Description
Symmetrical digital gangrene (SDG) is mostly due to low cardiac output and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) (table 1).1 We describe a 36-year-old right-handed man with SDG requiring amputation of 14 digits. He had received continuous intravenous infusion of epinephrine and dopamine given for a cardiac arrest that developed 1 hour after resection of a meningioma (table 2). In cardiogenic shock, he had decreased responsiveness, sinus tachycardia (135 bpm) and arterial hypotension (50/45 mm Hg). Advanced cardiac life support with mechanical ventilatory support was instituted. The administration of inotropic agents stabilised blood pressure to around 110/65, heart rate at 98 and mean arterial pressure (MAP) at 70 mm Hg. The patient's responsiveness improved gradually, but cardiovascular instability made him inotropic dependant.
Table 1.
Causes of symmetrical digital gangrene
| Hypercoagulable state |
Primary: Antithrombin III deficiency, protein C and protein S deficiency, abnormalities of the fibrinolytic system and dysfibrinogenemias. Secondary: DIC, malignancy, pregnancy, use of oral contraceptives, myeloproliferative disorders, hyperlipidaemia, diabetes mellitus, sickle cell anaemia, polycythemia rubra vera and Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia. |
| Ischaemic states | Low cardiac output, atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction. |
| Vasculitis |
Large vessels: Polymyalgia rheumatica, Takayasu's arteritis and temporal arteritis. Medium size vessels: Buerger's disease, cutaneous vasculitis, Kawasaki disease, and polyarteritis nodosa. Small vessels: Behçet's disease, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, cutaneous vasculitis, Henoch Schönlein purpura, microscopic polyangiitis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Golfer's vasculitis and cryoglobulinemia. |
| Autoimmune | Systemic lupus erythematous, connective tissue disease, antiphospholipid syndrome and Raynaud's phenomenon. |
| Drugs | Dopamine, epinephrine and norepinephrine. |
| Infection-sepsis | Septic shock, leprosy. |
| Physical agents | Trauma, vibration, electrical injuries, burns, lightning strike, low temperature (frostbite) and high altitude. |
| Other causes | Congenital erythropoietic porphyria, ainhum, Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, syringomyelia and long-term tobacco smoking. |
DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Table 2.
Drug therapy
| Intravenous therapy | Dosage | Period of treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Epinephrine | 1 mg intravenous push stat | Three times |
| Atropine | 1 mg intravenous push stat | Three times |
| Epinephrine | 10 mg/50 mL of solution 0.9% @ 8 mL/hour intravenous infusion | 4 days then the drug was weaned down in a period of 3 days |
| Dopamine | 400 mg/100 mL of solution 0.9% @ 10 mL/hour intravenous infusion | 4 days then the drug was wean down in a period of 3 days |
| Ceftriaxone | 2 g intravenous daily | 7 days |
| Subcutaneous drug | Dosage | Period of treatment |
| Enoxaparin | 40 mg subcutaneous daily | 10 days |
On day 3 postcardiac arrest, acute gangrene of the tips of 10 toes and right 4 fingers developed. There was painful inflammatory oedema with erythematous reaction in the regions of demarcation between the normal and the gangrenous areas. All peripheral pulses were normal and symmetric on palpation. The digits were cold and pale with no capillary refill distally. No other relevant findings on physical examination were found. A colour Doppler ultrasound scan of the upper and lower limb vessels indicated normal blood flow. The patient recovery from brain surgery and cardiorespiratory instability were uneventful. Inotropic agents were gradually weaned off and eventually discontinued. Mechanical ventilation support was discontinued successfully on day 7. Five tips of the toes underwent autoamputation over the next 3 months (figures 1A–E) after which the other affected distal phalanxes of the digits were surgically removed, and the stumps were surgically repaired (figures 2A,B). The patient's digit stumps healed satisfactorily. Extensive medical investigations were conducted, and differentials were ruled out (table 1). Blood cultures, urine cultures and swabs cultures from the wounds were sterile.
Figure 1.
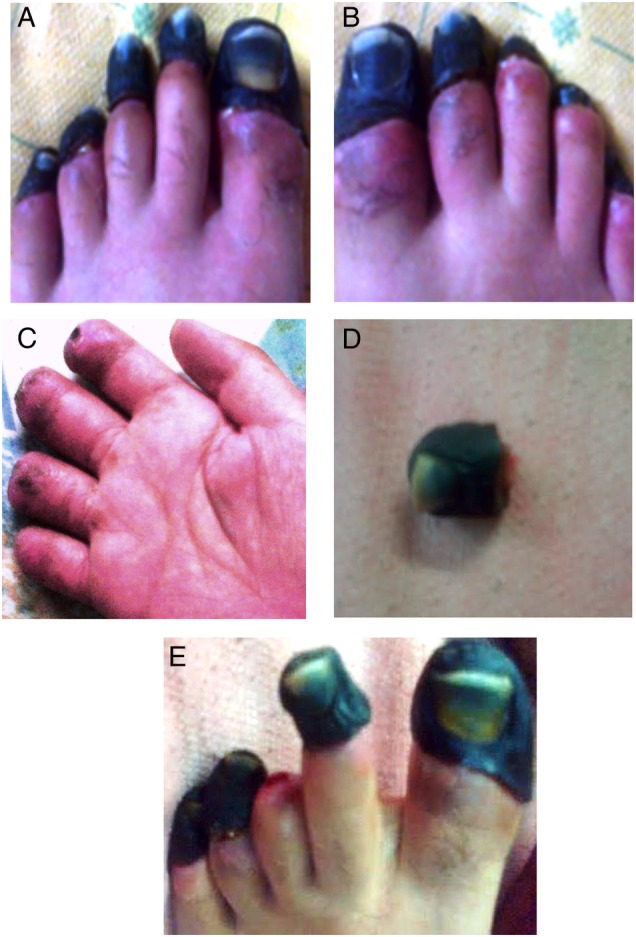
(A) Wet gangrene of all five toes of the left foot. (B) Wet gangrene of all five toes of the right foot. (C) Right four fingers after surgical amputation with good stump healing. (D) Big toe autoamputation showing gangrenous phalanx. (E) Third toe autoamputation left foot.
Figure 2.
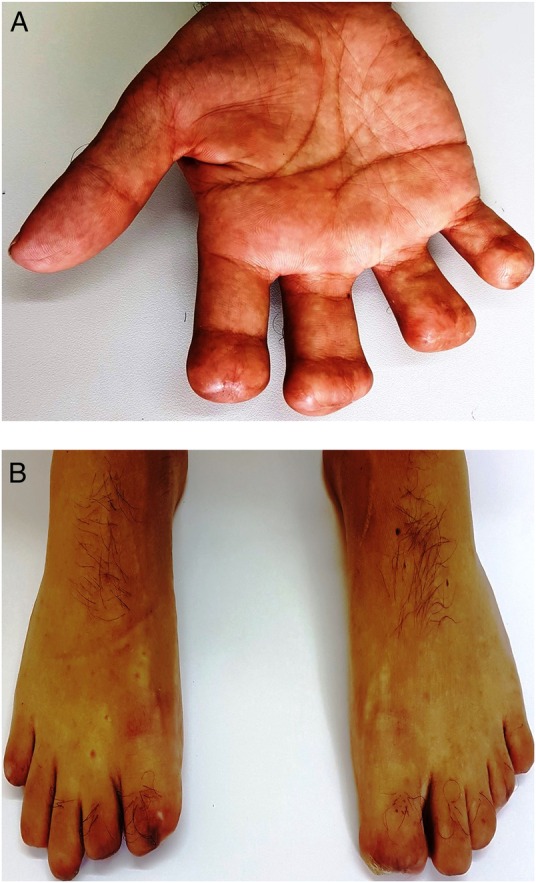
(A) Four right fingers stumps can be seen. (B) Ten toes stumps after 2 years are shown.
Two years later, the patient had normal cardiovascular and musculoskeletal systems, normal nerve conduction studies of the limbs and duplex ultrasound of the upper and lower limb vessels indicated normal flow bilaterally. The patient has remained on social welfare due to multiple digital amputations.
Cases of digital necrosis and amputation have been associated with accidental epinephrine injections in fingers or interdigital regions (EpiPens) and intravenous inotropic agents.2 3 SDG has been reported at dopamine intravenous infusion >5.1 µg/kg/min in patients who had DIC and hypovolaemia. SDG can occur as an adverse event even though at therapeutic epinephrine dose infusion. Studies have shown the occlusion of small blood vessels when the intraluminal pressure falls below a critical value leads to compromised flow through digital arteries at perfusion pressures between 36 and 60 mm Hg.1 We suggest this mechanism for the development of SDG in our patient. We believe severe hypotension may also have contributed to the SDG in our patient. Appropriate dosage of intravenous inotropic agents to treat hypovolemic shock, cardiogenic shock or other life-threatening cardiovascular depression or instability should be individualised according to age, body mass index, MAP and cardiovascular status of the patient.
Learning points.
Intravenous epinephrine and/or dopamine and/or norepinephrine are used commonly. They can cause digital gangrene as an adverse drug reaction even at recommended dosage levels.
Arterioles vasoconstriction seems to be the mechanism of gangrene induced by intravenous inotropic agents. Low cardiac output is also an important contributing factor to digital necrosis.
Dosage of intravenous inotropic agents should be calculated individually and according to age, body mass index, mean arterial pressure (MAP) and cardiovascular condition, which may be safer than the usual standard of keeping MAP around 70 mm Hg.
Digital gangrene has an increased risk of amputation of limbs with a decrease in functional capacity and quality of life.
Since the differential diagnosis of digital gangrene is vast and no specific treatment for gangrene induced by intravenous inotropic agents has been determined, treatment has to be individualised.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patient for allowing to use his medical data for teaching purposes. The authors also thank their other staff for caring for the patient. They are thankful to the photography department for preparing the images.
Footnotes
Contributors: The conception, design and acquisition of data were carried out by AJR. The drafting of the article was also carried out by AJR. All authors contributed to the revisions for intellectual content and approve of the final version. KR and AJR are accountable for the article and will ensure that all questions regarding the accuracy and integrity of the article are investigated and resolved.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent: Obtained.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.Colak T, Erdogan O, Yerebakan O et al. Symmetrical peripheral gangrene and dopamine. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2003;9:222–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Velissariou I, Cottrell S, Berry K et al. Management of adrenaline (epinephrine) induced digital ischaemia in children after accidental injection from an EpiPen. Emerg Med J 2004;21:387–8. doi:10.1136/emj.2003.005462 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Joynt G, Doedens L, Lipman J et al. High-dose adrenaline with low systemic vascular resistance and symmetrical peripheral gangrene. S Afr J Surg 1996;34:99–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


