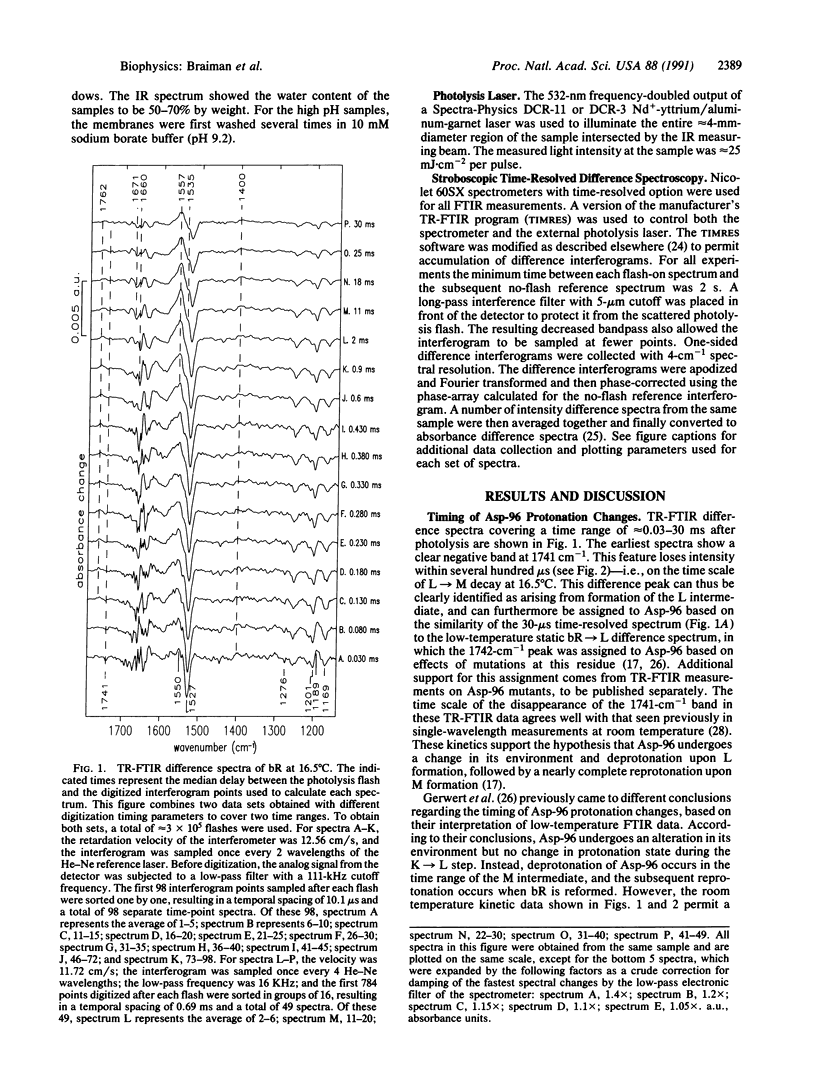
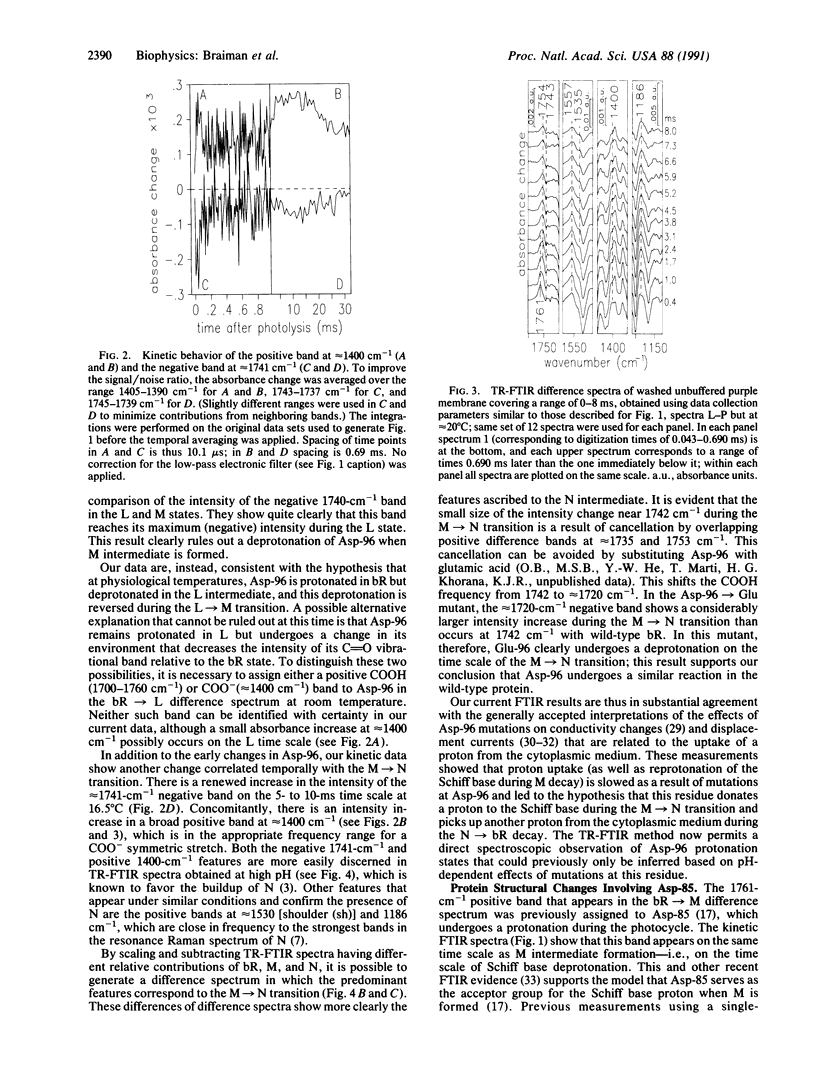
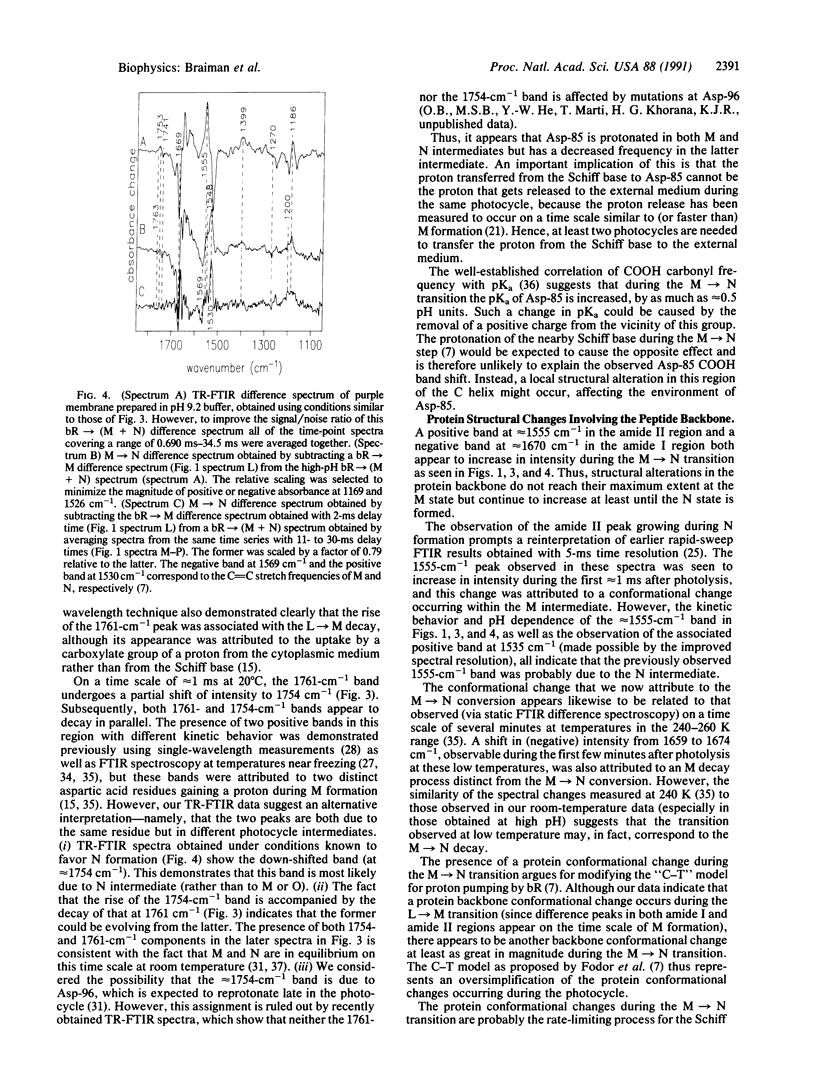
Abstract
The usefulness of stroboscopic time-resolved Fourier transform IR spectroscopy for studying the dynamics of biological systems is demonstrated. By using this technique, we have obtained broadband IR absorbance difference spectra after photolysis of bacteriorhodospin with a time resolution of approximately 50 microseconds, spectral resolution of 4 cm-1, and a detection limit of delta A less than or equal to 10(-4). These capabilities permit observation of detailed structural changes in individual residues as bacteriorhodopsin passes through its L, M, and N intermediate states near physiological temperatures. When combined with band assignments based on isotope labeling and site-directed mutagenesis, the stroboscopic Fourier transform IR difference spectra show that on the time scale of the L intermediate, Asp-96 has an altered environment that may be accompanied by change in its protonation state. On the time scale of the L----M transition, this Asp-96 perturbation/deprotonation is largely reversed, and Asp-85 becomes protonated. During the M----N transition, Asp-85 appears to remain protonated but undergoes a change in its environment as evidenced by a shift of vC = O from 1761 to 1755 cm-1. The retention of a proton on Asp-85 in the N state indicates that the proton transferred from the Schiff base to this residue in the L----M step is not released to the extracellular medium during the same photocycle, but rather during a subsequent one. Also during the M----N transition, Asp-96 undergoes a deprotonation (possibly for the second time in a single photocycle). Bands in the amide I and amide II spectral regions in the M----N difference spectrum indicate the occurrence of a conformational change involving one or more peptide groups in the protein backbone.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames J. B., Mathies R. A. The role of back-reactions and proton uptake during the N----O transition in bacteriorhodopsin's photocycle: a kinetic resonance Raman study. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 7;29(31):7181–7190. doi: 10.1021/bi00483a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagley K., Dollinger G., Eisenstein L., Singh A. K., Zimányi L. Fourier transform infrared difference spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin and its photoproducts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4972–4976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Ahl P. L., Rothschild K. J. Millisecond Fourier-transform infrared difference spectra of bacteriorhodopsin's M412 photoproduct. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5221–5225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Mogi T., Marti T., Stern L. J., Khorana H. G., Rothschild K. J. Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants: light-driven proton transport involves protonation changes of aspartic acid residues 85, 96, and 212. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8516–8520. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Mogi T., Stern L. J., Hackett N. R., Chao B. H., Khorana H. G., Rothschild K. J. Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants: I. Tyrosine-185 protonates and deprotonates during the photocycle. Proteins. 1988;3(4):219–229. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M., Mathies R. Resonance Raman spectra of bacteriorhodopsin's primary photoproduct: evidence for a distorted 13-cis retinal chromophore. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):403–407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt H. J., Fendler K., Bamberg E., Tittor J., Oesterhelt D. Aspartic acids 96 and 85 play a central role in the function of bacteriorhodopsin as a proton pump. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1657–1663. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollinger G., Eisenstein L., Lin S. L., Nakanishi K., Termini J. Fourier transform infrared difference spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin and its photoproducts regenerated with deuterated tyrosine. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6524–6533. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhard M., Gerwert K., Hess B., Kreutz W., Siebert F. Light-driven protonation changes of internal aspartic acids of bacteriorhodopsin: an investigation by static and time-resolved infrared difference spectroscopy using [4-13C]aspartic acid labeled purple membrane. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 15;24(2):400–407. doi: 10.1021/bi00323a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor S. P., Ames J. B., Gebhard R., van den Berg E. M., Stoeckenius W., Lugtenburg J., Mathies R. A. Chromophore structure in bacteriorhodopsin's N intermediate: implications for the proton-pumping mechanism. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):7097–7101. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwert K., Hess B., Soppa J., Oesterhelt D. Role of aspartate-96 in proton translocation by bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4943–4947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwert K., Souvignier G., Hess B. Simultaneous monitoring of light-induced changes in protein side-group protonation, chromophore isomerization, and backbone motion of bacteriorhodopsin by time-resolved Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec 15;87(24):9774–9778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Unwin P. N. Three-dimensional model of purple membrane obtained by electron microscopy. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):28–32. doi: 10.1038/257028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyn M. P., Westerhausen J., Wallat I., Seiff F. High-sensitivity neutron diffraction of membranes: Location of the Schiff base end of the chromophore of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2146–2150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz M., Drachev L. A., Mogi T., Otto H., Kaulen A. D., Heyn M. P., Skulachev V. P., Khorana H. G. Replacement of aspartic acid-96 by asparagine in bacteriorhodopsin slows both the decay of the M intermediate and the associated proton movement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2167–2171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz M., Lindau M., Heyn M. P. Distributed kinetics of the charge movements in bacteriorhodopsin: evidence for conformational substates. Biophys J. 1988 Apr;53(4):623–633. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83141-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama T., Nasuda-Kouyama A., Ikegami A., Mathew M. K., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin photoreaction: identification of a long-lived intermediate N (P,R350) at high pH and its M-like photoproduct. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):5855–5863. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin: a light-driven proton pump in Halobacterium Halobium. Biophys J. 1975 Sep;15(9):955–962. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85875-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinetti T., Subramaniam S., Mogi T., Marti T., Khorana H. G. Replacement of aspartic residues 85, 96, 115, or 212 affects the quantum yield and kinetics of proton release and uptake by bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):529–533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormos P. Infrared spectroscopic demonstration of a conformational change in bacteriorhodopsin involved in proton pumping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):473–477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto H., Marti T., Holz M., Mogi T., Lindau M., Khorana H. G., Heyn M. P. Aspartic acid-96 is the internal proton donor in the reprotonation of the Schiff base of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9228–9232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roepe P., Ahl P. L., Das Gupta S. K., Herzfeld J., Rothschild K. J. Tyrosine and carboxyl protonation changes in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. 1. M412 and L550 intermediates. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 20;26(21):6696–6707. doi: 10.1021/bi00395a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild K. J., Braiman M. S., He Y. W., Marti T., Khorana H. G. Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants. Evidence for the interaction of aspartic acid 212 with tyrosine 185 and possible role in the proton pump mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16985–16991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild K. J., Braiman M. S., Mogi T., Stern L. J., Khorana H. G. Conserved amino acids in F-helix of bacteriorhodopsin form part of a retinal binding pocket. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):448–452. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80774-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild K. J., Marrero H. Infrared evidence that the Schiff base of bacteriorhodopsin is protonated: bR570 and K intermediates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild K. J., Zagaeski M., Cantore W. A. Conformational changes of bacteriorhodopsin detected by Fourier transform infrared difference spectroscopy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 30;103(2):483–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90478-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert F., Mäntele W. Investigation of the primary photochemistry of bacteriorhodopsin by low-temperature Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;130(3):565–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert F., Mäntele W., Kreutz W. Flash-induced kinetic infrared spectroscopy applied to biochemical systems. Biophys Struct Mech. 1980;6(2):139–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00535750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. O., Lugtenburg J., Mathies R. A. Determination of retinal chromophore structure in bacteriorhodopsin with resonance Raman spectroscopy. J Membr Biol. 1985;85(2):95–109. doi: 10.1007/BF01871263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



