integrating conjugative elements of the SXT/R391 family from fish-isolated vibrios encode restriction–modification systems that confer resistance to bacteriophages. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 83, 457–467. 10.1111/1574-6941.12007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaber J. W., Hochhut B., Waldor M. K. (2002). Genomic and functional analyses of SXT, an integrating antibiotic resistance gene transfer element derived from Vibrio cholerae. J. Bacteriol. 184, 4259–4269. 10.1128/JB.184.15.4259-4269.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaber J. W., Hochhut B., Waldor M. K. (2004). SOS response promotes horizontal dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes. Nature 427, 72–74. 10.1038/nature02241 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett S. (2004). Solexa Ltd. Pharmacogenomics 5, 433–438. 10.1517/14622416.5.4.433 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bi D., Xu Z., Harrison E., Tai C., Wei Y., He X., et al. (2012). ICEberg: a web-based resource for integrative and conjugative elements found in Bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, D621–D626. 10.1093/nar/gkr846 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boltner D., MacMahon C., Pembroke J. T., Strike P., Osborn A. M. (2002). R391: a conjugative 334 integrating mosaic comprised of phage, plasmid, and transposon elements. J. Bacteriol. 184, 5158–5169. 10.1128/JB.184.18.5158-5169.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrus V., Marrero J., Waldor M. K. (2006). The current ICE age: biology and evolution of SXT-related integrating conjugative elements. Plasmid 55, 173–183. 10.1016/j.plasmid.2006.01.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrus V., Waldor M. K. (2003). Control of SXT integration and excision. J. Bacteriol. 185, 5045–5054. 10.1128/JB.185.17.5045-5054.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrus V., Waldor M. K. (2004a). Shaping bacterial genomes with integrative and conjugative elements. Res. Microbiol. 155, 376–386. 10.1016/j.resmic.2004.01.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrus V., Waldor M. K. (2004b). Formation of SXT tandem arrays and SXT-R391 hybrids. J. Bacteriol. 186, 2636–2645. 10.1128/JB.186.9.2636-2645.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camacho C., Coulouris G., Avagyan V., Ma N., Papadopoulos J., Bealer K., et al. (2009). BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 10:421. 10.1186/1471-2105-10-421 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraro N., Burrus V. (2014). Biology of three ICE families: SXT/R391, ICEBs1, and ICESt1/ICESt3. Microbiol. Spectr. 2, 1–20. 10.1128/microbiolspec.MDNA3-0008-2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraro N., Poulin D., Burrus V. (2015). Replication and active partition of integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs) of the SXT/R391 family: the line between ICEs and conjugative plasmids is getting thinner. PLoS Genet. 11:e1005298. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005298 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver T., Thomson N., Bleasby A., Berriman M., Parkhill J. (2009). DNAPlotter: circular and linear interactive genome visualization. Bioinformatics 25, 119–120. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn578 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli D., Daccord A., René M., Burrus V. (2008). Identification of the origin of transfer (oriT) and a new gene required for mobilization of the SXT/R391 family of integrating conjugative elements. J. Bacteriol. 190, 5328–5338. 10.1128/JB.00150-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coetzee J. N., Datta N., Hedges R. W. (1972). R factors from Proteus rettgeri. J. Gen. Microbiol. 72, 543–552. 10.1099/00221287-72-3-543 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong C., Bai X., Lai Q., Xie Y., Chen X., Shao Z. (2014). Draft genome sequence of Marinomonas sp. strain D104, a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium from the deep-sea sediment of the Arctic Ocean. Genome. Announc. 2, e1211–e1213. 10.1128/genomea.01211-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garriss G., Poulin-Laprade D., Burrus V. (2013). DNA-damaging agents induce the RecA-independent homologous recombination functions of integrating conjugative elements of the SXT/R391 family. J. Bacteriol. 195, 1991–2003. 10.1128/JB.02090-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garriss G., Waldor M. K., Burrus V. (2009). Mobile antibiotic resistance encoding elements promote their own diversity. PLoS Genet. 5:e1000775. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000775 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain E., Castro-Roa D., Zenkin N., Gerdes K. (2013). Molecular mechanism of bacterial persistence by HipA. Mol. Cell 52, 248–254. 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.045 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Ishii Y., Saga T., Tateda K., Yamaguchi K. (2010). Chromosomally encoded blaCMY-2 located on a novel SXT/R391-related integrating conjugative element in a Proteus mirabilis clinical isolate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54, 3545–3550. 10.1128/AAC.00111-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochhut B., Beaber J. W., Woodgate R., Waldor M. K. (2001). Formation of chromosomal tandem arrays of the SXT element and R391, two conjugative chromosomally integrating elements that share an attachment site. J. Bacteriol. 183, 1124–1132. 10.1128/JB.183.4.1124-1132.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochhut B., Waldor M. K. (1999). Site-specific integration of the conjugal Vibrio cholerae SXT element into prfC. Mol. Microbiol. 32, 99–110. 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01330.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. M., Grossman A. D. (2015). Integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs): what they do and how they work. Annu. Rev. Genet. 49, 577–601. 10.1146/annurev-genet-112414-055018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumari P., Poddar A., Das S. K. (2014). Marinomonas fungiae sp. nov., isolated from the coral Fungia echinata from the Andaman Sea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 64, 487–494. 10.1099/ijs.0.054809-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei C. W., Zhang A. Y., Wang H. N., Liu B. H., Yang L. Q., Yang Y. Q. (2016). Characterization of SXT/R391 integrative and conjugative elements in Proteus mirabilis isolates from food-producing animals in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60, 1935–1938. 10.1128/AAC.02852-15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo P., He X., Wang Y., Liu Q., Hu C. (2016). Comparative genomic analysis of six new-found integrative conjugative elements (ICEs) in Vibrio alginolyticus. BMC Microbiol. 16:79. 10.1186/s12866-016-0692-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrero J., Waldor M. K. (2005). Interactions between inner membrane proteins in donor and recipient cells limit conjugal DNA transfer. Dev. Cell 8, 963–970. 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.05.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrero J., Waldor M. K. (2007). The SXT/R391 family of integrative conjugative elements is composed of two exclusion groups. J. Bacteriol. 189, 3302–3305. 10.1128/JB.01902-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromatis K., Ivanova N. N., Chen I. M., Szeto E., Markowitz V. M., Kyrpides N. C. (2009). The DOE-JGI standard operating procedure for the annotations of microbial genomes. Stand. Genomic Sci. 1, 63–67. 10.4056/sigs.632 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osorio C. R., Marrero J., Wozniak R. A., Lemos M. L., Burrus V., Waldor M. K. (2008). Genomic and functional analysis of ICEPdaSpa1, a fish-pathogen-derived SXT related integrating conjugative element that can mobilize a virulence plasmid. J. Bacteriol. 190, 3353–3361. 10.1128/JB.00109-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pembroke J. T., Piterina A. V. (2006). A novel ICE in the genome of Shewanella putrefaciens W3-18-1: comparison with the SXT/R391 ICE-like elements. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 264, 80–88. 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00452.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulin-Laprade D., Burrus V. (2015). A λ Cro-like repressor is essential for the induction of conjugative transfer of SXT/R391 elements in response to DNA damage. J. Bacteriol. 197, 3822–3833. 10.1128/JB.00638-15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulin-Laprade D., Matteau D., Jacques P. E., Rodrigue S., Burrus V. (2015). Transfer activation of SXT/R391integrative and conjugative elements: unraveling the SetCD regulon. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, 2045–2056. 10.1093/nar/gkv071 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Blanco A., Lemos M. L., Osorio C. R. (2012). Integrating conjugative elements as vectors of antibiotic, mercury, and quaternary ammonium compound resistance in marine aquaculture environments. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 56, 2619–2626. 10.1128/AAC.05997-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Fritsch E. F., Maniatis T. A. (1989). In Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd Edn. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. [Google Scholar]
- Spagnoletti M., Ceccarelli D., Rieux A., Fondi M., Taviani E., Fani R., et al. (2014). Acquisition and evolution of SXT-R391 integrative conjugative elements in the seventh-pandemic Vibrio cholerae lineage. MBio 5:e01356–14. 10.1128/mBio.01356-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Stecher G., Peterson D., Filipski A., Kumar S. (2013). MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30, 2725–2729. 10.1093/molbev/mst197 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taviani E., Spagnoletti M., Ceccarelli D., Haley B. J., Hasan N. A., Chen A., et al. (2012). Genomic analysis of ICEVchBan8: an atypical genetic element in Vibrio cholerae. FEBS Lett. 586, 1617–1621. 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.03.064 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldor M. K., Tschäpe H., Mekalanos J. J. (1996). A new type of conjugative transposon encodes resistance to sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim, and streptomycin in Vibrio cholerae O139. J. Bacteriol. 178, 4157–4165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak R. A., Fouts D. E., Spagnoletti M., Colombo M. M., Ceccarelli D., Garriss G., et al. (2009). Comparative ICE genomics: insights into the evolution of the SXT/R391 family of ICEs. PLoS Genet. 5:e1000786. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000786 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak R. A., Waldor M. K. (2009). A toxin-antitoxin system promotes the maintenance of an integrative conjugative element. PLoS Genet. 5:e1000439. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000439 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerkandl E., Pauling L. (1965). Evolutionary divergence and convergence in proteins, in Evolving Genes and Proteins, eds Bryson V., Vogel H. J. (New York, NY: Academic Press; ), 97–166. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.