Abstract
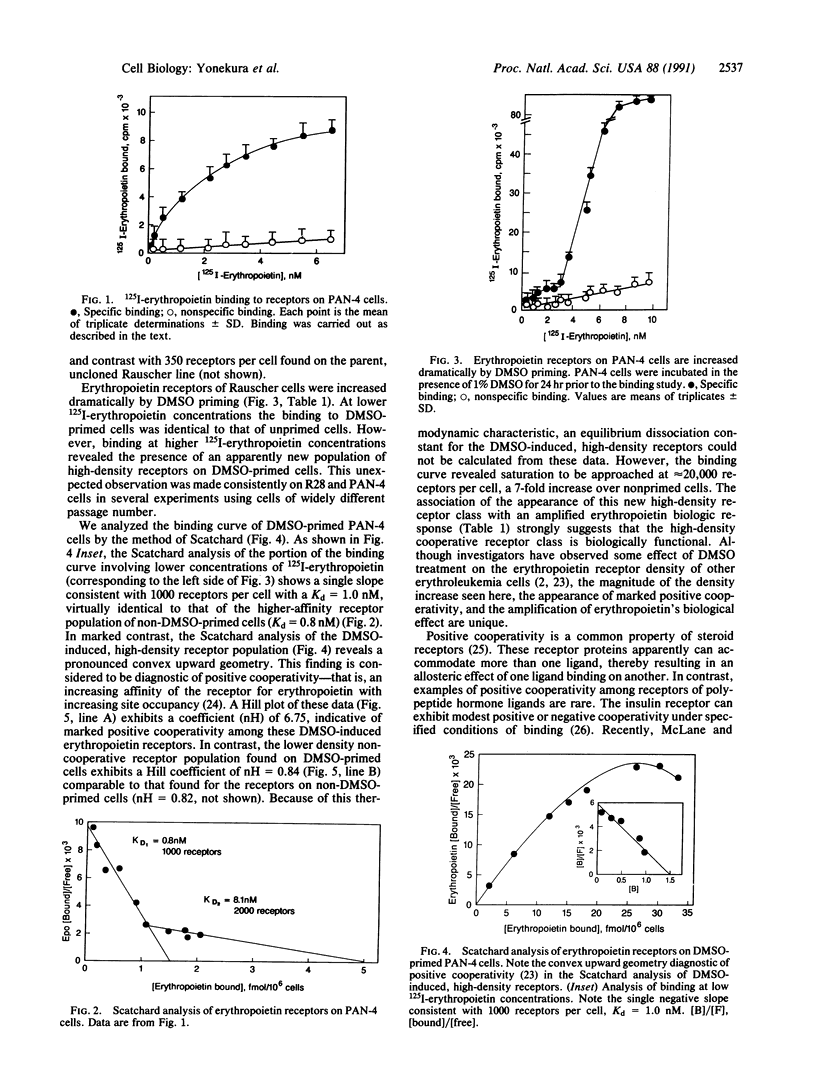
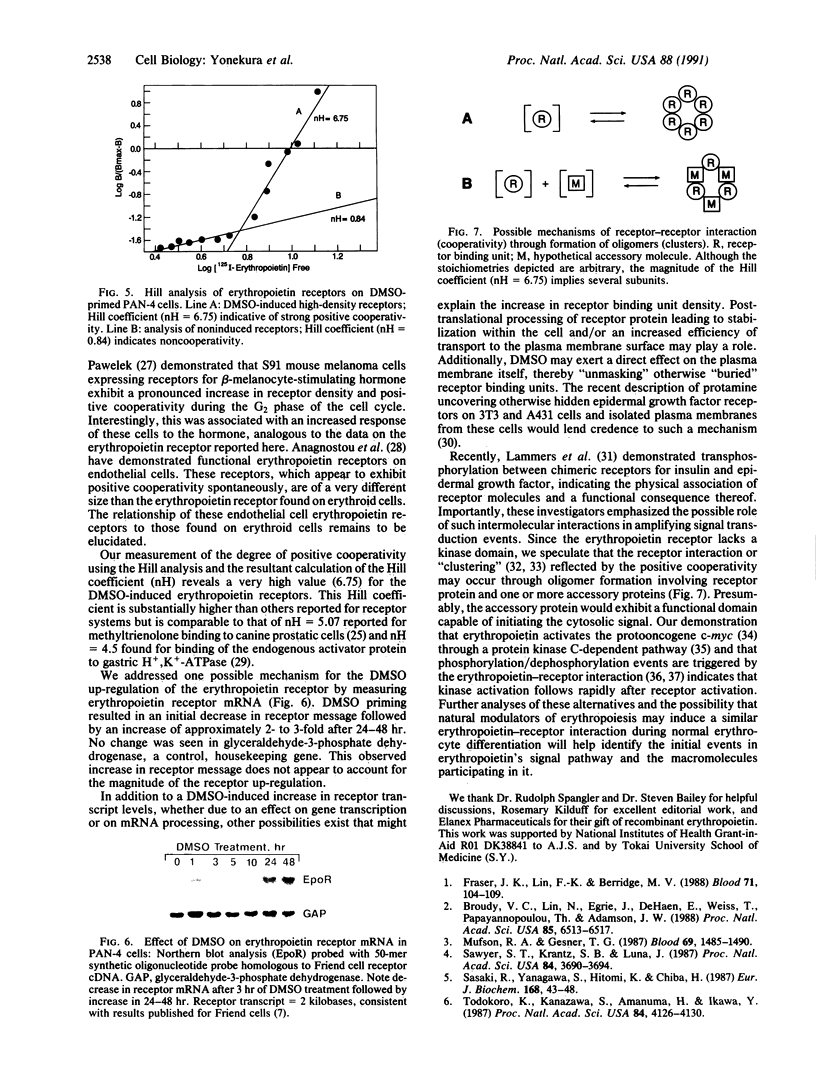
Erythropoietin triggers the differentiation of erythrocyte progenitors by binding to receptors on their plasma membrane. We report here that pretreatment of erythropoietin-responsive murine erythroleukemia cells with chemical inducers resulted in a striking increase in erythropoietin-specific hemoglobinization. This amplification of the erythropoietin biologic response was accompanied by the induction of a new population of high-density receptors (approximately 20,000 per cell) exhibiting marked positive cooperativity. Erythropoietin binding to new receptors displayed a convex upward Scatchard plot and a Hill coefficient (nH) of 6.75. Measurement of erythropoietin receptor mRNA demonstrated an initial decrease in receptor transcript followed by an approximately 2- to 3-fold increase after 24-48 hr. This increase in receptor message does not appear to account for the magnitude of the receptor up-regulation by dimethyl sulfoxide. We propose that this positive cooperativity reflects the interaction (clustering) of receptors, presumably through the formation of homooligomers or heterooligomers, and that this receptor interaction may amplify the erythropoietin signal transduction pathway.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostou A., Lee E. S., Kessimian N., Levinson R., Steiner M. Erythropoietin has a mitogenic and positive chemotactic effect on endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5978–5982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandopadhyay S., Das P. K., Wright M. V., Nandi J., Bhattacharyyay D., Ray T. K. Characteristics of a pure endogenous activator of the gastric H+,K+-ATPase system. Evaluation of the role as a possible intracellular regulator. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5664–5670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broudy V. C., Lin N., Egrie J., de Haën C., Weiss T., Papayannopoulou T., Adamson J. W. Identification of the receptor for erythropoietin on human and murine erythroleukemia cells and modulation by phorbol ester and dimethyl sulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6513–6517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chern Y., Spangler R., Choi H. S., Sytkowski A. J. Erythropoietin activates the receptor in both Rauscher and Friend murine erythroleukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2009–2012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chern Y., Yonekura S., Sytkowski A. J. Potentiation of the erythropoietin response by dimethyl sulfoxide priming of erythroleukemia cells: evidence for interaction of two signaling pathways. Blood. 1990 Dec 1;76(11):2204–2209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi H. S., Bailey S. C., Donahue K. A., Vanasse G. J., Sytkowski A. J. Purification and characterization of the erythropoietin-sensitive membrane phosphoprotein, pp43. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):4143–4148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi H. S., Wojchowski D. M., Sytkowski A. J. Erythropoietin rapidly alters phosphorylation of pp43, an erythroid membrane protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):2933–2936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A. D., Lodish H. F., Wong G. G. Expression cloning of the murine erythropoietin receptor. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90965-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. K., Lin F. K., Berridge M. V. Expression and modulation of specific, high affinity binding sites for erythropoietin on the human erythroleukemic cell line K562. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):104–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend C., Scher W., Holland J. G., Sato T. Hemoglobin synthesis in murine virus-induced leukemic cells in vitro: stimulation of erythroid differentiation by dimethyl sulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):378–382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S. Insulin receptors: binding kinetics and structure-function relationship of insulin. Physiol Rev. 1984 Oct;64(4):1321–1378. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.4.1321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal G. A simple microassay for erythropoietin based on 3H-thymidine incorporation into spleen cells from phenylhydrazine treated mice. Exp Hematol. 1983 Aug;11(7):649–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers R., Van Obberghen E., Ballotti R., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Transphosphorylation as a possible mechanism for insulin and epidermal growth factor receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16886–16890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lokeshwar V. B., Huang S. S., Huang J. S. Protamine enhances epidermal growth factor (EGF)-stimulated mitogenesis by increasing cell surface EGF receptor number. Implications for existence of cryptic EGF receptors. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19318–19326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffery P. J., Fraser J. K., Lin F. K., Berridge M. V. Subunit structure of the erythropoietin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10507–10512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLane J. A., Pawelek J. M. Receptors for B-melanocyte-stimulating hormone exhibit positive cooperativity in synchronized melanoma cells. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3743–3747. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson R. A., Gesner T. G. Binding and internalization of recombinant human erythropoietin in murine erythroid precursor cells. Blood. 1987 May;69(5):1485–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. S., Berkner K. L., Lebo R. V., Adamson J. W. Human erythropoietin gene: high level expression in stably transfected mammalian cells and chromosome localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6465–6469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki R., Yanagawa S., Hitomi K., Chiba H. Characterization of erythropoietin receptor of murine erythroid cells. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Oct 1;168(1):43–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer S. T., Krantz S. B., Luna J. Identification of the receptor for erythropoietin by cross-linking to Friend virus-infected erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3690–3694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer S. T. The two proteins of the erythropoietin receptor are structurally similar. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13343–13347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spangler R., Bailey S. C., Sytkowski A. J. Erythropoietin increases c-myc mRNA by a protein kinase C-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):681–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sytkowski A. J., Vogel Z., Nirenberg M. W. Development of acetylcholine receptor clusters on cultured muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):270–274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todokoro K., Kanazawa S., Amanuma H., Ikawa Y. Specific binding of erythropoietin to its receptor on responsive mouse erythroleukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4126–4130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo A., Fukamachi H., Saito T., Kasuga M., Urabe A., Takaku F. Induction of the receptor for erythropoietin in murine erythroleukemia cells after dimethyl sulfoxide treatment. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1818–1822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte G., Chapdelaine A., Chevalier S. Multiple binding components for methyltrienolone in canine prostatic epithelial cells. J Steroid Biochem. 1988 Dec;31(6):955–962. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(88)90338-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Sytkowski A. J., Nirenberg M. W. Acetylcholine receptors of muscle grown in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Both N. J., Vermey M., van't Hull E., Klootwijk-van-Dijke E., van Griensven L. J., Mol J. N., Stoof T. J. A new erythroid cell line induced by Rauscher murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):626–628. doi: 10.1038/272626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




