Abstract
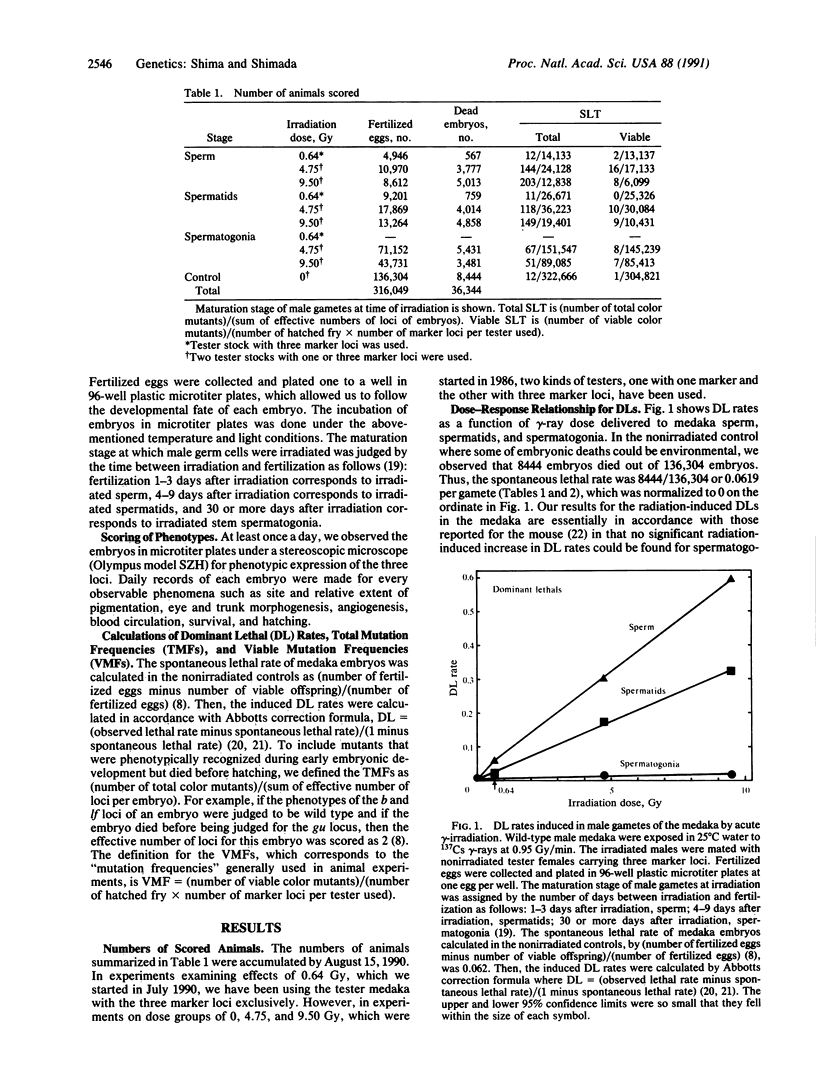
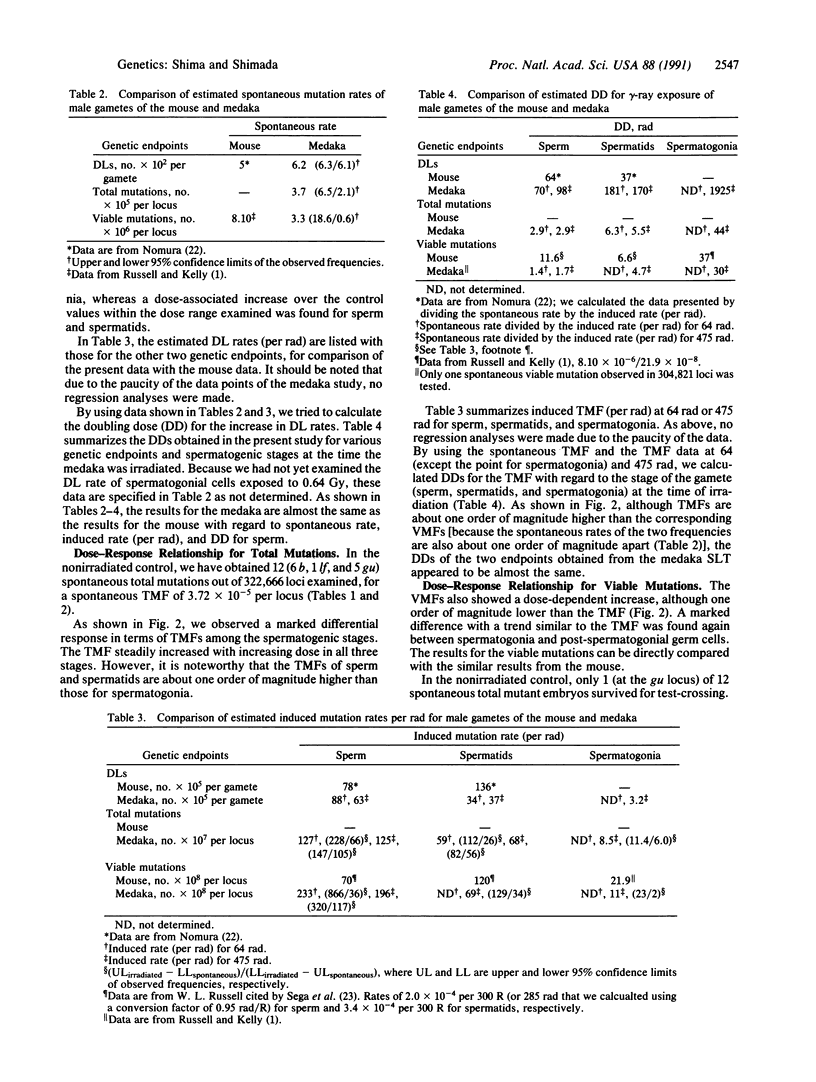
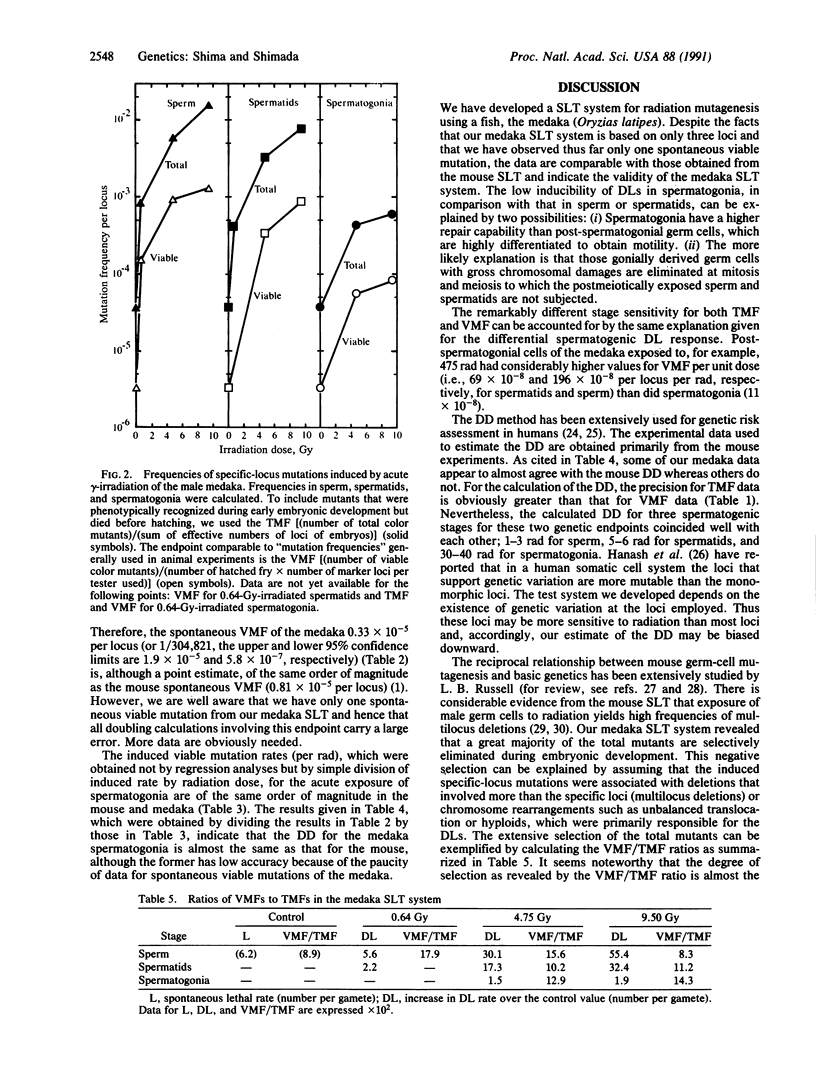
To develop a specific-locus test (SLT) system for environmental mutagenesis using vertebrate species other than the mouse, we first established a tester stock of the fish medaka (Oryzias latipes) that is homozygous recessive at three loci. The phenotypic expression of these loci can be easily recognized early in embryonic development by observation through the transparent egg membrane. We irradiated wild-type males with 137Cs gamma-rays to determine the dose-response relationships for dominant lethal and specific-locus mutations induced in sperm, spermatids, and spermatogonia. Through observation of 322,666 loci in control offspring and 374,026 loci in offspring obtained from 0.64-, 4.75-, or 9.50-Gy-irradiated gametes, specific-locus mutations were phenotypically detected during early development. These putative mutations, designated "total mutation," can be recognized only in embryos of oviparous animals. The developmental fate of these mutant embryos was precisely followed. During subsequent embryonic development, a large fraction died and thus was unavailable for test-crossing, which was used to identify "viable mutations." Our medaka SLT system demonstrates that the vast majority of total mutations is associated with dominant lethal mutations. Thus far only one spontaneous viable mutation has been observed, so that all doubling calculations involving this endpoint carry a large error. With these reservations, however, we conclude that the quantitative data so far obtained from the medaka SLT are quite comparable to those from the mouse SLT and, hence, indicate the validity of the medaka SLT as a possible nonmammalian test system.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chakrabarti S., Streisinger G., Singer F., Walker C. Frequency of gamma-Ray Induced Specific Locus and Recessive Lethal Mutations in Mature Germ Cells of the Zebrafish, BRACHYDANIO RERIO. Genetics. 1983 Jan;103(1):109–123. doi: 10.1093/genetics/103.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egami N., Hyodo-Taguchi Y. An autoradiographic examination of rate of spermatogenesis at different temperatures in the fish, Oryzias latipes. Exp Cell Res. 1967 Sep;47(3):665–667. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehling U. H. Germ-cell mutations in mice: standards for protecting the human genome. Mutat Res. 1989 May;212(1):43–53. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(89)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanash S. M., Boehnke M., Chu E. H., Neel J. V., Kuick R. D. Nonrandom distribution of structural mutants in ethylnitrosourea-treated cultured human lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):165–169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki T., Shima A. Number of major histocompatibility loci in inbred strains of the fish Oryzias latipes. Immunogenetics. 1989;30(3):226–228. doi: 10.1007/BF02421212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse K., Shima A. Linkage relationships of gene loci in the Medaka, Oryzias latipes (Pisces: Oryziatidae), determined by backcrosses and gynogenesis. Biochem Genet. 1989 Apr;27(3-4):183–198. doi: 10.1007/BF02401800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel J. V., Schull W. J., Awa A. A., Satoh C., Kato H., Otake M., Yoshimoto Y. The children of parents exposed to atomic bombs: estimates of the genetic doubling dose of radiation for humans. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jun;46(6):1053–1072. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura T. Parental exposure to x rays and chemicals induces heritable tumours and anomalies in mice. Nature. 1982 Apr 8;296(5857):575–577. doi: 10.1038/296575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinchik E. M., Bangham J. W., Hunsicker P. R., Cacheiro N. L., Kwon B. S., Jackson I. J., Russell L. B. Genetic and molecular analysis of chlorambucil-induced germ-line mutations in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1416–1420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell L. B. Functional and structural analyses of mouse genomic regions screened by the morphological specific-locus test. Mutat Res. 1989 May;212(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(89)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell L. B., Hunsicker P. R., Cacheiro N. L., Bangham J. W., Russell W. L., Shelby M. D. Chlorambucil effectively induces deletion mutations in mouse germ cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3704–3708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell L. B., Montgomery C. S., Raymer G. D. Analysis of the albino-locus region of the mouse: IV. Characterization of 34 deficiencies. Genetics. 1982 Mar;100(3):427–453. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.3.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell L. B. Reciprocal relationship between mouse germ-cell mutagenesis and basic genetics: from early beginnings to future opportunities. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1989;14 (Suppl 16):23–29. doi: 10.1002/em.2850140607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. L., Kelly E. M. Mutation frequencies in male mice and the estimation of genetic hazards of radiation in men. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):542–544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. H., Holzberg S. Population genetics of Lebistes (Poecilia) reticulatus Peters (Poeciliidae; Pisces). I. Effects of radiation-induced mutations on the segregation ratio in postirradiation F 2 . Genetics. 1972 Apr;70(4):621–630. doi: 10.1093/genetics/70.4.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. H. X-ray-induced mutations in the poeciliid fish, Lebistes reticulatus Peters. Mutat Res. 1969 Jan-Feb;7(1):75–90. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(69)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sega G. A., Sotomayor R. E., Owens J. G. A study of unscheduled DNA synthesis induced by X-rays in the germ cells of male mice. Mutat Res. 1978 Feb;49(2):239–257. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(78)90163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shima A., Shimada A. Induction of mutations in males of the fish Oryzias latipes at a specific locus after gamma-irradiation. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;198(1):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(88)90044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



