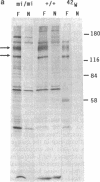
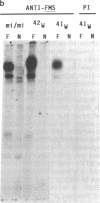
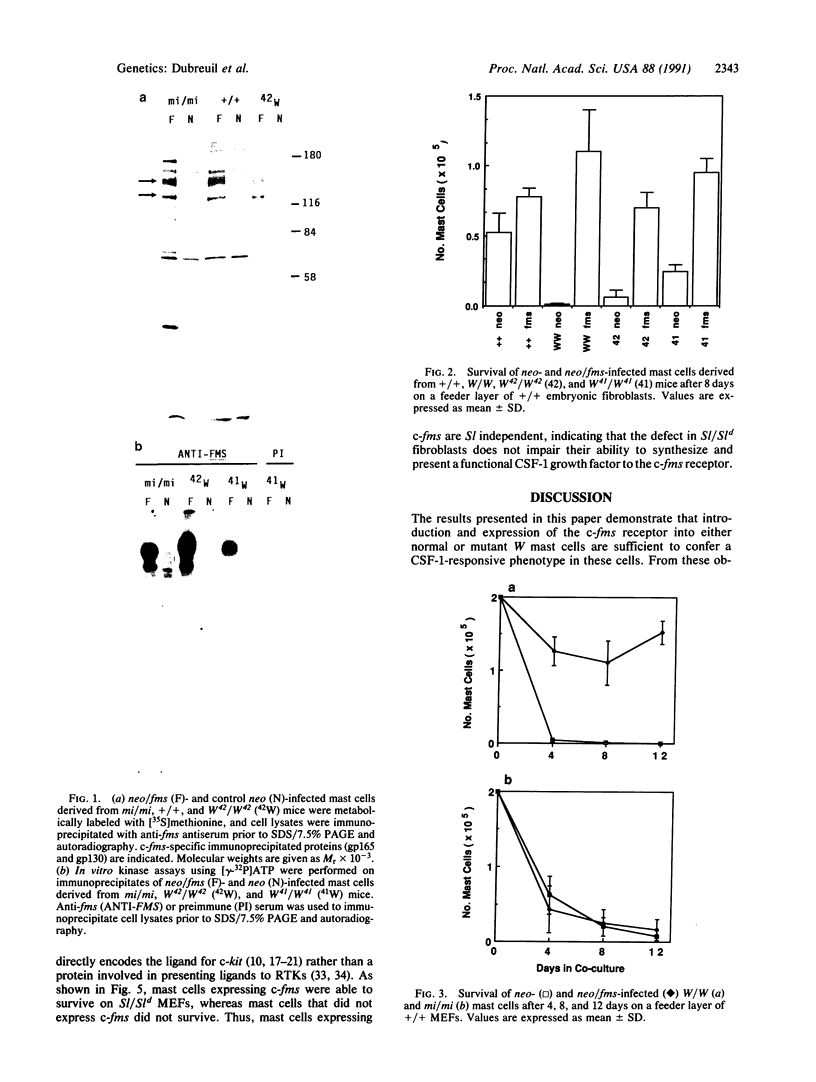
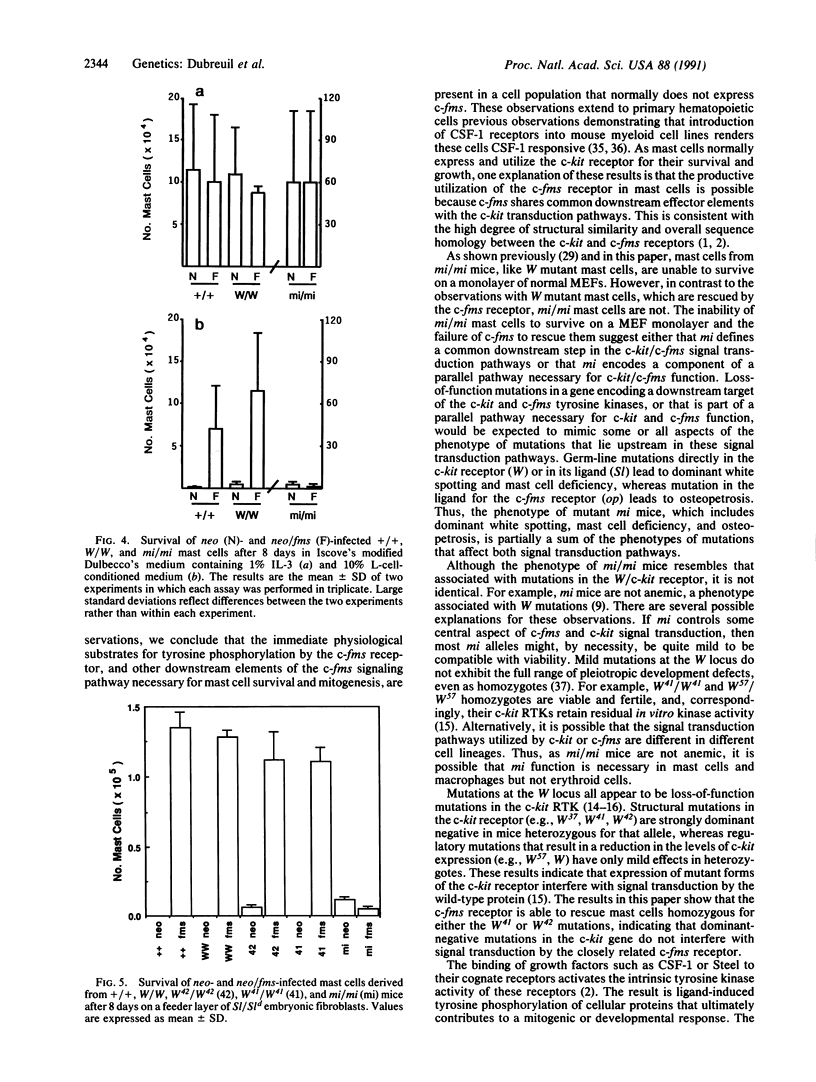
Abstract
Mutations at three loci in the mouse--W, Steel Sl), and microphthalmia (mi)--can lead to a deficiency in melanocytes and mast cells. As well, W and Sl mutants can be anemic and sterile, whereas mi mice are osteopetrotic due to a monocyte/macrophage defect. Recent data have shown that the c-kit receptor tyrosine kinase is the gene product of the W locus, whereas Sl encodes the ligand for this growth factor receptor. We show here that ectopic expression of c-fms, a gene that encodes a macrophage growth factor receptor that is closely related to the c-kit receptor, complements mutations at the W locus in an in vitro mast cell/fibroblast coculture system but is unable to reverse the inability of mi/mi mast cells to survive under these conditions. Furthermore, mast cells expressing the c-fms receptor survive on a monolayer of fibroblasts homozygous for the Sl mutation. These results suggest that ligand binding to the c-kit or c-fms receptor activates identical or overlapping signal transduction pathways. Furthermore, they suggest that mi encodes a protein necessary for transducing signals mediated by way of either the c-kit or c-fms receptor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brady G., Williams R. L., Nordström K., Vennström B., Iscove N. N. A selectable temperature-sensitive v-src Moloney retrovirus. Oncogene. 1988 Dec;3(6):687–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Stephenson D. A., Chapman V. M., Besmer P., Bernstein A. The proto-oncogene c-kit encoding a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor maps to the mouse W locus. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):88–89. doi: 10.1038/335088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. C., Kamen R. The human hematopoietic colony-stimulating factors. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1229–1237. doi: 10.1126/science.3296190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Cho B. C., Donovan P. J., Jenkins N. A., Cosman D., Anderson D., Lyman S. D., Williams D. E. Mast cell growth factor maps near the steel locus on mouse chromosome 10 and is deleted in a number of steel alleles. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90298-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebi Y., Kasugai T., Seino Y., Onoue H., Kanemoto T., Kitamura Y. Mechanism of mast cell deficiency in mutant mice of mi/mi genotype: an analysis by co-culture of mast cells and fibroblasts. Blood. 1990 Mar 15;75(6):1247–1251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J., Bernstein A. Gene targeting with retroviral vectors: recombination by gene conversion into regions of nonhomology. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1621–1627. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Leder P. The kit ligand: a cell surface molecule altered in steel mutant fibroblasts. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90299-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita J., Nakayama H., Onoue H., Ebi Y., Kanakura Y., Kuriu A., Kitamura Y. Failure of W/Wv mouse-derived cultured mast cells to enter S phase upon contact with NIH/3T3 fibroblasts. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):463–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita J., Onoue H., Ebi Y., Nakayama H., Kanakura Y. In vitro duplication and in vivo cure of mast-cell deficiency of Sl/Sld mutant mice by cloned 3T3 fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2888–2891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler E. N., McFarland E. C., Russell E. S. Analysis of pleiotropism at the dominant white-spotting (W) locus of the house mouse: a description of ten new W alleles. Genetics. 1981 Feb;97(2):337–361. doi: 10.1093/genetics/97.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler E. N., Ryan M. A., Housman D. E. The dominant-white spotting (W) locus of the mouse encodes the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E., Nocka K., Beier D. R., Chu T. Y., Buck J., Lahm H. W., Wellner D., Leder P., Besmer P. The hematopoietic growth factor KL is encoded by the Sl locus and is the ligand of the c-kit receptor, the gene product of the W locus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90303-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Sherr C. J. Human colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1) receptor confers CSF-1 responsiveness to interleukin-3-dependent 32DC13 mouse myeloid cells and abrogates differentiation in response to granulocyte CSF. Blood. 1990 May 1;75(9):1780–1787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz D., Goff S., Bank A. A safe packaging line for gene transfer: separating viral genes on two different plasmids. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1120–1124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1120-1124.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks S. C., Jr Congenital osteopetrotic mutations as probes of the origin, structure, and function of osteoclasts. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984 Oct;(189):239–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison-Graham K., Bork T., Weston J. A. Association between collagen and glycosaminoglycans is altered in dermal extracellular matrix of fetal Steel (Sld/Sld) mice. Dev Biol. 1990 Jun;139(2):308–313. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90300-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison-Graham K., West-Johnsrud L., Weston J. A. Extracellular matrix from normal but not Steel mutant mice enhances melanogenesis in cultured mouse neural crest cells. Dev Biol. 1990 Jun;139(2):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90299-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy H. M. The osteopetrotic syndrome in the microphthalmic mutant mouse. Calcif Tissue Res. 1973;13(1):19–26. doi: 10.1007/BF02015392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocka K., Majumder S., Chabot B., Ray P., Cervone M., Bernstein A., Besmer P. Expression of c-kit gene products in known cellular targets of W mutations in normal and W mutant mice--evidence for an impaired c-kit kinase in mutant mice. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):816–826. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocka K., Tan J. C., Chiu E., Chu T. Y., Ray P., Traktman P., Besmer P. Molecular bases of dominant negative and loss of function mutations at the murine c-kit/white spotting locus: W37, Wv, W41 and W. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1805–1813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Bernstein A. Receptor tyrosine kinases: genetic evidence for their role in Drosophila and mouse development. Trends Genet. 1990 Nov;6(11):350–356. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90276-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith A. D., Rottapel R., Giddens E., Brady C., Forrester L., Bernstein A. W mutant mice with mild or severe developmental defects contain distinct point mutations in the kinase domain of the c-kit receptor. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):390–400. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R., Metcalf D. Induction of macrophage colony-stimulating factor-dependent growth and differentiation after introduction of the murine c-fms gene into FDC-P1 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5081–5092. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell E. S. Hereditary anemias of the mouse: a review for geneticists. Adv Genet. 1979;20:357–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Rettenmier C. W., Sacca R., Roussel M. F., Look A. T., Stanley E. R. The c-fms proto-oncogene product is related to the receptor for the mononuclear phagocyte growth factor, CSF-1. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):665–676. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J. C., Nocka K., Ray P., Traktman P., Besmer P. The dominant W42 spotting phenotype results from a missense mutation in the c-kit receptor kinase. Science. 1990 Jan 12;247(4939):209–212. doi: 10.1126/science.1688471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thesingh C. W., Scherft J. P. Fusion disability of embryonic osteoclast precursor cells and macrophages in the microphthalmic osteopetrotic mouse. Bone. 1985;6(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(85)90406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. G. Bone resorption restored in osteopetrotic mice by transplants of normal bone marrow and spleen cells. Science. 1975 Nov 21;190(4216):784–785. doi: 10.1126/science.1105786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor-Jedrzejczak W., Bartocci A., Ferrante A. W., Jr, Ahmed-Ansari A., Sell K. W., Pollard J. W., Stanley E. R. Total absence of colony-stimulating factor 1 in the macrophage-deficient osteopetrotic (op/op) mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4828–4832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. E., Eisenman J., Baird A., Rauch C., Van Ness K., March C. J., Park L. S., Martin U., Mochizuki D. Y., Boswell H. S. Identification of a ligand for the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90297-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Hayashi S., Kunisada T., Ogawa M., Nishikawa S., Okamura H., Sudo T., Shultz L. D., Nishikawa S. The murine mutation osteopetrosis is in the coding region of the macrophage colony stimulating factor gene. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):442–444. doi: 10.1038/345442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsebo K. M., Williams D. A., Geissler E. N., Broudy V. C., Martin F. H., Atkins H. L., Hsu R. Y., Birkett N. C., Okino K. H., Murdock D. C. Stem cell factor is encoded at the Sl locus of the mouse and is the ligand for the c-kit tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90302-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]