Abstract
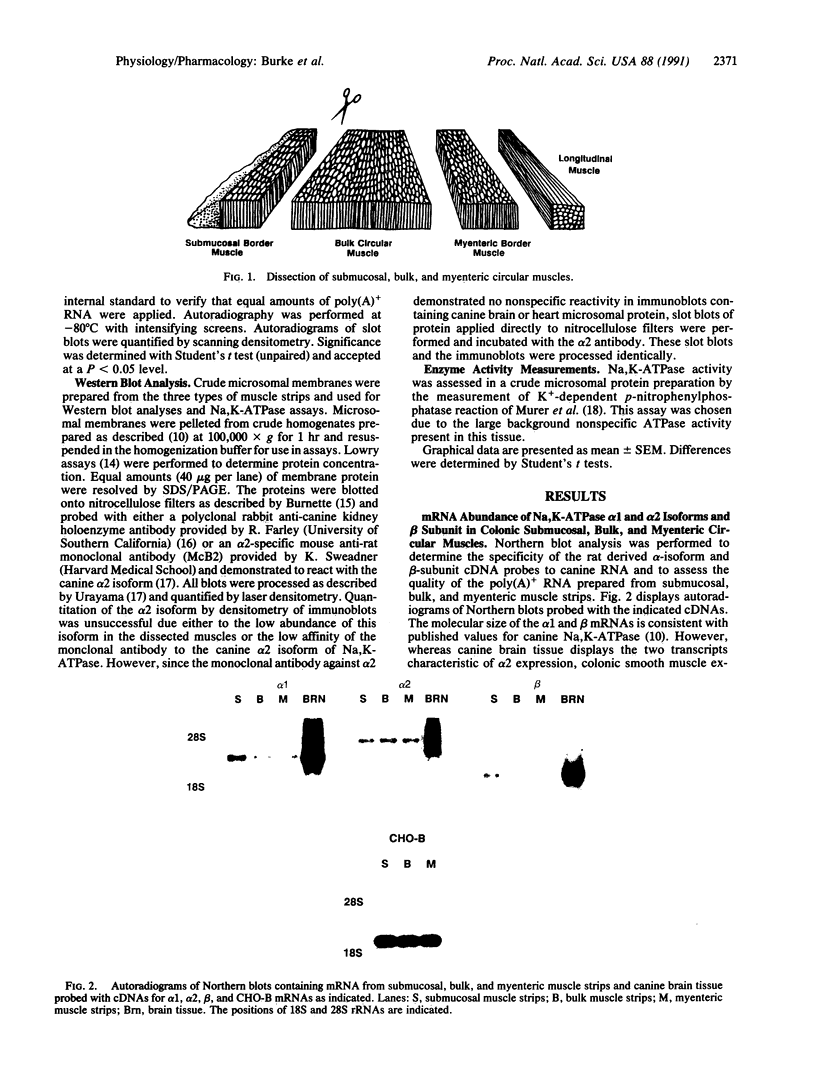
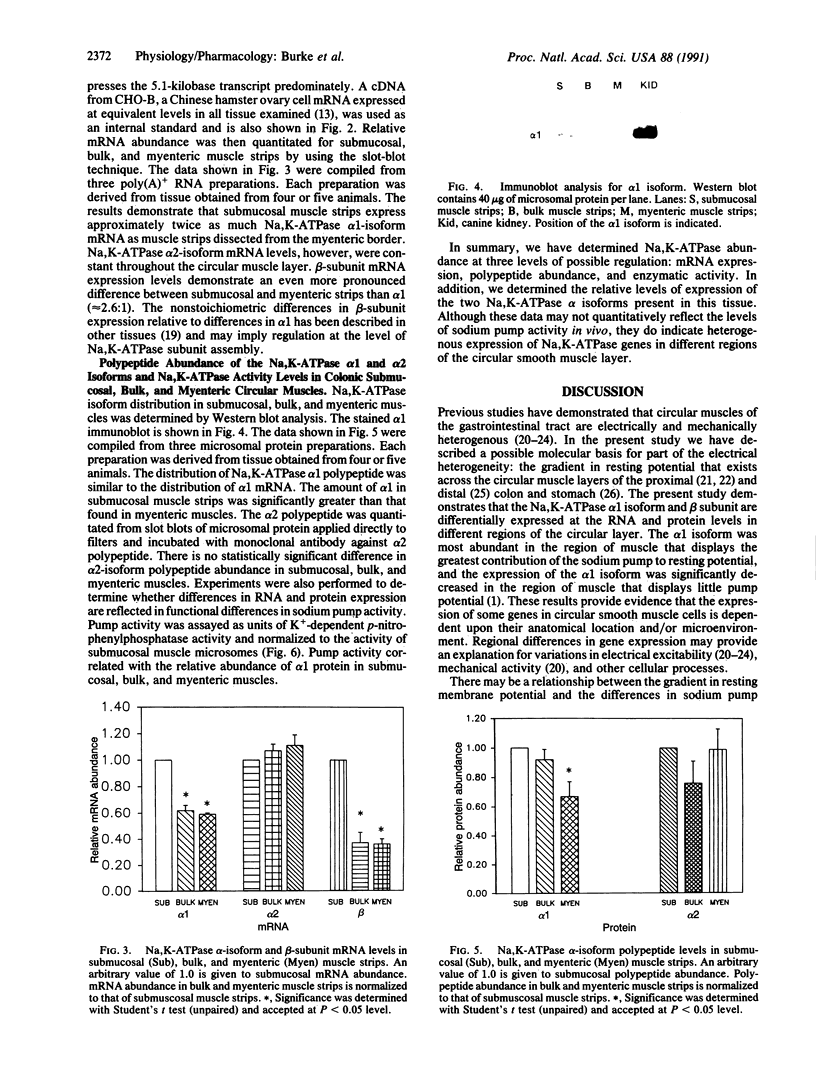
Molecular analyses of Na,K-ATPase abundance and alpha-subunit isoform distribution were performed to determine whether pump expression varies at different points through the thickness of the circular layer of colonic smooth muscle. The mRNA and polypeptides of Na,K-ATPase alpha 1 and beta subunits were twice as abundant in the submucosal region of the circular layer, which has previously been shown to generate large pump potentials. Sodium pump activity directly correlated with the relative abundance of the alpha 1 polypeptide. These data show that sodium pump expression varies in electrically dissimilar regions of the circular layer.
Full text
PDF
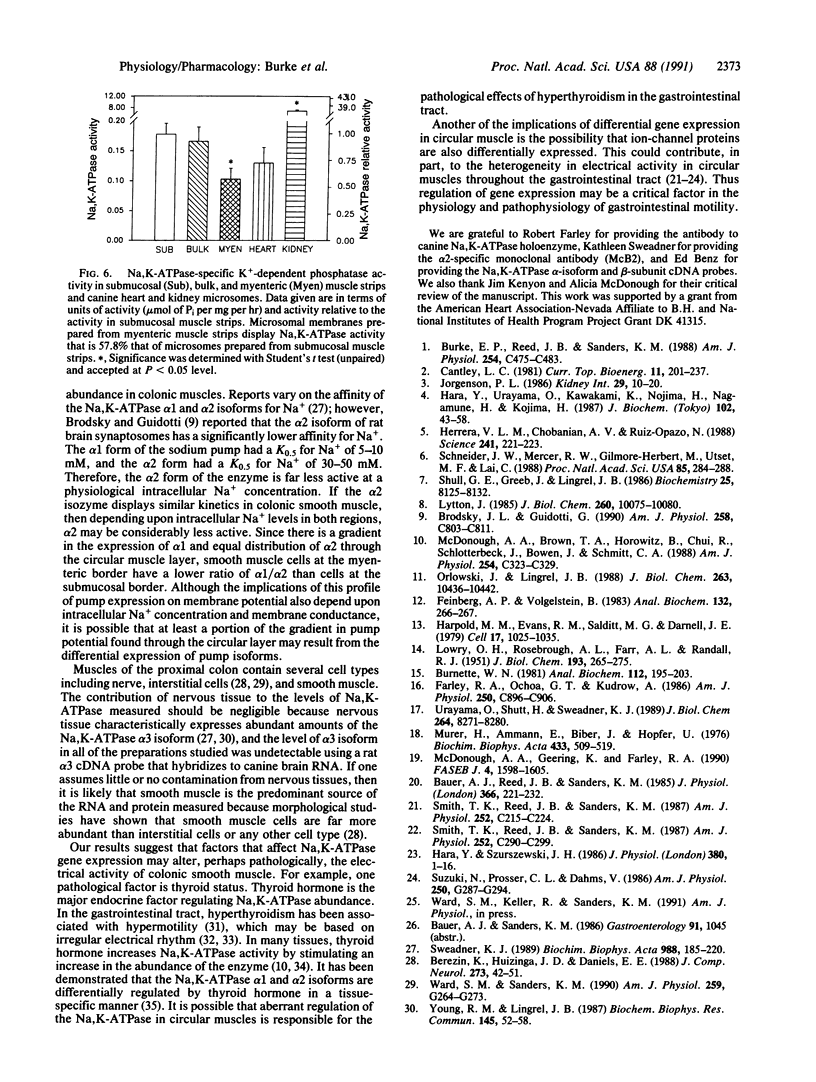

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. J., Reed J. B., Sanders K. M. Slow wave heterogeneity within the circular muscle of the canine gastric antrum. J Physiol. 1985 Sep;366:221–232. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berezin I., Huizinga J. D., Daniel E. E. Interstitial cells of Cajal in the canine colon: a special communication network at the inner border of the circular muscle. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Jul 1;273(1):42–51. doi: 10.1002/cne.902730105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky J. L., Guidotti G. Sodium affinity of brain Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase is dependent on isozyme and environment of the pump. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 1):C803–C811. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.5.C803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke E. P., Reed J. B., Sanders K. M. Role of sodium pump in membrane potential gradient of canine proximal colon. Am J Physiol. 1988 Apr;254(4 Pt 1):C475–C483. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.4.C475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTENSEN J., SCHEDL H. P., CLIFTON J. A. THE BASIC ELECTRICAL RHYTHM OF THE DUODENUM IN NORMAL HUMAN SUBJECTS AND IN PATIENTS WITH THYROID DISEASE. J Clin Invest. 1964 Aug;43:1659–1667. doi: 10.1172/JCI105041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifton J. A., Christensen J., Schedl H. P. The human small intestinal slow wave. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 1966;77:217–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley R. A., Ochoa G. T., Kudrow A. Location of major antibody binding domains on alpha-subunit of dog kidney Na+-K+-ATPase. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 1):C896–C906. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.6.C896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganitkevich VYa, Shuba M. F., Smirnov S. V. Potential-dependent calcium inward current in a single isolated smooth muscle cell of the guinea-pig taenia caeci. J Physiol. 1986 Nov;380:1–16. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gick G. G., Ismail-Beigi F., Edelman I. S. Thyroidal regulation of rat renal and hepatic Na,K-ATPase gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16610–16618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara Y., Urayama O., Kawakami K., Nojima H., Nagamune H., Kojima T., Ohta T., Nagano K., Nakao M. Primary structures of two types of alpha-subunit of rat brain Na+,K+,-ATPase deduced from cDNA sequences. J Biochem. 1987 Jul;102(1):43–58. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpold M. M., Evans R. M., Salditt-Georgieff M., Darnell J. E. Production of mRNA in Chinese hamster cells: relationship of the rate of synthesis to the cytoplasmic concentration of nine specific mRNA sequences. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):1025–1035. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera V. L., Chobanian A. V., Ruiz-Opazo N. Isoform-specific modulation of Na+, K+-ATPase alpha-subunit gene expression in hypertension. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):221–223. doi: 10.1126/science.2838907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz B., Hensley C. B., Quintero M., Azuma K. K., Putnam D., McDonough A. A. Differential regulation of Na,K-ATPase alpha 1, alpha 2, and beta subunit mRNA and protein levels by thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14308–14314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L. Structure, function and regulation of Na,K-ATPase in the kidney. Kidney Int. 1986 Jan;29(1):10–20. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalewski K., Kolodej A. Myoelectrical and mechanical activity of stomach and intestine in hypothyroid dogs. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Mar;22(3):235–240. doi: 10.1007/BF01072282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytton J. Insulin affects the sodium affinity of the rat adipocyte (Na+,K+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10075–10080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough A. A., Brown T. A., Horowitz B., Chiu R., Schlotterbeck J., Bowen J., Schmitt C. A. Thyroid hormone coordinately regulates Na+-K+-ATPase alpha- and beta-subunit mRNA levels in kidney. Am J Physiol. 1988 Feb;254(2 Pt 1):C323–C329. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.2.C323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough A. A., Geering K., Farley R. A. The sodium pump needs its beta subunit. FASEB J. 1990 Apr 1;4(6):1598–1605. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.6.2156741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murer H., Ammann E., Biber J., Hopfer U. The surface membrane of the small intestinal epithelial cell. I. Localization of adenyl cyclase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 21;433(3):509–519. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski J., Lingrel J. B. Tissue-specific and developmental regulation of rat Na,K-ATPase catalytic alpha isoform and beta subunit mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10436–10442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. W., Mercer R. W., Gilmore-Hebert M., Utset M. F., Lai C., Greene A., Benz E. J., Jr Tissue specificity, localization in brain, and cell-free translation of mRNA encoding the A3 isoform of Na+,K+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):284–288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Greeb J., Lingrel J. B. Molecular cloning of three distinct forms of the Na+,K+-ATPase alpha-subunit from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8125–8132. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. K., Reed J. B., Sanders K. M. Interaction of two electrical pacemakers in muscularis of canine proximal colon. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 1):C290–C299. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.3.C290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. K., Reed J. B., Sanders K. M. Origin and propagation of electrical slow waves in circular muscle of canine proximal colon. Am J Physiol. 1987 Feb;252(2 Pt 1):C215–C224. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.2.C215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Prosser C. L., Dahms V. Boundary cells between longitudinal and circular layers: essential for electrical slow waves in cat intestine. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 1):G287–G294. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.250.3.G287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweadner K. J. Isozymes of the Na+/K+-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 9;988(2):185–220. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urayama O., Shutt H., Sweadner K. J. Identification of three isozyme proteins of the catalytic subunit of the Na,K-ATPase in rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8271–8280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. M., Sanders K. M. Pacemaker activity in septal structures of canine colonic circular muscle. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 1):G264–G273. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.2.G264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. M., Lingrel J. B. Tissue distribution of mRNAs encoding the alpha isoforms and beta subunit of rat Na+,K+-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 29;145(1):52–58. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91286-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]