Abstract
Background
Despite their versatile functions in multimeric protein complexes, in the modification of enzymatic activities, intercellular communication or regulatory processes, proteins shorter than 80 amino acids (μ-proteins) are a systematically underestimated class of gene products in bacteria. Photosynthetic cyanobacteria provide a paradigm for small protein functions due to extensive work on the photosynthetic apparatus that led to the functional characterization of 19 small proteins of less than 50 amino acids. In analogy, previously unstudied small ORFs with similar degrees of conservation might encode small proteins of high relevance also in other functional contexts.
Results
Here we used comparative transcriptomic information available for two model cyanobacteria, Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and Synechocystis sp. PCC 6714 for the prediction of small ORFs. We found 293 transcriptional units containing candidate small ORFs ≤80 codons in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, also including the known mRNAs encoding small proteins of the photosynthetic apparatus. From these transcriptional units, 146 are shared between the two strains, 42 are shared with the higher plant Arabidopsis thaliana and 25 with E. coli. To verify the existence of the respective μ-proteins in vivo, we selected five genes as examples to which a FLAG tag sequence was added and re-introduced them into Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. These were the previously annotated gene ssr1169, two newly defined genes norf1 and norf4, as well as nsiR6 (nitrogen stress-induced RNA 6) and hliR1(high light-inducible RNA 1) , which originally were considered non-coding. Upon activation of expression via the Cu2+.responsive petE promoter or from the native promoters, all five proteins were detected in Western blot experiments.
Conclusions
The distribution and conservation of these five genes as well as their regulation of expression and the physico-chemical properties of the encoded proteins underline the likely great bandwidth of small protein functions in bacteria and makes them attractive candidates for functional studies.
Keywords: Cyanobacteria, Nitrogen deprivation, Photosynthesis, Synechocystis, Small proteins
Background
Proteins with less than 80 amino acids in prokaryotes or 100 amino acids in eukaryotes are defined as short proteins (μ-proteins). During standard genome annotation these short protein-coding genes are frequently neglected and proteomics-based analyses fail to detect this class of peptides routinely. As a result, μ-protein-coding genes are a systematically underestimated class of gene products.
In strong contrast is the finding that small ORFs constitute the most frequent essential genomic component in bacteria, even more than conventional ORFs [1]. Indeed, the functional characterization of selected examples of μ-proteins has revealed their critical involvement in processes such as quorum sensing or interspecies communication [2], regulatory functions [3–6] and in the formation of multi-subunit protein complexes. An increasing number of μ-proteins is being discovered also in eukaryotes [7–10], and archaea [11], indicating their ubiquity in all three domains of life. Nevertheless, the likely diverse functions of short proteins are largely unknown, even for simple unicellular bacteria.
Photosynthetic cyanobacteria provide a paradigm for small protein functions due to extensive work on the photosynthetic apparatus that led to the functional characterization of 19 μ-proteins of less than 50 amino acids, that play a role in photosystem II (genes psbM, psbT (ycf8), psbI, psbL, psbJ, psbY, psbX, psb30 (ycf12), psbN, psbF, psbK [12, 13]), in photosystem I (psaM, psaJ, psaI [14]), photosynthetic electron transport (Cytb 6 f complex; petL, petN, petM, petG [15–17]), or have accessory functions (hliC (scpB) [18]). The shortest annotated protein conserved in cyanobacteria is with 29 amino acids the cytochrome b 6 f complex subunit VIII, encoded by petN [19].
Several cyanobacterial model species have been studied by transcriptomics [20–28] and proteomics [29–31] approaches but there are no reports specifically targeting μ-proteins. Based on extensive comparative transcriptome and genome information we used the model cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 (Synechocystis 6803) and the closely related strain Synechocystis sp. PCC 6714 (Synechocystis 6714) [20–22, 32] for the prediction of possible μ-ORFs. We found 293 transcriptional units (TU) containing candidate small ORFs ≤80 codons in Synechocystis 6803, including all known mRNAs encoding small proteins of the photosynthetic apparatus.
We chose 5 examples from Synechocystis 6803 for experimental analysis. These were norf1 and norf4 (for novel orf 1 and 4, [22]), nsiR6 and hliR1 (for nitrogen stress-induced RNA 6 and high light inducible RNA 1), the latter two transcripts originally considered non-coding [33] as well as the short gene ssr1169, which was predicted as protein-coding in the current version of the genome sequence [NCBI reference NC_000911]. All five proteins could be detected after FLAG tagging in vivo. Their modes of regulation, conservation and physico-chemical properties make these five μ-proteins interesting candidates for functional studies.
Methods
Strains and growth conditions
Synechocystis 6803, substrain “PCC-M” [34], served as WT and was grown in Cu2+-free, TES-buffered (20 mM, pH 8.0) liquid BG11 medium [35] with gentle agitation or on agar-solidified (0.9% [w/v] Kobe I agar, Roth, Germany) BG11 supplemented with 0.3% (w/v) sodium thiosulfate at 30 °C under continuous illumination with white light of ~40 μmol photons m−2 s−1. To induce expression of FLAG - tagged μ-proteins from the Cu2+-responsive petE promoter [36] 2 μM CuSO4 was added to exponentially growing cells. Different environmental conditions were applied for induction of gene expression under control of native promoters: (i) high light, 300 μmol photons m−2 s−1; (ii) dark, flasks wrapped with aluminium foil; (iii) nitrogen deficiency, cells were pelleted by centrifugation, washed once and resuspended in NO3 −-free BG11. Samples for protein extraction were taken just before and 6 h (Norf1, HliR1) or 24 h (NsiR6, Norf4) after induction of gene expression. Ssr1169 was expected to be most expressed in exponential growth phase, hence samples were taken from exponentially growing cells at two consecutive days. Synechocystis 6803 strain pUR-PpetJ-3xFlag-sfGFP [37] was used as positive control for the detection of FLAG-tagged proteins by Western blots. E. coli strains TOP10F’ and J53/RP4 were used for generating Synechocystis 6803 mutant strains by conjugation. In liquid BG11 medium 5 μg ml−1 gentamicin or 50 μg ml−1 kanamycin and 5 μg ml−1 gentamicin were used to maintain recombinant strains (see below).
For examination of gene expression by Northern blot analysis, exponentially growing WT cells were transferred to the different environmental conditions described above. Cultivation under high light was followed by a shift back to standard light conditions (40 μmol photons m−2 s−1)). Cultures grown in the dark as well as nitrogen deprived cultures were additionally aerated with ambient air through a glass tube and a sterile filter for constant and fast growth.
Computational methods
Small ORFs and their orthologs were identified and annotated in Synechocystis 6803 and 6714 in three steps.
BlastN searches returning hits with E values ≤1e−2 were performed against the NCBI nt database [38] for all intergenic regions covered by TUs [20, 21]. From the blast results, multiple alignments were created with ClustalW [39] and analyzed for their coding potential with RNAcode [40]. The significant (p ≤0.05) small ORF candidates were manually curated.
To annotate candidate small ORFs, blastP queries with E values ≤1e−2 were done against the NCBI nr database [38].
Orthologs of existing and newly detected small ORFs were identified in Synechocystis 6803 and 6714 via a reciprocal best hit approach using blastP with a minimum E value ≤1e−2 and allowing a difference in length of ≤20% and a maximum length of 80 amino acids in both strains.
Genes of small ORFs that were covered by a predicted TU were considered to be expressed. Transmembrane helices were predicted with TMHMM Server v. 2.0 [41].
Generation of mutant strains
Gene constructs for ectopic expression of FLAG - tagged Norf1 under control of the petE promoter or the native promoter were generated via gene synthesis (Eurofins). The constructs consisted of the upstream sequence of petE (PpetE = −273 to +100 referring to the first transcribed nucleotide as +1) or the upstream sequence of norf1 (Pnorf1 = −328 to +143), the norf1 coding sequence omitting the stop codon (+144 to +287, corresponding to genome positions 298829 to 298972), a 3xFLAG coding tag (sequence: ATGGATTATAAAGATCATGATGGCGATTATAAAGATCATGATATTGATTATAAAGATGATGATGATAAA) followed by a stop codon (TAG), the norf1 3′UTR (+291 to +425) and the bacteriophage lambda oop terminator. The obtained PpetE::norf1::3xFLAG::Toop and Pnorf1::norf1::3xFLAG::Toop constructs were digested with XhoI and HindIII and introduced into self-replicating vector pVZ322 [42]. The resulting plasmids were transferred into Synechocystis 6803 WT via triparental mating with E. coli J53/RP4 and TOP10F’ [43]. These two recombinant strains were selected on BG11 agar containing 10 μg ml−1 gentamicin.
To establish ectopic expression of FLAG - tagged NsiR6, HliR1, Ssr1169 and Norf4, the respective genomic sequences (nsiR6 729671 to 729868, hliR1 1606868 to1606978, ssr1169 3084421 to 3084582, norf4 2425146 to 2425238) were amplified using the primer pairs nsiR6_fw/nsiR6_rev, PpetE::hliR1_fw/3xFlag_hliR1_rev, PpetE::ssr1169_fw/3xFlag_ssr1169_rev and PpetE::Norf4_fw/3xFlag_Norf4_rev. All oligonucleotides used in this study are listed in Table 1. The petE promoter was amplified separately for each construct to generate overlaps with the particular μ-ORFs using the primer pUC19-XbaI_PpetE_fw in different combinations with nsiR6::PpetE_rev, hliR1::PpetE_rev, ssr1169::PpetE_rev or Norf4::PpetE_rev. The 3′ segments consisting of the sequence encoding the 3xFLAG tag (+ stop codon TAG), the 3′UTR of the norf1 mRNA and the oop terminator were amplified from the plasmid obtained via gene synthesis described above using the primer 3xFlag_PstI-pUC19_rev in combination with nsiR6_3xFlag_fw, hliR1_3xFlag_fw, ssr1169_3xFlag_fw or Norf4_3xFlag_fw, respectively. Fragments belonging together were combined by Gibson Assembly® Master Mix (New England Biolabs) according to the manufacturer’s instructions utilizing XbaI and PstI digested pUC19 as vector backbone. For expression of the small proteins under control of their native promoters the obtained plasmids served as templates for amplifying corresponding coding sequences associated with the 3′ segment described above using the primer 3xFlag_PstI-pUC19_rev in combination with CDSnsiR6::PnsiR6_fw, CDShliR1::PhliR1_fw, CDSnorf4::Pnorf4 or CDSssr1169::Pssr1169_fw. Upstream sequences of nsiR6, hliR1, norf4 and ssr1169 considered as promoter sequences (PnsiR6 = 729258 to 729670, PhliR1 = 1606503 to 1606867, Pnorf4 = 2424768 to 2425145, Pssr1169 3084025 to 3084420) were amplified from Synechocystis 6803 genomic DNA with the primer pairs pUC19::PnsiR6_fw/PnsiR6::CDSnsiR6_rev, pUC19::PhliR1_fw/PhliR1::CDShliR1_rev, pUC19::Pnorf4_fw/Pnorf4::CDSnorf4_rev or pUC19::Pssr1169_fw/Pssr1169::CDSssr1169_rev. Related fragments were combined by Gibson Assembly® Master Mix as described above. All resulting cassettes were released by restriction, introduced into pVZ322 [42] and transferred into Synechocystis 6803 WT via triparental mating. Additionally, the empty vector pVZ322 was introduced into the wild type to create a control strain. The recombinant strains were selected on BG11 agar containing 10 μg ml−1 gentamicin and 50 μg ml−1 kanamycin.
Table 1.
List of oligonucleotides
| Name of Oligonucleotide | Sequence (in 5′ – 3′ direction) | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Probe_norf1_fw | GTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGACCATCGACTATTCTTCAGTACTGTTTAC | Amplification of probe template norf1 (168 nt) for in vitro-transcription (T7 promoter is underlined) |
| Probe_norf1_rev | TTGAGATGCTACAGGACCTTATGC | |
| Pnorf1_fw | taccggtGCCTAGGGGATACCTCTCCCC | Amplification of putative norf1 promoter for ligation into pILA reporter plasmid |
| Pnorf1_rev | tggccggcCTCCGTCCCAATGGGGGAAAC | |
| nsiR6_probe_fw | GTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGATTACCGATCGCCGCTTCATC | Amplification of probe template nsiR6 (166 nt) for in vitro-transcription (T7 promoter is underlined) |
| nsiR6_probe_rev | TGTGTGGCGTCACCATTGAAAATG | |
| hliR1_probe_fw | GTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGACTCGGGAAGATTAAGACTGGTTTTG | Amplification of probe template hliR1 (135 nt) for in vitro-transcription (T7 promoter is underlined) |
| hliR1_probe_rev | ATGTCTAATTTGATTGCTGTTGCTTTC | |
| norf4_probe_fw | GTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGACCCCCTTTAGCAAAACTACCCATC | Amplification of probe template norf4 (116 nt) for in vitro-transcription (T7 promoter is underlined) |
| norf4_probe_rev | ATGACCGCCGATCAACTGTTG | |
| nsiR6_fw | gccaagaagtATGAGTGTTTTCCCCGCAGA | Amplification of nsiR6 generating overlaps with PpetE and 3xFLAG::3′UTR norf1::Toop |
| nsiR6_rev | tataatccatGTCGTAATAATCCCGGCTGG | |
| PpetE::hliR1_fw | gccaagaagtATGTCTAATTTGATTGCTGTTG | Amplification of hliR1 generating overlaps with PpetE and 3xFLAG::3′UTR norf1::Toop |
| 3xFlag_hliR1_rev | tataatccatCTCGGGAAGATTAAGACTGG | |
| PpetE::ssr1169_fw | gccaagaagtATGGATATTGTTAAGATCATTTGTGCGATTC | Amplification of ssr1169 generating overlaps with PpetE and 3xFLAG::3′UTR norf1::Toop |
| 3xFlag_ssr1169_rev | tataatccatACGTTCCCTGGCAATGACCC | |
| PpetE::Norf4_fw | gccaagaagtATGACCGCCGATCAACTGTT | Amplification of n orf4 generating overlaps with PpetE and 3xFLAG::3′UTR n orf1::Toop |
| 3xFlag_Norf4_rev | tataatccatACCCCCTTTAGCAAAACTAC | |
| pUC19-XbaI_PpetE_fw | gctcggtacccggggatcctctagaCTGGGCCTACTGGGCTATTC | Amplification of PpetE introducing XbaI site (underlined) + creating overlaps with pUC19 and nsiR1, hliR 1, ssr1169 or n orf4 |
| nsiR6::PpetE_rev | aaacactcatACTTCTTGGCGATTGTATCTATAGG | |
| hliR1::PpetE_rev | aattagacatACTTCTTGGCGATTGTATCTATAGG | |
| ssr1169::PpetE_rev | caatatccatACTTCTTGGCGATTGTATCTATAGG | |
| Norf4::PpetE_rev | gatcggcggtcatACTTCTTGGCGATTGTATCTATAGG | |
| 3xFlag_PstI-pUC19_rev | gccaagcttgcatgcctgcagAATAAAAAACGCCCGGCGGC | Amplification of 3xFLAG::3′UTR norf1::Toop introducing PstI site (underlined) + creating overlaps with pUC19 and nsiR1, hlirR, ssr1169 or norf4 or amplification of particular CDS associated with 3xFLAG__3′UTR norf1::Toop introducing PstI site (underlined) + creating overlaps with pUC19 and respective promoter sequence |
| nsiR6_3xFlag_fw | ttattacgacATGGATTATAAAGATCATGATGGCGATTATAAAG | |
| hliR1_3xFlag_fw | tcttcccgagATGGATTATAAAGATCATGATGGCGATTATAAAG | |
| ssr1169_3xFlag_fw | cagggaacgtATGGATTATAAAGATCATGATGGCGATTATAAAG | |
| Norf4_3xFlag_fw | taaagggggtATGGATTATAAAGATCATGATGGCGATTATAAAG | |
| CDSnsiR6::PnsiR6_fw | ataaatactcATGAGTGTTTTCCCCGCAGAAAC | |
| CDShliR1::PhliR1_fw | aaattaactaaATGTCTAATTTGATTGCTGTTGCTTTCTG | |
| CDSNorf4::PNorf4_fw | aatttttaccATGACCGCCGATCAACTGTTG | |
| CDSssr1169::Pssr1169_fw | gagtgaactaATGGATATTGTTAAGATCATTTGTGCGATTC | |
| pUC19::PnsiR6_fw | gctcggtacccggggatcctctagaATCGCCGTATTACACCTCTG | Amplification of PnsiR6 introducing XbaI site (underlined) + generating overlaps with pUC19 and nsiR6. |
| PnsiR6::CDSnsiR6_rev | aaacactcatGAGTATTTATTCCTAGTGAATGAATTAGAAG | |
| pUC19::PhliR1_fw | gctcggtacccggggatcctctagaGGAGTTTACAGCGAGATTTG | Amplification of PhliR1 introducing XbaI site (underlined) + generating overlaps with pUC19 and hliR1. |
| PhliR::CDShliR1_rev | aattagacatTTAGTTAATTTTTGTAACGGGAG | |
| pUC19::PNorf4_fw | gctcggtacccggggatcctctagaAGGTGATGATTATGAGCCGTC | Amplification of Pnorf4 introducing XbaI site (underlined) + generating overlaps with pUC19 and norf4. |
| PNorf4::CDSNorf4_rev | gatcggcggtcatGGTAAAAATTCCACTAATTCAAAAAAC | |
| pUC19::Pssr1169_fw | gctcggtacccggggatcctctagaCGAGTAGCCAGCCAAAGCAG | Amplification of Pssr1169 introducing XbaI site (underlined) + generating overlaps with pUC19 and ssr1169. |
| Pssr1169::CDSssr1169_rev | caatatccatTAGTTCACTCCAATATGTCGGGATAATTAG |
RNA extraction and analysis
Synechocystis 6803 cells were harvested by vacuum filtration on hydrophilic polyethersulfone filters (Pall Supor®-800, 0.8 μm), immediately immersed in 1 ml PGTX [44] and frozen in liquid nitrogen. RNA extraction was performed by 15 min incubation at 65 °C followed by chloroform washing and isopropanol precipitation as previously described [45]. Northern hybridization with 32P-labelled, single-stranded transcript probes was carried out as described [46]. Oligonucleotide sequences for PCR amplification of probe templates used for in vitro transcription are listed in Table 1.
Protein purification and immunodetection
Cells for protein extraction were collected by centrifugation (4000 × g, 10 min, 4 °C), resuspended in PBS buffer (137 mM sodium chloride, 2.7 mM potassium chloride, 10 mM disodium phosphate, 1.8 mM potassium dihydrogen phosphate, pH 7.4) in the presence of protease inhibitor cocktail (cOmplete, Roche) and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen. Cells were mechanically disrupted by using glass beads (diameter 0.1–0.25 mm) and a Precellys® 24 homogenizer (Bertin Technologies) at 6000 rpm and 4 °C applying six cycles of 3 × 10 s homogenization. Glass beads were removed by centrifugation (1000 × g, 1 min, 4 °C). To solubilize membrane proteins, samples were heated for 30 min at 50 °C with 2% SDS (w/v) followed by determination of the protein concentration using Direct Detect Spectrometer (Merck Millipore).
Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE on 15% (w/v) polyacrylamide gels and stained with GelCode® Blue Stain Reagent (Thermo Scientific). PageRuler™ Prestained Protein Ladder (10–170 kDa, Fermentas) was used as molecular weight marker.
For immunoblot analysis, separated proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes (Hybond™-ECL, GE Healthcare). Membranes were blocked over night at 4 °C with 5% low fat milk powder in TBS-T and subsequently probed with monoclonal ANTI-FLAG® M2-Peroxidase (HRP) antibody raised in mouse (Sigma-Aldrich) in TBS-T for 1 h at room temperature in the dark. All washing steps were performed with gentle agitation in TBS-T (20 mM Tris pH 7.6, 150 mM NaCl, 0.1% (v/v) Tween-20) at room temperature. Signals were detected with ECL™ start Western blotting detection reagent (GE Healthcare) on a chemiluminescence imager system (Fusion SL, Vilber Lourmat) and subsequently visualized using FUSION-CAP (Vilber Lourmat) and Quantity One software (BIO-RAD).
Reporter gene assays
To measure promoter activity as a function of bioluminescence the putative norf1 promoter sequence and its 5′UTR (−328 to +137, TSS at +1) was fused to promoterless luxAB reporter genes by PCR, followed by cloning into the promoter probe vector pILA as described [47]. The resulting pILA derivative was used for transformation of a Synechocystis 6803 strain expressing the luxCDE genes encoding enzymes for the synthesis of decanal, the luciferase substrate, under control of the strong promoter of the ncRNA Yfr2a [48].
Cells were grown in the presence of 10 mM glucose to provide energy for the luciferase reaction also in darkness. Bioluminescence was measured in vivo at different time points after inducing dark conditions as described [47].
Results
Comparative transcriptomics for the identification of μ-proteins in Synechocystis
The extensive comparative transcriptome and genome information for the model cyanobacterium Synechocystis 6803 [21, 22] and the closely related strain Synechocystis 6714 [20, 32] was utilized for the prediction of possible μ-ORFs. In our previous studies [20, 21] transcriptional units (TUs) had been defined, combining information on the transcriptional start sites, the lengths of transcribed UTRs, operons, coding and non-coding regions.
Here we judged all possible non-coding transcripts by the program RNAcode [40] for their protein-coding potential. RNAcode detects protein-coding regions in any given sequence on the basis of multiple sequence alignments and the evolutionary signatures that are associated with a coding sequence [40]. After combination with the pre-existing annotation, this analysis led to the prediction of 293 potential small proteins with a maximum of 80 amino acids in Synechocystis 6803 and possibly 773 in Synechocystis 6714 (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
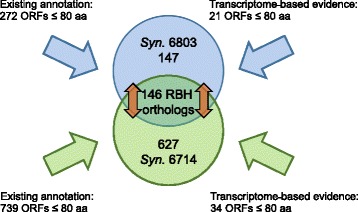
Scheme of computational prediction of small ORFs in cyanobacteria. Small ORFs were detected based on the transcriptome information for expressed intergenic regions [20–22] and their coding potential evaluated with RNAcode [40]. This information was merged with the pre-existing annotation [32]. Orthologs between the two small ORF populations were detected when they were identified as reciprocal best hits (RBH) by blastP with e ≤ 1e−2
The resulting sets of candidate μ-proteins were compared against the predicted proteome of the respective other Synechocystis strain, against E. coli and the higher plant Arabidopsis thaliana as reference organisms for proteins possibly conserved among bacteria or among photosynthetic organisms. This procedure led to the identification of 146 μ-proteins shared between the two Synechocystis strains, as well as 42 and 29 μ-proteins which are shared between Synechocystis 6803 and A. thaliana or E. coli, respectively. Interestingly, we found the 42 proteins shared with higher plants to be identical in both Synechocystis strains. In contrast to observations in other bacteria, a relatively high number of the predicted proteins in the smallest fraction (≤50) had assigned functions (e.g., in photosynthesis) and a matching protein in the higher plant Arabidopsis thaliana or in E. coli (Table 2).
Table 2.
Predicted and previously annotated proteins ≤50 amino acids in Synechocystis 6803
| Start | End | S | L | Locus_tag | Gene | Product | 6714 | A. th. | E. coli |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 608828 | 608748 | - | 26 | Chr_ORF_4 | NA | Hypothetical protein | N | N | N |
| 1840846 | 1840926 | + | 26 | Chr_ORF_10 | NA | Hypothetical protein | Y | N | N |
| 160004 | 160093 | - | 29 | sml0004 | petN | Cytochrome b 6 f complex subunit VIII | Y | Y | N |
| 586617 | 586525 | - | 30 | Chr_ORF_3 | NA | Hypothetical protein | Y | N | N |
| 2414584 | 2414679 | + | 31 | smr0001 | psbT, ycf8 | Photosystem II PsbT protein | Y | Y | N |
| 467201 | 467296 | + | 31 | smr0005 | psaM | Photosystem I subunit XII | Y | N | N |
| 1148230 | 1148325 | - | 31 | Norf4 | norf4 | Norf4 | Y | N | N |
| 1643502 | 1643600 | - | 32 | ssl3803 | petL | Cytochrome b 6 f complex subunit PetL | Y | N | N |
| 3097275 | 3097379 | + | 34 | smr0002 | NA | Transposase, fragment | Y | N | N |
| 146724 | 146831 | - | 35 | sml0003 | psbM | Photosystem II reaction center M protein | Y | Y | N |
| 468997 | 468887 | - | 36 | Chr_ORF_2 | NA | Hypothetical protein | Y | N | N |
| 3118192 | 3118302 | + | 36 | smr0003 | petM | Cytochrome b 6 f complex subunit PetM | Y | N | N |
| 1606868 | 1606978 | + | 37 | hliR1 | hliR1 | HliR1 | Y | N | N |
| 473802 | 473915 | - | 37 | sml0009 | NA | VapC fragment | Y | N | Y |
| 32865 | 32978 | - | 37 | ssl5031 | NA | NA | Y | N | N |
| 831101 | 831217 | - | 38 | sml0006 | rpl36 | 50S ribosomal protein L36 | Y | Y | Y| |
| 1823570 | 1823686 | + | 38 | smr0010 | petG | Cytochrome b 6 f complex subunit 5 | Y | Y | N |
| 2350140 | 2350256 | - | 38 | sml0001 | psbI | Photosystem II reaction center PsbI protein | Y | Y | N |
| 571084 | 571203 | + | 39 | smr0007 | psbL | Photosystem II PsbL protein | Y | Y | N |
| 571236 | 571355 | + | 39 | smr0008 | psbJ | Photosystem II PsbJ protein | Y | Y | N |
| 1268189 | 1268308 | - | 39 | sml0007 | psbY | Photosystem II protein Y | Y | N | N |
| 2613481 | 2613600 | - | 39 | sml0002 | psbX | Photosystem II PsbX protein | Y | N | N |
| 2816991 | 2817110 | - | 39 | sgl0001 | NA | Hypothetical protein | Y | N | N |
| 3140045 | 3140164 | - | 39 | sll0047 | ycf12 | Psb30, YCF12 | Y | N | N |
| 1687326 | 1687448 | - | 40 | sml0008 | psaJ | Photosystem I subunit IX | Y | Y | N |
| 3458023 | 3458145 | + | 40 | smr0004 | psaI | Photosystem I subunit VIII | Y | Y | N |
| 3188105 | 3188227 | - | 40 | sml0013 | ndhP | NdhP | Y | Y | N |
| 2138496 | 2138621 | + | 41 | Chr_ORF12 | NA | Hypothetical protein | Y | N | N |
| 633626 | 633754 | + | 42 | Chr_ORF5 | NA | Transposase, fragment | Y | N | N |
| 273512 | 273381 | - | 43 | Chr_ORF1 | NA | Hypothetical protein | Y | N | N |
| 1167333 | 1167464 | + | 43 | smr0009 | psbN | Photosystem II PsbN protein | Y | Y | N |
| 570940 | 571074 | + | 44 | smr0006 | psbF | Cytochrome b559 b subunit | Y | Y | N |
| 3067172 | 3067306 | - | 44 | Norf8 | NA | NA | Y | N | N |
| 30142 | 30008 | - | 44 | pSYSA_ORF3 | NA | N terminus of bifunctional aconitate hydratase 2/2-methylisocitrate dehydratase; similar short homologs also in other bacteria | Y | N | Y |
| 553065 | 553202 | - | 45 | sml0005 | psbK | Photosystem II PsbK protein | Y | Y | N |
| 1826764 | 1826901 | + | 45 | smr0011 | rpl34 | 50S ribosomal protein L34 | Y | Y | Y |
| 903627 | 903764 | - | 45 | sml0012 | NA | Hypothetical protein | Y | N | N |
| 14477 | 14340 | - | 45 | pSYSM_ORF1 | NA | O-acetyl-N-acetylneuraminate esterase, partial | Y | N | N |
| 1842716 | 1842856 | - | 46 | Norf6 | ndhQ | NdhQ subunit of the NDH-1 L complex | Y | N | N |
| 1141803 | 1141946 | - | 47 | ssl1633 | hliC, scpB | HliC, CAB/ELIP /HLIP superfamily | Y | Y | N |
| 298826 | 298972 | - | 48 | Norf1 | norf1 | Norf1 | Y | N | N |
| 572978 | 573124 | - | 48 | sml0010 | NA | Transposase | Y | N | N |
| 159812 | 159961 | - | 49 | sgl0002 | NA | Hypothetical protein | Y | N | N |
| 2595112 | 2595264 | - | 50 | ssl0090 | NA | Hypothetical protein | Y | N | N |
The start and end positions according to the chromosomal or plasmid sequences in Genbank files (accessions NC_000911, AP004311 and AP004310), the location (S) on the forward (+) or reverse strand (−) and respective length (L; in amino acids) are given, followed by the locus tag ID, gene name and product if assigned. Location on chromosome or one of the plasmids is prefixed by “Chr” or the name of the plasmid. The existence of homologs in Synechocystis 6714, A. thaliana and E. coli is indicated by “Y” for yes or “N” for no. Homologs tagged and detected in this study are highlighted in boldface letters. Names of genes tested in this work are in boldface
In vivo tagging and detection of cyanobacterial μ-proteins
We chose 5 examples for closer analysis: Norf1, NsiR6, HliR1, Ssr1169 and Norf4. Norf1 and Norf4 were previously defined based on transcriptomic evidence [22]. The protein Ssr1169 was previously modelled as part of the existing annotation, but there is no information on possible functions nor that their very existence was shown thus far. NsiR6 and HliR1 are not annotated in the genome but were found by transcriptomics [21, 33]. Although these RNAs harbor potential open reading frames they were initially indicated as non-coding. After FLAG - tagging and inducing their expression in Synechocystis 6803, all five proteins were detected by Western blotting (Fig. 2). HliR1 and Ssr1169 showed a tendency for aggregation, even under the used denaturing conditions, possibly related to their hydrophobicity and the predicted presence of transmembrane regions (Table 3).
Fig. 2.
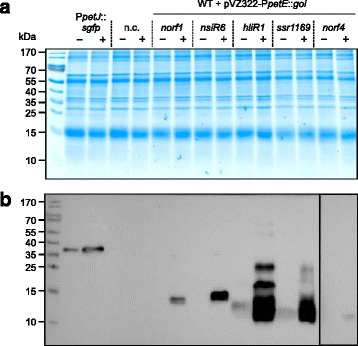
Western blot detection of small proteins. Recombinant Synechocystis 6803 cells carrying the genes of interest (goi) under control of the petE promoter on pVZ322 vector were collected before (−) or 24 h after induction of gene expression (+) for the extraction of total proteins. FLAG-tagged superfolder GFP (sfGFP) under the control of the petJ promoter [37] served as positive control, a WT strain carrying an empty pVZ322 vector was used as negative control (n.c.). Theoretical protein masses are listed in Table 3. Two gels were run in parallel. a Proteins (30 μg) were separated on a 15% (w/v) SDS polyacrylamide gel and subjected to colloidal Coomassie G-250 staining as a loading control. b Immunoblot with the same loading order probed with specific ANTI-FLAG® M2-Peroxidase (HRP) antibody
Table 3.
Physicochemical properties of μ-proteins overexpressed in Synechocystis 6803. TMR, putative transmembrane domains, predicted using TMHMM v. 2.0 [41]
| Protein | Length (aa) | MW untagged | + FLAG tag | Predicted protein | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [kDa] | pI | [kDa] | pI | Domains | ||
| Norf4 | 31 | 3.16 | 5.59 | 5.99 | 4.08 | 1 TMR |
| HliR1 | 37 | 4.11 | 7.92 | 6.93 | 4.30 | 1 TMR |
| Norf1 | 48 | 5.47 | 3.76 | 8.30 | 3.88 | |
| Ssr1169 | 54 | 6.09 | 7.96 | 8.92 | 4.48 | Pmp3; 2 TMR |
| NsiR6 | 66 | 7.10 | 6.05 | 9.92 | 4.40 | PHA02325 |
The NsiR6 transcript is highly induced upon nitrogen deprivation
NsiR6 was not previously known as a protein-coding gene. Its mRNA originates from a TSS at position 729645f in the chromosome of Synechocystis 6803 (Fig. 4a, data extracted from reference [21]). Previously, we introduced the UEF (unique expression factor) to identify genes whose expression was enhanced at a single from ten tested environmental conditions [21]. This factor gives the ratio of the transcriptome read counts for the condition with the highest and the one with the second highest expression for a single TU. Thus, TUs with a high UEF respond strongly to a particular stimulus. For NsiR6, the UEF was 9.65, ranking on position 4 of the most-strongly induced genes, both in Synechocystis 6803 as well as in strain 6714 [20, 21], when the cells were deprived of sources of combined nitrogen (Fig. 3). This induction was confirmed by independently performed Northern blots, indicating a rapid induction of expression, reaching a peak at 6 h with an about 10-fold higher transcript accumulation, followed by a declining abundance which remained higher than at the beginning of the experiment (Fig. 4b and c). The nitrogen-stress-dependent induction is likely mediated via a conserved NtcA binding site 5′-GTAacatttgtGAC-3′, centered 42 nt upstream the transcription initiation site in both strains (Fig. 4a). NtcA-binding sites frequently overlap the −35 promoter region and are centered close to position −41.5 with respect to the TSS when they mediate activation [23, 49]. Homologs of NsiR6 are widely conserved throughout the cyanobacterial phylum and in the Paulinella chromatophora chromatophore genome, consistent with its occurrence in the genomes of α-cyanobacteria, but not in any other bacteria or plants. The alignment of these homologs shows two pairs of conserved cysteine residues which might be involved in redox control, protein-protein interactions or structure formation (Fig. 4d). Two pairs of cysteine residues occur also in another short protein, the 70 amino acid CP12 protein, which mediates the formation of a complex between glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and phosphoribulokinase in response to changes in light intensity, characterizing it as a thioredoxin-mediated metabolic switch [50]. In CP12, the cysteine pairs confer the redox input via post-translational thiol-disulfide bridge conversion. The arrangement ‘CPVC’ of the first cysteine pair (Fig. 4d) matches the C-(X)2-C motif, which frequently is involved in metal-binding [51]. Hence, the putative cysteine pairs in NsiR6 may confer redox control or metal binding.
Fig. 4.
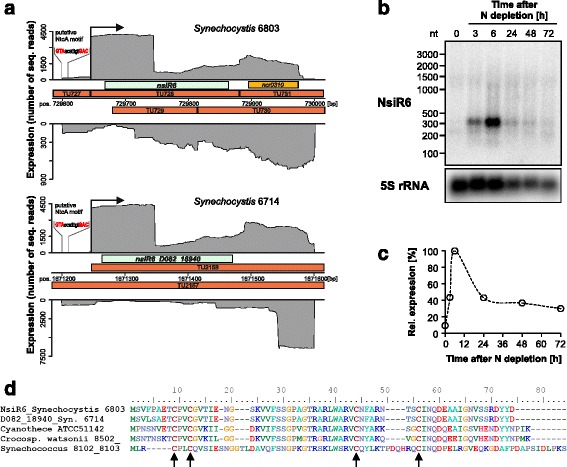
The NsiR6 peptide. a Transcriptomic datasets indicated high read coverage in a region without annotation in Synechocystis 6803 [21], which contains the here defined nsiR6 gene. The homolog in Synechocystis 6714 is D082_18940 [20]. Shown is the read coverage (grey) resulting from previous transcriptome analysis, including the respective transcriptional units (TU) defined in that work [20, 21] and a putative NtcA binding site, centered 42 nt upstream the transcription initiation site in both strains. Relevant transcription initiation sites appear as steep increase in read coverage and are labelled by a black arrow. The length of the 5’-UTRs is 26 nt in both strains. Other non-coding TUs are colored orange. There is transcription in antisense orientation in both strains but with much lower coverage. b Northern blot showing the nitrogen stress-induced transcript accumulation of the NsiR6 mRNA in Synechocystis 6803 over 72 h. Time point 0 refers to the nitrogen-replete condition. c Time course of NsiR6 mRNA accumulation after normalization to 5S rRNA. The data are presented as relative to the signal at 6 h after diminishing N (=100%). d Sequence comparison of NsiR6 homologs from the two Synechocystis strains, Cyanothece ATCC 51142, Crocosphaera watsonii WH 8502 and the two marine Synechococcus strains WH 8102 and WH 8103 which harbor an identical protein. Four conserved cysteine residues are highlighted by arrows. These are conserved in all 63 homologs detected throughout the cyanobacterial phylum
Fig. 3.
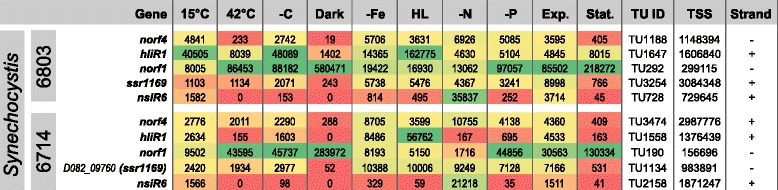
Heatmap indicating the expression of the genes encoding the five investigated small proteins in Synechocystis strains PCC 6803 and PCC 6714 under 10 different growth conditions: exponential (Exp.) and stationary growth phase (Stat.); cold (15 °C) and heat (42 °C) stress for 30 min each; depletion of inorganic carbon (−C), cells were washed 3 times with carbon-free BG11 and cultivated further for 20 h; dark, no light for 12 h; Fe2+ limitation (−Fe), addition of iron-specific chelator desferrioxamine B (DFB) and further cultivation for 24 h; high light (HL), 470 μmol photons m−2s−1 for 30 min; nitrogen depletion (−N), cells were washed 3 times with nitrogen-free BG11 and cultivated further for 12 h; phosphate depletion (−P), cells were washed 3 times with phosphate-free BG11 and further incubated for 12 h. Data derived from previous genome-wide expression analysis by differential RNA-Seq [20, 21]. Values indicate sequencing read counts for the primary 5′ end (= transcriptional start site [TSS]) of the corresponding transcriptional unit (TU). The TSS positions are given for the Synechocystis genomes available under accession numbers BA000022 and CP007542. The colour varies from red (no expression) to yellow (intermediate expression) to green (high expression)
Norf1 is highly induced upon dark incubation
Norf1 is specific for cyanobacteria but widely conserved throughout this phylum. It is present in 138 (68%) of 202 cyanobacterial genomes available in the JGI database [52] (blastP + tblastN, E value ≤1e−5). Homologs are lacking in early-branching cyanobacteria such as Gloeobacteria and thermophilic Synechococcus JA-2-3B’a(2–13) and JA-3-3Ab and also in marine picocyanobacteria. An alignment of representative homologs is shown in Fig. 5a.
Fig. 5.
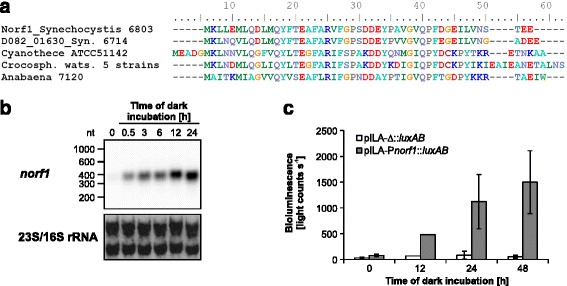
Sequence comparison and regulated expression of the norf1 gene. a Sequence comparison of Norf1 homologs from the two Synechocystis strains, Cyanothece ATCC 51142, 5 different strains of Crocosphaera encoding an identical protein and Anabaena (Nostoc) sp. PCC 7120. b Expression of norf1 in Synechocystis 6803 is strongly upregulated after transfer to darkness. c Bioluminescence of a Synechocystis 6803 reporter strain harboring a transcriptional fusion of Pnorf1 (−328 to +137, TSS at +1) and luxAB genes in response to transfer to darkness. Representative bioluminescence dataset indicating means ± SD of measurements for two biological replicates (= independent transformants). A strain carrying a promoterless luxAB was used as a negative control (measured in two independent cultures each)
Strong accumulation of the norf1 mRNA was observed in response to darkness (Fig. 5b). The UEF for this condition was 2.66 in Synechocystis 6803, but the gene was expressed also under the other tested conditions (Fig. 3) [21]. To examine whether the dark-related expression of norf1 is under transcriptional control, we conducted reporter gene assays. The upstream sequence of Synechocystis 6803 norf1 was fused to luxAB reporter genes encoding luciferase, and expression was monitored as bioluminescence in vivo. Indeed, the promoter activity showed a positive response after transfer into darkness as seen for the mRNA accumulation (Fig. 5b and c). We conclude that the observed induction of norf1 in response to shifts from light exposure to darkness is under transcriptional control.
The high expression of the norf1 gene in darkness sets it apart from the vast majority of genes. Among the previously tested 10 different growth conditions, in Synechocystis 6803 only 70 out of 4091 TUs and in Synechocystis 6714 only 57 out of 4292 TUs defined in total had their maximum expression after dark incubation [20, 21].
The Norf4 μ-protein is highly conserved and its mRNA overlaps the gap1 gene
Norf4 is encoded within a TU much longer than is needed to encode the 31 amino acids: TU1188 in Synechocystis 6803 is 704 nt and TU3474 in Synechocystis 6714 is 534 nt (Fig. 6a). These TUs partially overlap the gap1 gene encoding glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 on the complementary DNA strand. As a result, these TUs overlap the gap1 mRNA by 702 and 373 nt, respectively. Transcriptomic evidence suggested that both the gap1 and the norf4 mRNAs were co-regulated with each other, with a mild up-regulation upon the removal of nitrogen (Fig. 3). Thus, the norf4 transcript does not function as an antisense RNA with a co-degradation function, which was observed previously for other pairs of overlapping transcripts in Synechocystis 6803 [53, 54]. However, co-regulation between an asRNA and its cognate mRNA was previously observed for the psbA asRNA protecting its 5′ leader from RNase E-mediated degradation [55]. The expression of norf4 was stimulated upon removal of nitrogen, but its expression was detectable under most of the previously tested conditions, although at a lower level (especially low in darkness and after heat stress; Fig. 3). Dual-function RNAs are transcripts which assume a regulatory function as sRNA and additionally act as short protein-coding mRNA. Exploring this possibility for norf4, we checked the accumulation of norf4 transcripts during the removal of combined nitrogen. Northern blot analysis showed the existence of a prominent transcript of ~200 nt which declined initially (Fig. 6b). Due to the localization of the RNA probe used in the detection of norf4 transcripts, this prominent transcript corresponds to the coding part of TU1188. However, with increasing duration of the nitrogen stress, we noticed the overaccumulation of a longer transcript, of about 600–800 nt that appeared more diffuse (Fig. 6b). Quantitative analysis of transcript accumulation showed that this longer norf4 transcript was only transiently accumulated, with a peak at the 24 h time points (Fig. 6c).
Fig. 6.
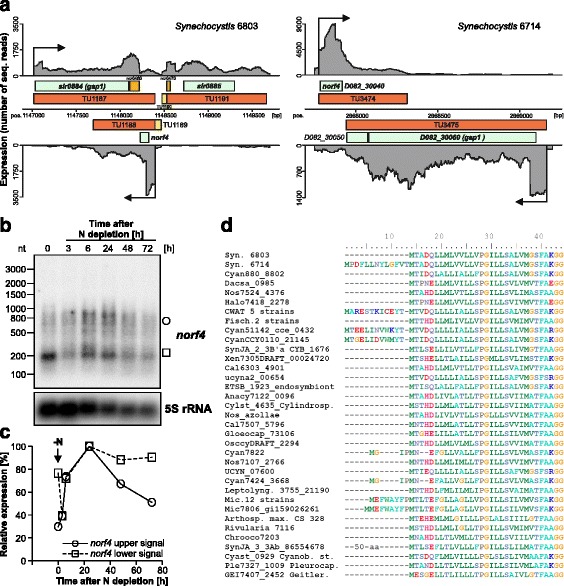
The Norf4 peptide. a Datasets from the previously performed primary transcriptome analysis showed that Norf4 expression responded positively to nitrogen depletion in both Synechocystis 6803 [21] and Synechocystis 6714 [20], when 11 different growth conditions were tested. The mRNAs of norf4 and gap1 are co-regulated and overlap by several hundred nt. The previously mapped transcriptional start sites are labelled by black arrows. b Northern blot analysis of norf4 mRNA accumulation in a time course experiment up to 72 h after the removal of nitrogen. The same RNA samples were used as in Fig. 4. c The signals obtained from the Northern blots (panel b) were evaluated densitometrically after normalization by the level of 5S rRNA. The relative norf4 expression is shown with respect to the maximum expression after transfer to nitrogen-free conditions (24 h = 100%). The bands at 200 nt (filled circles) and at 800 nt (empty circles) were analyzed separately from each other. d Multiple sequence alignment of 35 homologs from 51 different cyanobacterial genome sequences (homologs are identical among 12 Microcystis, five Crocosphaera watsonii and two Fischerella genome sequences)
With very few amino acid substitutions, Norf4 is extremely conserved, including a predicted transmembrane region (Fig. 6d). Homologs can be detected in 51 cyanobacterial genome sequences from all 5 morphological subsections, comprising free-living unicellular as well as multicellular strains, marine and freshwater isolates, thermophiles and symbionts. The presence of norf4 in the two available genome sequences of Candidatus Atelocyanobacterium thalassa suggests their positive selection in these highly streamlined genomes [56, 57]. However, homologs are lacking in α-cyanobacteria, which are mainly marine Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus. The homologs from the two used Synechocystis strains are identical, except for a possible N-terminal extension by 13 amino acids in Synechocystis 6714 (Fig. 6d). However, such extensions appear questionable also in other strains, because the start codon corresponding to the Synechocystis 6803 ORF is 100% conserved. Moreover, the homologs in 12 Microcystis genomes are identical to each other, as are the homologs in five Crocosphaera watsonii and in two Fischerella genome sequences.
Our data suggest that Norf4 is a previously unknown membrane-bound μ-protein and that the norf4 transcript may play a dual role, with a mainly coding function during nitrogen-sufficient conditions and a possibly RNA-mediated regulatory function on the gap1 mRNA during nitrogen stress.
HliR1 and Ssr1169
HliR1 was chosen because of its very high induction under high light (UEF of 5.47) and the gene location upstream of sodB encoding superoxide dismutase. Whereas the homologs from the two Synechocystis strains are conserved in length, sequence (2 substitutions over 35 amino acids) and the likely presence of a transmembrane region (Fig. 7a), no possible homologs were detected beyond the genus Synechocystis. The location upstream of sodB and the shape of the read coverage in transcriptome analysis (Fig. 7b) suggested a possible link between the two genes. Indeed, Northern analysis confirmed the inducibility by high light (Fig. 7c and d) and in addition showed the presence of two major transcripts, ~450 and 1400 nt in length. The longer form should encompass also the complete sodB gene. Thus, transcription from the upstream located hliR1 promoter will lead by read-though to an enhanced sodB gene expression under high light. Hence, it is tempting to speculate, that HliR1 is a membrane-bound peptide with a regulatory function on the superoxide dismutase.
Fig. 7.
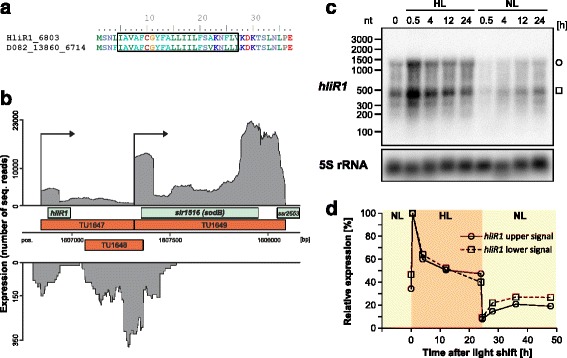
The HliR1 peptide in Synechocystis 6803. a Pairwise sequence alignment of the HliR1 peptides from Synechocystis 6803 and Synechocystis 6714. A predicted transmembrane region is boxed. b Data replotted from the primary transcriptome analysis of Synechocystis 6803 suggest that HliR1 expression is induced by high light and that transcripts may extend into the subsequent TU1649 covering the sodB gene [21]. c Northern analysis of hliR1 mRNA accumulation upon transfer to high light (HL) or normal light (NL). d Quantification of the hliR1 mRNA accumulation shown in panel c after normalization to the 5S rRNA level. Relative values refer to the maximum level at 0.5 h after HL shift (=100%)
The previously annotated short gene ssr1169 was chosen because of its expression under several different conditions (Fig. 3) and its physicochemical characterization as a hydrophobic protein. Features of all 5 investigated μ-proteins are summarized in Table 3.
Homologs of Ssr1169 are frequently encoded by a small gene family and exist in plants (best homolog in A. thaliana: Low temperature and salt responsive protein, gi|15223610|ref|NP_176067.1|, E value 3e-11; Table 2; Fig. 8), in E. coli (gi|446430313|ref|WP_000508168.1|, E value 3e−8; Table 2) and in many other bacteria and other eukaryotic organisms, including yeast and C. elegans. Expression of the homologs RCI2A and RCI2B in A. thaliana became induced upon exposure to low temperature, dehydration, salt stress, or abscisic acid [58]. Ssr1169 homologs possess two transmembrane helices (Fig. 8) that form a Pmp3 domain and might be a stress induced proteolipid membrane modulator.
Fig. 8.
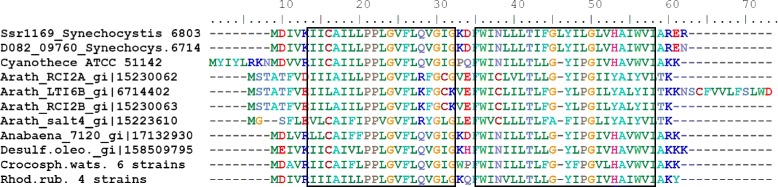
Sequence alignment of Ssr1169 homologs from cyanobacteria with those from Arabidopsis thaliana, Desulfococcus oleovorans Hxd3, and identical proteins in 4 strains of Rhodospirillum rubrum. Putative transmembrane domains were predicted using TMHMM v. 2.0 [41] and are boxed
All five μ-proteins can be expressed from their native promoters in a regulated fashion
In the previous sections we verified the transcription of the five selected μ-protein encoding genes (Figs. 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7) as well as their translation from an mRNA harboring the regulatory sequence elements (e.g. ribosome binding site) of the petE gene (Fig. 2). However, despite verifying a stable accumulation of the translated protein the latter approach renders the possibility of translating all RNAs as long as they contain an open reading frame. To exclude this possibility, we repeated the experiment from Fig. 2 but placed all five FLAG-tagged μ-ORFs under control of their own, native promoter and 5′UTRs. After introduction of these constructs into Synechocystis 6803 we subjected the resulting cultures to an inducing condition according to the transcriptome analysis. Samples from cultures grown at standard conditions or the inducing conditions were taken and analyzed by Western blot experiments (Fig. 9). The results showed unambiguously the expression of all five μ-proteins when placed under control of their own promoters and 5′ UTRs, i.e., their expression was not artificially induced by the ectopic fusion of their ORFs to the petE promoter and 5′ UTR. We noticed a strong upregulation of NsiR6 accumulation 24 h after transfer to nitrogen starvation and of HliR1 accumulation 6 h after exposure to high light as well as a mild upregulation of Norf4 accumulation 24 h after transfer to nitrogen starvation (Fig. 9). The accumulation of Norf1 increased somewhat 6 h after the shift to darkness. These data show that the observed regulation of gene expression at RNA level has a strong effect on the amounts of three of the respective proteins and a milder on one of the other two.
Fig. 9.
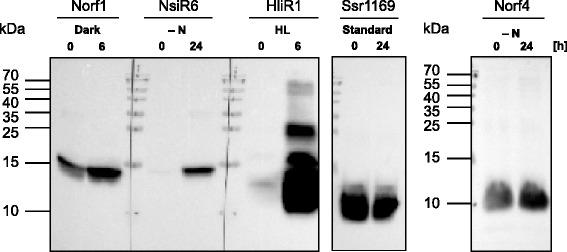
Detection of μ-proteins upon expression from their native promoters and 5′ UTRs. Recombinant Synechocystis 6803 cells carrying the respective genes under control of their own promoters and 5′UTRs on vector pVZ322 were collected from cultures grown at standard conditions (0) and after transfer to the respective inducing condition at indicated time points (6 or 24 h) or in case of Ssr1169 after 24 h at standard condition. The Western blot was probed with specific ANTI-FLAG® M2-Peroxidase (HRP) antibody. All samples were separated on the same gel and transferred to the same membrane but the part probed for Norf4 had to be exposed longer because of its lower expression. Prestained Protein Ladder (10–170 kDa, Fermentas) was used as molecular weight marker
Discussion
For Synechocystis 6803 alone, more than 50 independent proteomic studies identified a total of 2967 proteins at least once (reviewed by Gao et al., [59]), representing 80.8% of the entire predicted proteome. However, the percentage of identified proteins was only 34.4% for small proteins (<100 aa) of high hydrophobicity [59]. In addition, as we show in this study, very short protein-coding genes might not even be modelled and annotated at all. Thus, due to the challenges in their identification and biochemical detection, μ-proteins were in the past either not detected or were ignored. However, systematic genome-wide approaches have recently reported an increasing number of μ-proteins in pro- and eukaryotes [8, 10, 11, 19, 60]. Besides the short ORFs within 5′ leader and 3′ trailer sequences of mRNAs, known for a long time [61–65], μ-peptides were recently also described to originate from long ncRNAs, i.e. transcripts, which were previously assumed to be non-coding [60, 66].
In E. coli approximately 60 genes encoding μ-proteins have previously been reported [67]. Expression profiling showed that many μ-proteins accumulate under specific growth conditions or are induced by stress [68]. A particular group of small proteins are toxic due to their integration into the cell membrane as peptide component of a type I toxin-antitoxin system [69–71]. In the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus, four small secreted proteins have been suggested to be involved in biofilm development [72]. Small proteins of the type II toxin-antitoxin category in Synechocystis 6803 have been catalogued separately [73] but the majority of them are somewhat larger than the here considered μ-proteins.
Here, we found 293 candidate genes for small proteins ≤80 amino acids in the model cyanobacterium Synechocystis 6803 and demonstrate the synthesis of five examples by C-terminal FLAG-tagging and immune detection. Three of these five small proteins are predicted to contain one or two transmembrane helices (Table 3), placing them in the category of proteins that are particularly challenging to verify by proteomic approaches [59]. Hence, our list of predicted proteins provides a solid basis for functional studies.
Regulated expression suggests involvement in stress adaptation for some of the here investigated small proteins. This applies especially to HliR1, NsiR6 and Norf1, whose expression is activated in response to high light, nitrogen stress or transfer into darkness (Figs. 3, 4, 5 and 9).
The fact that some of the here described proteins are part of TUs much longer than needed points to the possibility that some of them could constitute dual function RNAs. Such dual-function RNAs that in addition to their role as a regulatory RNA molecule also encode a functional peptide, have been identified in bacteria. A prominent example for a dual function RNA is the 43 amino acid peptide SgrT encoded in the 5′ region of the E. coli SgrS transcript, which regulates the glucose transporter PtsG at protein level, whilst the SgrS 3′ region contains a regulatory domain that targets the ptsG mRNA by base-pairing [74].
In Bacillus subtilis, SR1 is a highly conserved dual-function sRNA that acts as a base-pairing regulatory RNA on the ahrC mRNA (encoding AhrC, the transcriptional activator of arginine catabolic operons) and in addition encodes the 39 amino acid peptide SR1P. Interestingly, this peptide binds GapA (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase), thereby stabilizing the gapA operon mRNA [75, 76]. In analogy, it is interesting to note that the here described cyanobacterial Norf4 μ-protein overlaps the gap1 mRNA and appears to be co-regulated with it.
The high total numbers of predicted μ-ORFs, together with the distribution, conservation, regulation of gene expression and the physicochemical properties of the five examples studied here in more detail, underline the likely great bandwidth of small protein functions in bacteria and makes them attractive candidates for functional studies.
Conclusions
Synechocystis 6803 is a widely used model cyanobacterium that possess with 44 genes encoding small proteins ≤50 amino acids and potentially 293 proteins ≤80 amino acids a high number of such μ-ORFs. These numbers are certainly no overestimation: due to the previous extensive work to elucidate all subunits of the photosynthetic apparatus, 52% of the small proteins ≤50 amino acids have a known function. This sets the small proteome of cyanobacteria apart from that of other bacteria: in addition to the 19 photosynthesis-related small proteins only five other in the size category ≤50 are functionally annotated (NdhP,NdhQ, RpL34, Rpl36 and a VapC toxin homolog). Hence, about half of the predicted small proteins are uncharacterized. When analysing small proteins up to 80 aa, we found 235 of the 293 predicted small proteins (80%) without annotation. The experimental results and expression data for the five here selected proteins (three ≤50 aa and another two larger, but ≤70 aa) underline that it is worthwhile to study small protein functions directly in cyanobacteria. The here provided data and strains will be useful for such studies in a systematic way.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Thomas Wallner for providing Synechocystis 6803 strain pUR-PpetJ-3xFlag-sfGFP and Dr. Martin Hagemann for critical reading.
Funding
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
Previously generated transcriptomic datasets re-analysed during the current study are available from the NCBI Sequence Read Archive under accessions SRP032228 and SRP032230. All other data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Authors’ contributions
DB, carried out the molecular genetic and biochemical analyses, MK performed the bioinformatics analyses, WRH designed the study and all authors analyzed data. DB and WRH drafted the manuscript and MK, CS and SK revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- HliR1
High light inducible RNA 1
- Norf1 and Norf4
Novel orf 1 and 4
- NsiR6
Nitrogen stress-induced RNA 6
- TU
Transcriptional unit
- UEF
Unique expression factor
Contributor Information
Desiree Baumgartner, Email: desireebaumgartner@gmx.de.
Matthias Kopf, Email: kopf.matthias@gmail.com.
Stephan Klähn, Email: stephan.klaehn@biologie.uni-freiburg.de.
Claudia Steglich, Email: Claudia.Steglich@biologie.uni-freiburg.de.
Wolfgang R. Hess, Phone: +49-761-2032796, Email: wolfgang.hess@biologie.uni-freiburg.de
References
- 1.Lluch-Senar M, Delgado J, Chen W-H, Lloréns-Rico V, O’Reilly FJ, Wodke JA, et al. Defining a minimal cell: essentiality of small ORFs and ncRNAs in a genome-reduced bacterium. Mol Syst Biol. 2015;11:780. doi: 10.15252/msb.20145558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Thoendel M, Kavanaugh JS, Flack CE, Horswill AR. Peptide signaling in the Staphylococci. Chem Rev. 2011;111:117–51. doi: 10.1021/cr100370n. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Alix E, Blanc-Potard A-B. Hydrophobic peptides: novel regulators within bacterial membrane. Mol Microbiol. 2009;72:5–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jean-Francois FL, Dai J, Yu L, Myrick A, Rubin E, Fajer PG, et al. Binding of MgtR, a Salmonella transmembrane regulatory peptide, to MgtC, a Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence factor: a structural study. J Mol Biol. 2014;426:436–46. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.10.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Choi E, Lee K-Y, Shin D. The MgtR regulatory peptide negatively controls expression of the MgtA Mg2+ transporter in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;417:318–23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.11.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Galperin MY, Mekhedov SL, Puigbo P, Smirnov S, Wolf YI, Rigden DJ. Genomic determinants of sporulation in Bacilli and Clostridia: towards the minimal set of sporulation-specific genes. Environ Microbiol. 2012;14:2870–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02841.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Landry CR, Zhong X, Nielly-Thibault L, Roucou X. Found in translation: functions and evolution of a recently discovered alternative proteome. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2015;32:74–80. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2015.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tavormina P, De Coninck B, Nikonorova N, De Smet I, Cammue BPA. The plant peptidome: an expanding repertoire of structural features and biological functions. Plant Cell. 2015;27:2095–118. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.00440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Staudt A-C, Wenkel S. Regulation of protein function by “microProteins”. EMBO Rep. 2011;12:35–42. doi: 10.1038/embor.2010.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Andrews SJ, Rothnagel JA. Emerging evidence for functional peptides encoded by short open reading frames. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15:193–204. doi: 10.1038/nrg3520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Prasse D, Thomsen J, De Santis R, Muntel J, Becher D, Schmitz RA. First description of small proteins encoded by spRNAs in Methanosarcina mazeistrain Gö1. Biochimie. 2015;117:138–48. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 12.Guskov A, Kern J, Gabdulkhakov A, Broser M, Zouni A, Saenger W. Cyanobacterial photosystem II at 2.9-A resolution and the role of quinones, lipids, channels and chloride. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009;16:334–42. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kashino Y, Lauber WM, Carroll JA, Wang Q, Whitmarsh J, Satoh K, et al. Proteomic analysis of a highly active photosystem II preparation from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 reveals the presence of novel polypeptides. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2002;41:8004–12. doi: 10.1021/bi026012+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fromme P, Melkozernov A, Jordan P, Krauss N. Structure and function of photosystem I: interaction with its soluble electron carriers and external antenna systems. FEBS Lett. 2003;555:40–4. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(03)01124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Baniulis D, Yamashita E, Whitelegge JP, Zatsman AI, Hendrich MP, Hasan SS, et al. Structure-function, stability, and chemical modification of the cyanobacterial cytochrome b6f complex from Nostoc sp. PCC 7120. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:9861–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Allen JF. Cytochrome b6f: structure for signalling and vectorial metabolism. Trends Plant Sci. 2004;9:130–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2004.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schneider D, Volkmer T, Rögner M. PetG and PetN, but not PetL, are essential subunits of the cytochrome b6f complex from Synechocystis PCC 6803. Res Microbiol. 2007;158:45–50. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2006.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Knoppová J, Sobotka R, Tichy M, Yu J, Konik P, Halada P, et al. Discovery of a chlorophyll binding protein complex involved in the early steps of photosystem II assembly in Synechocystis. Plant Cell. 2014;26:1200–12. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.123919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hobbs EC, Fontaine F, Yin X, Storz G. An expanding universe of small proteins. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2011;14:167–73. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2011.01.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kopf M, Klähn S, Scholz I, Hess WR, Voß B. Variations in the non-coding transcriptome as a driver of inter-strain divergence and physiological adaptation in bacteria. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9560. doi: 10.1038/srep09560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kopf M, Klähn S, Scholz I, Matthiessen JKF, Hess WR, Voß B. Comparative analysis of the primary transcriptome of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. DNA Res. 2014;21:527–39. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsu018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mitschke J, Georg J, Scholz I, Sharma CM, Dienst D, Bantscheff J, et al. An experimentally anchored map of transcriptional start sites in the model cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:2124–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 23.Mitschke J, Vioque A, Haas F, Hess WR, Muro-Pastor AM. Dynamics of transcriptional start site selection during nitrogen stress-induced cell differentiation in Anabaena sp. PCC7120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:20130–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 24.McClure RS, Overall CC, McDermott JE, Hill EA, Markillie LM, McCue LA, et al. Network analysis of transcriptomics expands regulatory landscapes in Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:8810–25. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pfreundt U, Kopf M, Belkin N, Berman-Frank I, Hess WR. The primary transcriptome of the marine diazotroph Trichodesmium erythraeum IMS101. Sci Rep. 2014;4:6187. doi: 10.1038/srep06187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kopf M, Möke F, Bauwe H, Hess WR, Hagemann M. Expression profiling of the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Nodularia CCY9414 under light and oxidative stress conditions. ISME J. 2015;9:2139–52. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2015.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Flaherty BL, Van Nieuwerburgh F, Head SR, Golden JW. Directional RNA deep sequencing sheds new light on the transcriptional response of Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 to combined-nitrogen deprivation. BMC Genomics. 2011;12:332. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Welkie D, Zhang X, Markillie ML, Taylor R, Orr G, Jacobs J, et al. Transcriptomic and proteomic dynamics in the metabolism of a diazotrophic cyanobacterium, Cyanothece sp. PCC 7822 during a diurnal light–dark cycle. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:1185. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wegener KM, Singh AK, Jacobs JM, Elvitigala T, Welsh EA, Keren N, et al. Global proteomics reveal an atypical strategy for carbon/nitrogen assimilation by a cyanobacterium under diverse environmental perturbations. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010;9:2678–89. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M110.000109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Spät P, Maček B, Forchhammer K. Phosphoproteome of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and its dynamics during nitrogen starvation. Front Microbiol. 2015;6:248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 31.Teikari J, Österholm J, Kopf M, Battchikova N, Wahlsten M, Aro E-M, et al. Transcriptomics and proteomics profiling of Anabaena sp. strain 90 under inorganic phosphorus stress. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015;81(15):5212–22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 32.Kopf M, Klähn S, Pade N, Weingärtner C, Hagemann M, Voß B, et al. Comparative genome analysis of the closely relatedSynechocystis strains PCC 6714 and PCC 6803. DNA Res. 2014;21:255–66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 33.Kopf M, Hess WR. Regulatory RNAs in photosynthetic cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2015;39:301–15. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuv017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Trautmann D, Voß B, Wilde A, Al-Babili S, Hess WR. Microevolution in cyanobacteria: re-sequencing a motile substrain of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. DNA Res. 2012;19:435–48. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dss024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY. Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. Microbiology. 1979;111:1–61. doi: 10.1099/00221287-111-1-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhang L, McSpadden B, Pakrasi HB, Whitmarsh J. Copper-mediated regulation of cytochrome c553 and plastocyanin in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis 6803. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:19054–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Schuergers N, Nürnberg DJ, Wallner T, Mullineaux CW, Wilde A. PilB localization correlates with the direction of twitching motility in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Microbiol Read Engl. 2015;161:960–6. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.NCBI database. http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/.
- 39.Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:2947–8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Washietl S, Findeiss S, Müller SA, Kalkhof S, von Bergen M, Hofacker IL, et al. RNAcode: robust discrimination of coding and noncoding regions in comparative sequence data. RNA. 2011;17:578–94. doi: 10.1261/rna.2536111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer EL. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol. 2001;305:567–80. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zinchenko VV, Piven IV, Melnik VA, Shestakov SV. Vectors for the complementation analysis of cyanobacterial mutants. Russ J Genet. 1999;35:228–32. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Scholz I, Lange SJ, Hein S, Hess WR, Backofen R. CRISPR-Cas systems in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 exhibit distinct processing pathways involving at least two Cas6 and a Cmr2 protein. PLoS One. 2013;8:e56470. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pinto FL, Thapper A, Sontheim W, Lindblad P. Analysis of current and alternative phenol based RNA extraction methodologies for cyanobacteria. BMC Mol Biol. 2009;10:79. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-10-79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hein S, Scholz I, Voß B, Hess WR. Adaptation and modification of three CRISPR loci in two closely related cyanobacteria. RNA Biol. 2013;10:852–64. doi: 10.4161/rna.24160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Steglich C, Futschik ME, Lindell D, Voß B, Chisholm SW, Hess WR. The challenge of regulation in a minimal photoautotroph: non-coding RNAs in Prochlorococcus. PLoS Genet. 2008;4:e1000173. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Klähn S, Baumgartner D, Pfreundt U, Voigt K, Schön V, Steglich C, et al. Alkane biosynthesis genes in cyanobacteria and their transcriptional organization. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2014;2:24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 48.Voss B, Georg J, Schön V, Ude S, Hess WR. Biocomputational prediction of non-coding RNAs in model cyanobacteria. BMC Genomics. 2009;10:123. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Herrero A, Muro-Pastor AM, Flores E. Nitrogen control in cyanobacteria. J Bacteriol. 2001;183:411–25. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.2.411-425.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.López-Calcagno PE, Howard TP, Raines CA. The CP12 protein family: a thioredoxin-mediated metabolic switch? Front Plant Sci. 2014;5:9. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Miseta A, Csutora P. Relationship between the occurrence of cysteine in proteins and the complexity of organisms. Mol Biol Evol. 2000;17:1232–9. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.JGI database. jgi.doe.gov.
- 53.Eisenhut M, Georg J, Klähn S, Sakurai I, Mustila H, Zhang P, et al. The antisense RNA As1_flv4 in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 prevents premature expression of the flv4-2 operon upon shift in inorganic carbon supply. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:33153–62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.391755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Dühring U, Axmann IM, Hess WR, Wilde A. An internal antisense RNA regulates expression of the photosynthesis gene isiA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:7054–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600927103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sakurai I, Stazic D, Eisenhut M, Vuorio E, Steglich C, Hess WR, et al. Positive regulation of psbA gene expression by cis-encoded antisense RNAs in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant Physiol. 2012;160:1000–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 56.Bombar D, Heller P, Sanchez-Baracaldo P, Carter BJ, Zehr JP. Comparative genomics reveals surprising divergence of two closely related strains of uncultivated UCYN-A cyanobacteria. ISME J. 2014;8:2530–42. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2014.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Thompson A, Carter BJ, Turk-Kubo K, Malfatti F, Azam F, Zehr JP. Genetic diversity of the unicellular nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria UCYN-A and its prymnesiophyte host. Environ Microbiol. 2014;16:3238–49. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Medina J, Catala R, Salinas J. Developmental and stress regulation of RCI2A and RCI2B, two cold-inducible genes of Arabidopsis encoding highly conserved hydrophobic proteins. Plant Physiol. 2001;125:1655–66. doi: 10.1104/pp.125.4.1655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gao L, Wang J, Ge H, Fang L, Zhang Y, Huang X, et al. Toward the complete proteome of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Photosynth Res. 2015;126:203–19. doi: 10.1007/s11120-015-0140-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Mackowiak SD, Zauber H, Bielow C, Thiel D, Kutz K, Calviello L, et al. Extensive identification and analysis of conserved small ORFs in animals. Genome Biol. 2015;16:179. doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0742-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sonnleitner E, Gonzalez N, Sorger-Domenigg T, Heeb S, Richter AS, Backofen R, et al. The small RNA PhrS stimulates synthesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal. Mol Microbiol. 2011;80:868–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Vecerek B, Moll I, Bläsi U. Control of Fur synthesis by the non-coding RNA RyhB and iron-responsive decoding. EMBO J. 2007;26:965–75. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.von Arnim AG, Jia Q, Vaughn JN. Regulation of plant translation by upstream open reading frames. Plant Sci Int J Exp Plant Biol. 2014;214:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Barbosa C, Peixeiro I, Romão L. Gene expression regulation by upstream open reading frames and human disease. PLoS Genet. 2013;9:e1003529. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Somers J, Pöyry T, Willis AE. A perspective on mammalian upstream open reading frame function. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45:1690–700. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.04.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Anderson DM, Anderson KM, Chang C-L, Makarewich CA, Nelson BR, McAnally JR, et al. A micropeptide encoded by a putative long noncoding RNA regulates muscle performance. Cell. 2015;160:595–606. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hemm MR, Paul BJ, Schneider TD, Storz G, Rudd KE. Small membrane proteins found by comparative genomics and ribosome binding site models. Mol Microbiol. 2008;70:1487–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06495.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Hemm MR, Paul BJ, Miranda-Ríos J, Zhang A, Soltanzad N, Storz G. Small stress response proteins in Escherichia coli: proteins missed by classical proteomic studies. J Bacteriol. 2010;192:46–58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 69.Fozo EM. New type I toxin-antitoxin families from “wild” and laboratory strains of E. coli: Ibs-Sib, ShoB-OhsC and Zor-Orz. RNA Biol. 2012;9:1504–12. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 70.Fozo EM, Hemm MR, Storz G. Small toxic proteins and the antisense RNAs that repress them. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2008;72:579–89. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00025-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Fozo EM, Makarova KS, Shabalina SA, Yutin N, Koonin EV, Storz G. Abundance of type I toxin-antitoxin systems in bacteria: searches for new candidates and discovery of novel families. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:3743–59. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Parnasa R, Nagar E, Sendersky E, Reich Z, Simkovsky R, Golden S, et al. Small secreted proteins enable biofilm development in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32209. doi: 10.1038/srep32209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kopfmann S, Roesch SK, Hess WR. Type II toxin-antitoxin systems in the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Toxins.2016;8:228.1–228.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 74.Vanderpool CK, Balasubramanian D, Lloyd CR. Dual-function RNA regulators in bacteria. Biochimie. 2011;93:1943–9. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.07.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Gimpel M, Preis H, Barth E, Gramzow L, Brantl S. SR1--a small RNA with two remarkably conserved functions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:11659–72. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Gimpel M, Heidrich N, Mäder U, Krügel H, Brantl S. A dual-function sRNA from B. subtilis: SR1 acts as a peptide encoding mRNA on the gapA operon. Mol Microbiol. 2010;76:990–1009. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Previously generated transcriptomic datasets re-analysed during the current study are available from the NCBI Sequence Read Archive under accessions SRP032228 and SRP032230. All other data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.


