Abstract
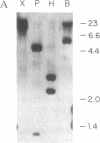
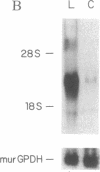
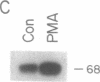
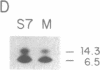
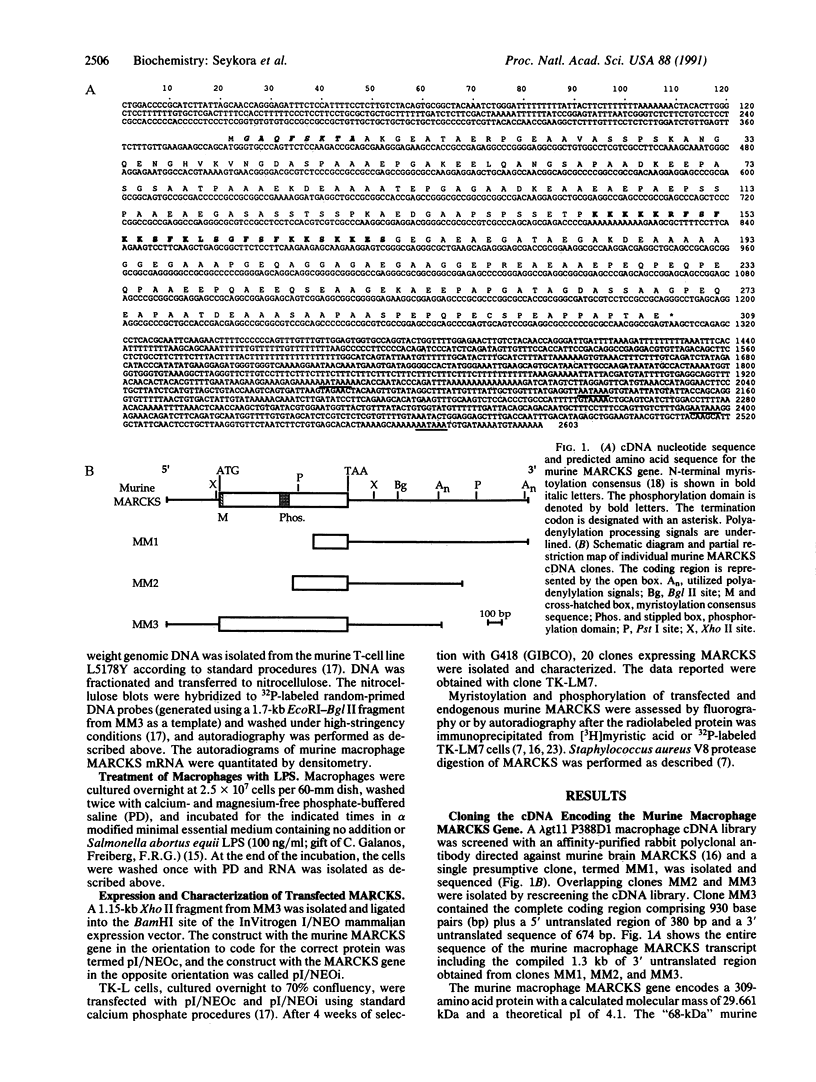
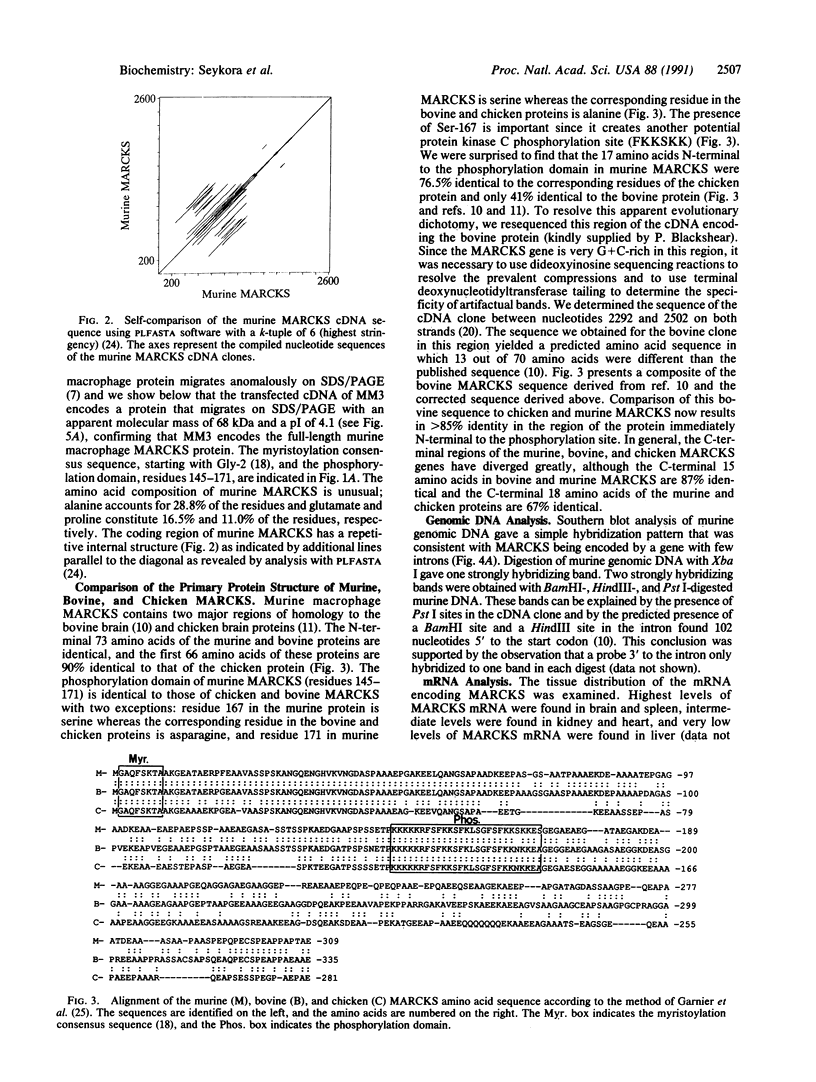
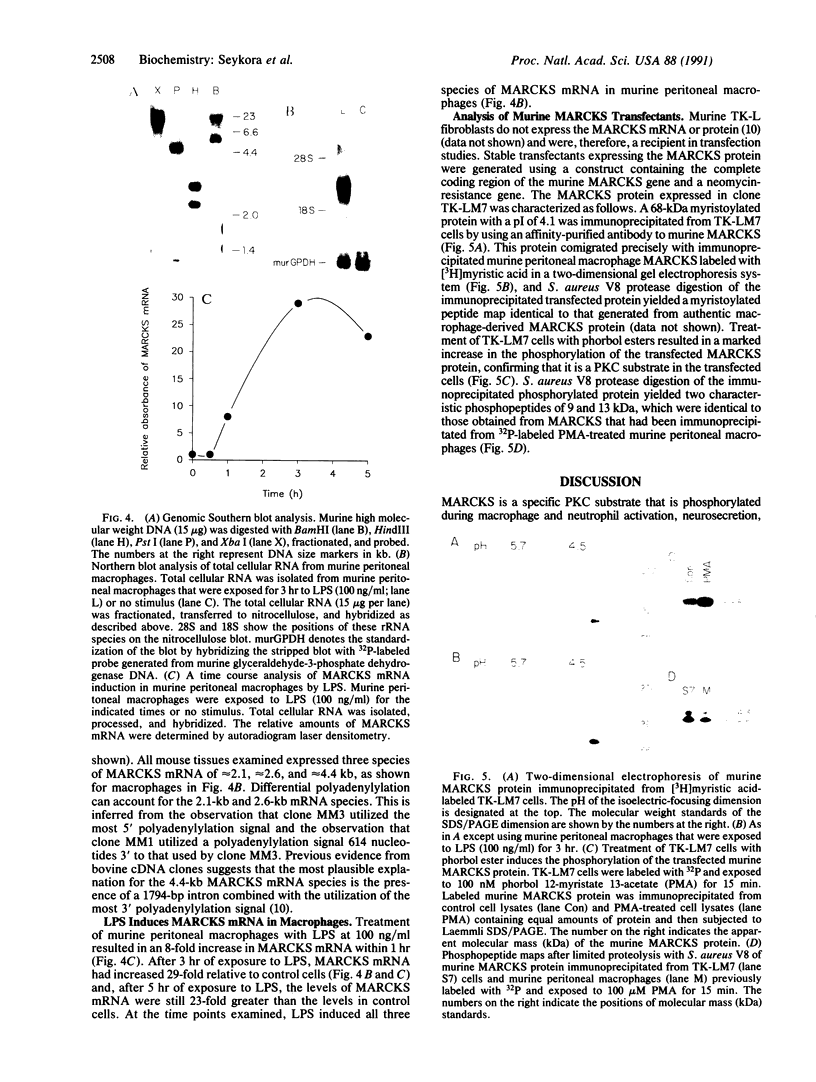
We have isolated and characterized a cDNA clone encoding the murine macrophage 68-kDa protein kinase C substrate, which is homologous to the 80- to 87-kDa protein identified by the acronym MARCKS (myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate). The murine MARCKS cDNA clone encodes an acidic protein of 309 amino acids with a calculated molecular weight of 29,661. Transfection of the murine MARCKS gene into TK-L fibroblasts produced a myristoylated protein kinase C substrate that migrated on SDS/PAGE with an apparent molecular mass of 68 kDa. Peptide mapping studies indicated that MARCKS produced by the transfected gene was indistinguishable from the endogenous murine macrophage protein. Comparison of the murine macrophage sequence with the previously published chicken and bovine brain sequences revealed two conserved domains: an N-terminal membrane-binding domain and a phosphorylation domain that also contains calmodulin and actin binding sites. In murine peritoneal macrophages, bacterial lipopolysaccharide increased MARCKS mRNA levels by greater than 30-fold. Multiple MARCKS transcripts were observed and could be accounted for by differential polyadenylylation and incomplete processing. Genomic Southern blot analysis suggested a single MARCKS gene per haploid genome.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderem A. A., Albert K. A., Keum M. M., Wang J. K., Greengard P., Cohn Z. A. Stimulus-dependent myristoylation of a major substrate for protein kinase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):362–364. doi: 10.1038/332362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aderem A. A., Cohen D. S., Wright S. D., Cohn Z. A. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides prime macrophages for enhanced release of arachidonic acid metabolites. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):165–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aderem A. A., Keum M. M., Pure E., Cohn Z. A. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides, phorbol myristate acetate, and zymosan induce the myristoylation of specific macrophage proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5817–5821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert K. A., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. The 87-kDa protein, a major specific substrate for protein kinase C: purification from bovine brain and characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Wen L., Glynn B. P., Witters L. A. Protein kinase C-stimulated phosphorylation in vitro of a Mr 80,000 protein phosphorylated in response to phorbol esters and growth factors in intact fibroblasts. Distinction from protein kinase C and prominence in brain. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1459–1469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farago A., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C in transmembrane signalling. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 1;268(2):350–354. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81284-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett T. W., Bartlett G. An effective method for eliminating "artifact banding" when sequencing double-stranded DNA templates. Biotechniques. 1990 Jul;9(1):46–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graff J. M., Gordon J. I., Blackshear P. J. Myristoylated and nonmyristoylated forms of a protein are phosphorylated by protein kinase C. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):503–506. doi: 10.1126/science.2814478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graff J. M., Stumpo D. J., Blackshear P. J. Molecular cloning, sequence, and expression of a cDNA encoding the chicken myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS). Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1903–1906. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-11-1903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graff J. M., Young T. N., Johnson J. D., Blackshear P. J. Phosphorylation-regulated calmodulin binding to a prominent cellular substrate for protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21818–21823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kligman D., Patel J. A protein modulator stimulates C kinase-dependent phosphorylation of a 90K substrate in synaptic membranes. J Neurochem. 1986 Jul;47(1):298–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb02862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlroy B. K., Walters J. D., Blackshear P. J., Johnson J. D. Phosphorylation-dependent binding of a synthetic MARCKS peptide to calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4959–4964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel J., Kligman D. Purification and characterization of an Mr 87,000 protein kinase C substrate from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16686–16691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prockop D. J. Mutations that alter the primary structure of type I collagen. The perils of a system for generating large structures by the principle of nucleated growth. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15349–15352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen A., Keenan K. F., Thelen M., Nairn A. C., Aderem A. Activation of protein kinase C results in the displacement of its myristoylated, alanine-rich substrate from punctate structures in macrophage filopodia. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1211–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen A., Nairn A. C., Greengard P., Cohn Z. A., Aderem A. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide regulates the phosphorylation of the 68K protein kinase C substrate in macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9118–9121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Rodriguez-Pena M., Smith K. A. Phorbol esters, phospholipase C, and growth factors rapidly stimulate the phosphorylation of a Mr 80,000 protein in intact quiescent 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7244–7248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpo D. J., Graff J. M., Albert K. A., Greengard P., Blackshear P. J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and expression of a cDNA encoding the "80- to 87-kDa" myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate: a major cellular substrate for protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4012–4016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpo D. J., Graff J. M., Albert K. A., Greengard P., Blackshear P. J. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA for the bovine myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3987–3988. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M., Rosen A., Nairn A. C., Aderem A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha modifies agonist-dependent responses in human neutrophils by inducing the synthesis and myristoylation of a specific protein kinase C substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5603–5607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D. A., Gordon J. I., Adams S. P., Glaser L. The biology and enzymology of eukaryotic protein acylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:69–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. C., Walaas S. I., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Calcium/phospholipid regulates phosphorylation of a Mr "87k" substrate protein in brain synaptosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5249–5253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]