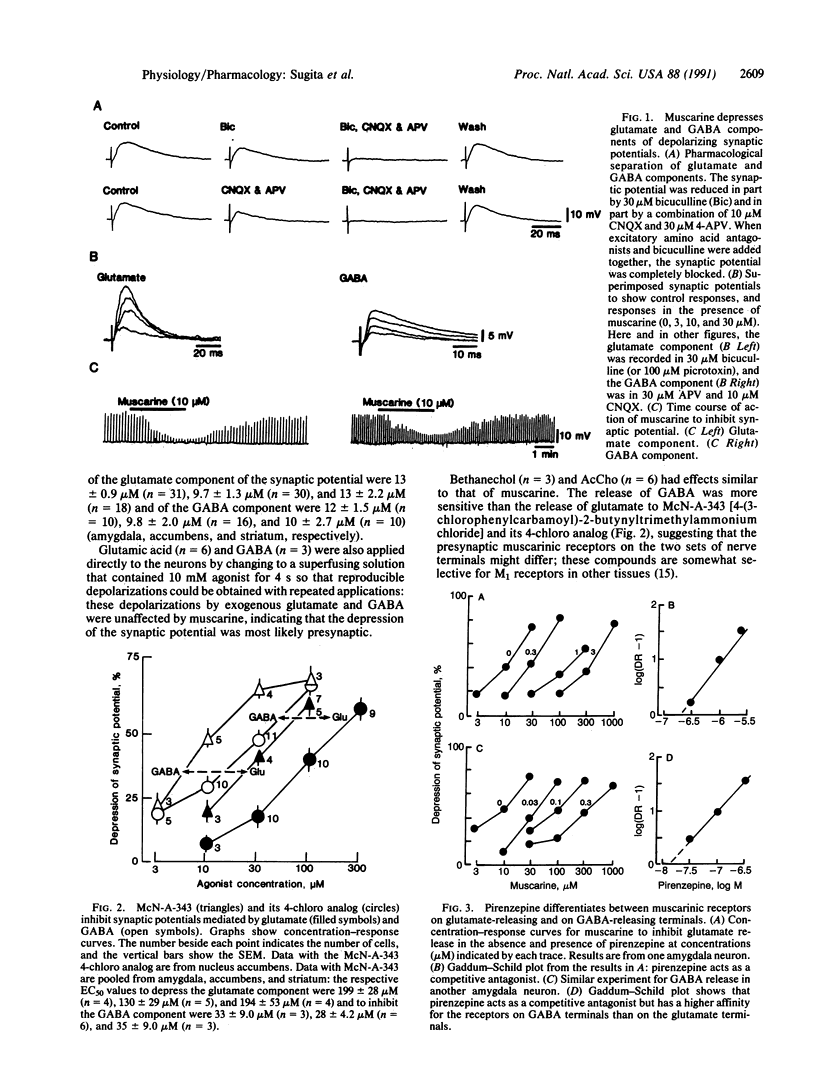
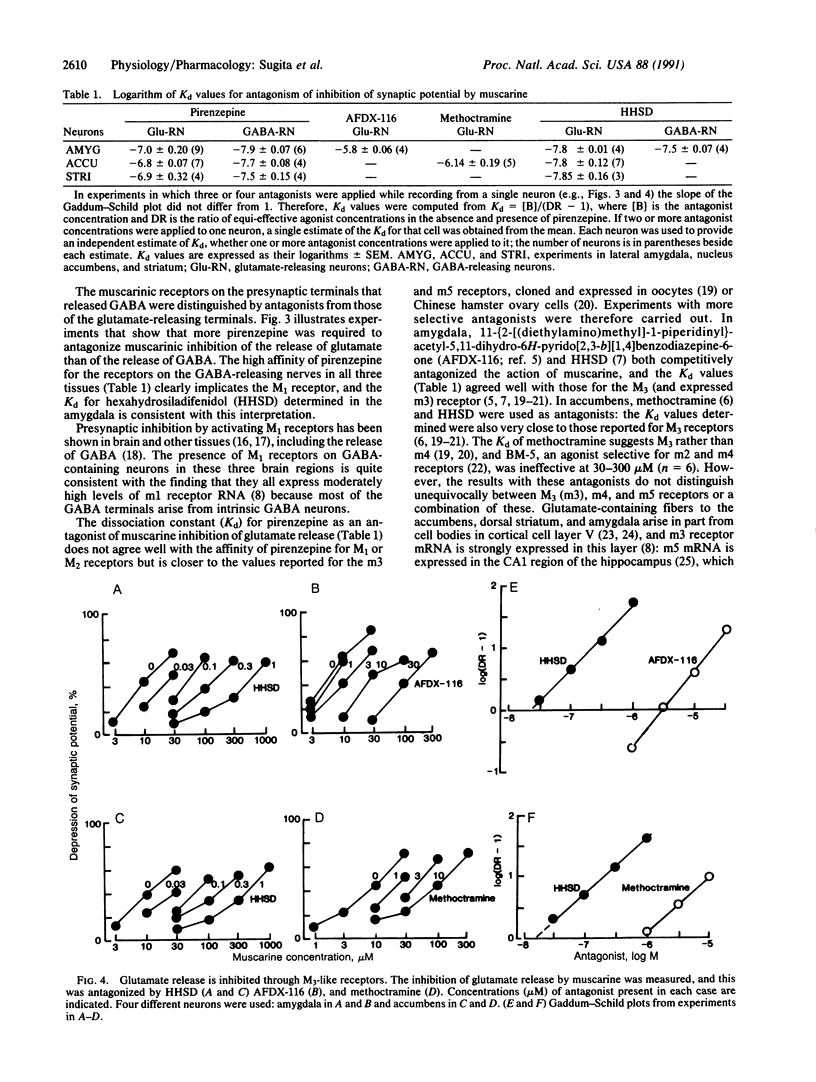
Abstract
Intracellular recordings were made from neurons of rat lateral amygdala, nucleus accumbens, and striatum in vitro. Synaptic potentials mediated by gamma-aminobutyric acid and by excitatory amino acids were isolated pharmacologically by using receptor antagonists, and their amplitudes were used as a measure of transmitter release. Muscarine and acetylcholine inhibited the release of both gamma-aminobutyric acid and excitatory amino acids, but measurements of the dissociation equilibrium constants for the antagonists pirenzepine, 11-(2-[(diethylamino)methyl]-1-piperidinyl)acetyl-5,11-dihydro-6H-pyrido [2,3-b][1,4]benzodiazepine-6-one, methoctramine, and hexahydrosiladifenidol indicated clearly that different muscarinic receptors were involved (M1 and probably M3, respectively). The differential localization of distinct muscarinic receptor subtypes on terminals releasing the major inhibitory and excitatory transmitters of the brain could be exploited therapeutically in some movement disorders and Alzheimer disease.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiba I., Kubo T., Maeda A., Bujo H., Nakai J., Mishina M., Numa S. Primary structure of porcine muscarinic acetylcholine receptor III and antagonist binding studies. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 1;235(1-2):257–261. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgold J., Drobnick A. An agonist that is selective for adenylate cyclase-coupled muscarinic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;36(3):465–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I. New subtypes of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Dec;Suppl:11–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I. The molecular basis of muscarinic receptor diversity. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Apr;12(4):148–151. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley N. J., Bonner T. I., Brann M. R. Localization of a family of muscarinic receptor mRNAs in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1988 Dec;8(12):4646–4652. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-12-04646.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley N. J., Bonner T. I., Buckley C. M., Brann M. R. Antagonist binding properties of five cloned muscarinic receptors expressed in CHO-K1 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;35(4):469–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. J., Summers R. J., Stephenson J. A., Cook C. J., Beart P. M. Excitatory amino acid projections to the nucleus accumbens septi in the rat: a retrograde transport study utilizing D[3H]aspartate and [3H]GABA. Neuroscience. 1987 Aug;22(2):425–439. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90345-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodt H. U., Misgeld U. Muscarinic slow excitation and muscarinic inhibition of synaptic transmission in the rat neostriatum. J Physiol. 1986 Nov;380:593–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eltz M., Gmelin G., Wess J., Strohmann C., Tacke R., Mutschler E., Lambrecht G. Presynaptic muscarinic receptors mediating inhibition of neurogenic contractions in rabbit vas deferens are of the ganglionic M1-type. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec 13;158(3):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giachetti A., Micheletti R., Montagna E. Cardioselective profile of AF-DX 116, a muscarine M2 receptor antagonist. Life Sci. 1986 May 5;38(18):1663–1672. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90410-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R., Berrie C. P., Birdsall N. J., Burgen A. S., Hulme E. C. Pirenzepine distinguishes between different subclasses of muscarinic receptors. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):90–92. doi: 10.1038/283090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasuo H., Gallagher J. P., Shinnick-Gallagher P. Disinhibition in the rat septum mediated by M1 muscarinic receptors. Brain Res. 1988 Jan 12;438(1-2):323–327. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91356-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamada M., Mehraein P. Verteilungsmuster der senilen Veränderungen im Gehirn. Die Beteiligung des limbischen Systems bei hirnatrophischen Prozessen des Seniums und bei Morbus Alzheimer. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr (1970) 1968;211(3):308–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00340827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. G., Coulter J. D., Burton H., Porter R. Cells of origin and terminal distribution of corticostriatal fibers arising in the sensory-motor cortex of monkeys. J Comp Neurol. 1977 May 1;173(1):53–80. doi: 10.1002/cne.901730105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazareno S., Roberts F. F. Functional and binding studies with muscarinic M2-subtype selective antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;98(1):309–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb16896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara J. O. Role of neurotransmitters in seizure mechanisms in the kindling model of epilepsy. Fed Proc. 1984 Jul;43(10):2516–2520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchiorre C., Cassinelli A., Quaglia W. Differential blockade of muscarinic receptor subtypes by polymethylene tetraamines. Novel class of selective antagonists of cardiac M-2 muscarinic receptors. J Med Chem. 1987 Jan;30(1):201–204. doi: 10.1021/jm00384a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchimura N., Cherubini E., North R. A. Inward rectification in rat nucleus accumbens neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Dec;62(6):1280–1286. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.62.6.1280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchimura N., Higashi H., Nishi S. Hyperpolarizing and depolarizing actions of dopamine via D-1 and D-2 receptors on nucleus accumbens neurons. Brain Res. 1986 Jun 11;375(2):368–372. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90760-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchimura N., North R. A. Muscarine reduces inwardly rectifying potassium conductance in rat nucleus accumbens neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Mar;422:369–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilaró M. T., Palacios J. M., Mengod G. Localization of m5 muscarinic receptor mRNA in rat brain examined by in situ hybridization histochemistry. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Jul 3;114(2):154–159. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90064-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerberg V., Corcoran M. E. Antagonism of central but not peripheral cholinergic receptors retards amygdala kindling in rats. Exp Neurol. 1987 Jan;95(1):194–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(87)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. H., Constanti A. Quantitative effects of some muscarinic agonists on evoked surface-negative field potentials recorded from the guinea-pig olfactory cortex slice. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;93(4):846–854. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11471.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



