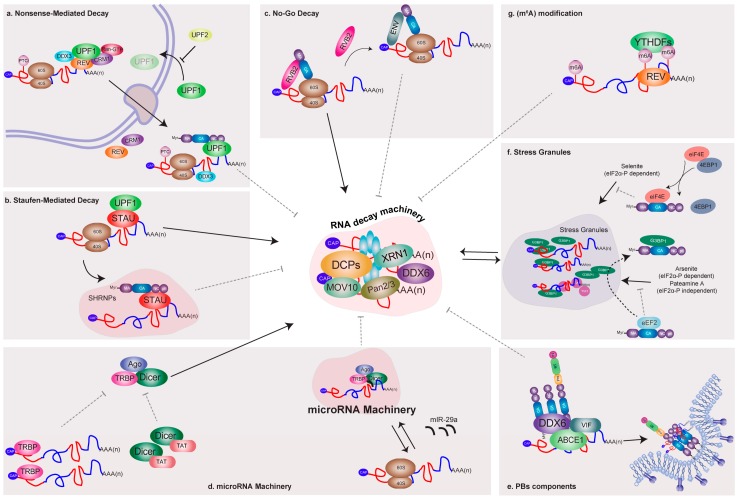
Figure 2.
The HIV-1 unspliced mRNA has been shown to recruit components of different mRNA decay pathways including: (a) UPF1 (NMD, nonsense-mediated decay); (b) STAU1/2 (SMD, STAU-mediated mRNA decay); (c) RuvB-like 2 (RVB2) (NGD, No-Go decay); (d) HIV-1 trans-activating response (TAR) RNA-binding protein (TRBP) and Argonaute (Ago) (microRNA Machinery); (e) DDX6 (PBs, processing bodies); (f) eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF2) and GTPase activating protein (GAP) SH3 domain-binding protein 1 (G3BP1) (SGs, stress granules); and (g) YTHDF2 (N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-dependent mRNA decay). Interestingly, most of these associations have been demonstrated to be beneficial for viral replication, suggesting that HIV-1 has evolved mechanisms to interact with these host factors in order to divert them from their functions in mRNA decay.