Abstract
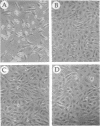
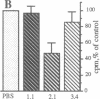
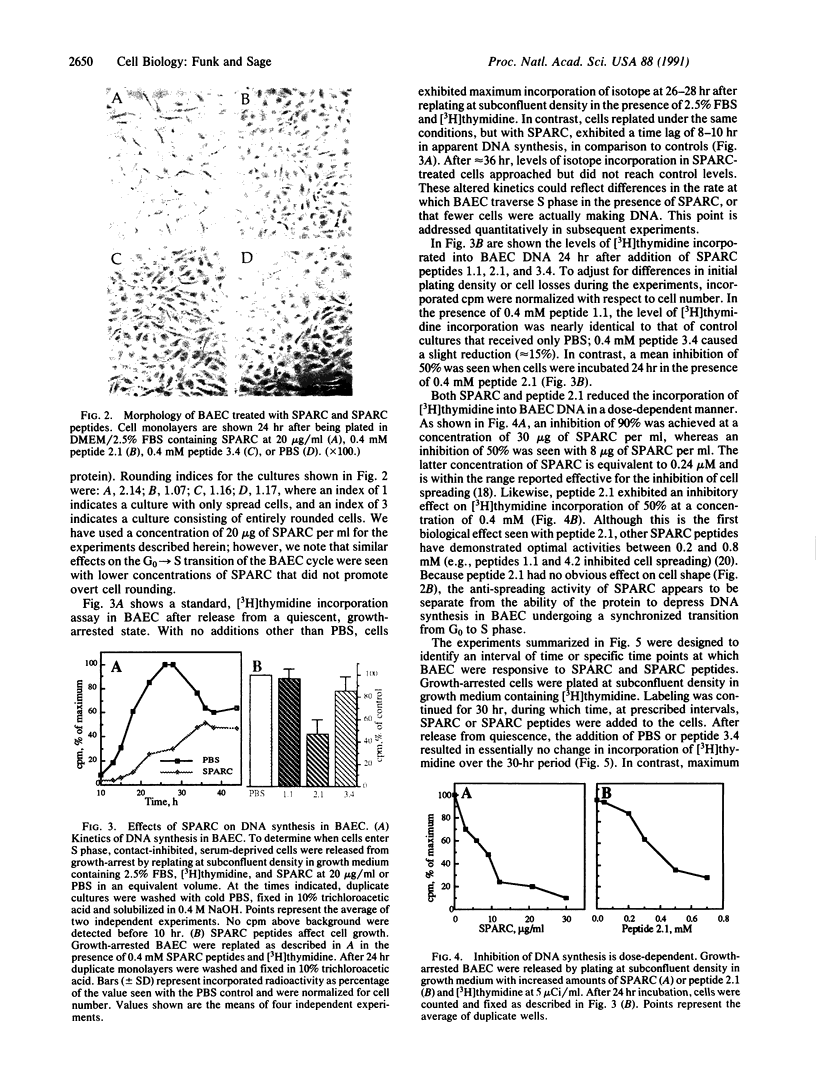
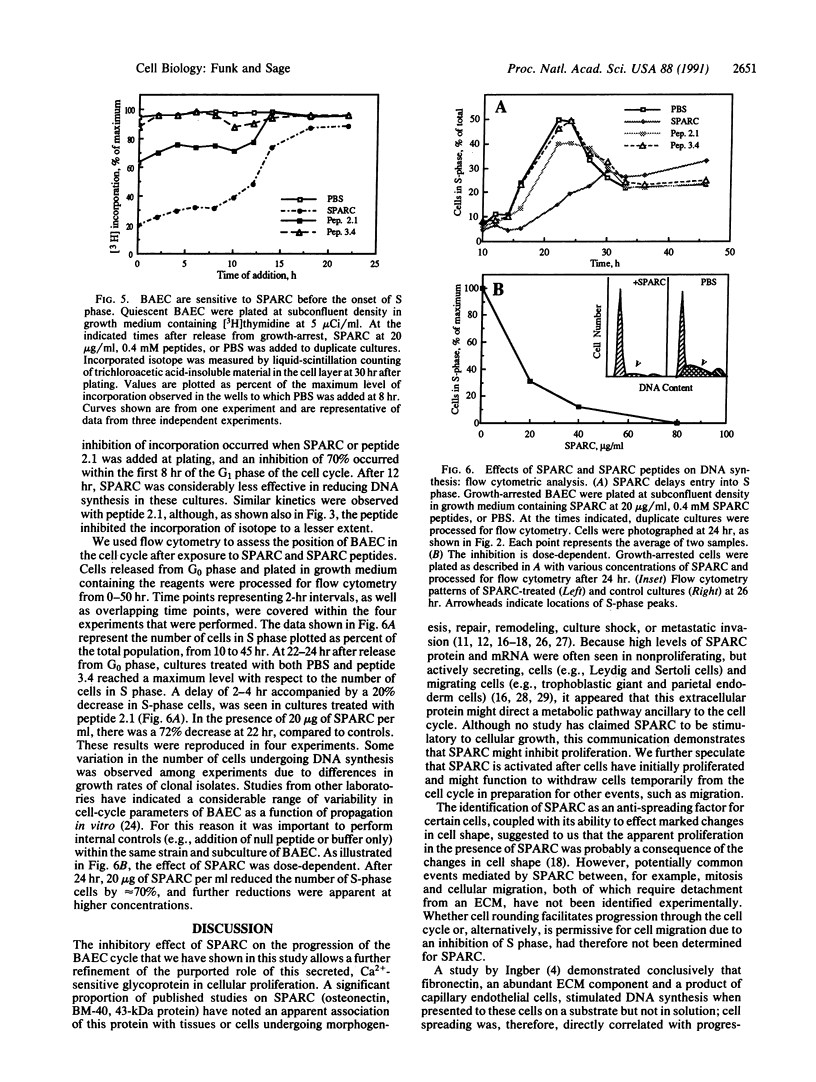
SPARC (secreted protein, acidic and rich in cysteine) is an extracellular, Ca2(+)-binding protein associated with cellular populations undergoing migration, proliferation, and/or differentiation. Active preparations of SPARC bind to specific components of the extracellular matrix and cause mesenchymal cells to assume a rounded phenotype. In this study we show that SPARC modulates the progression of bovine aortic endothelial cells through the cell cycle. At a concentration of 20 micrograms/ml, SPARC inhibited the incorporation of [3H]thymidine into newly synthesized DNA by approximately 70%, as compared to control cultures within 24 hr after the release from G0 phase. The effect was dose-dependent and reached greater than 90% inhibition at 30 micrograms of SPARC per ml after 24 hr. A 20-residue synthetic peptide (termed 2.1) from a non-Ca2(+)-binding, disulfide-rich domain of SPARC also exhibited a dose-dependent inhibition of [3H]thymidine uptake in endothelial cells within 24 hr after release from G0 phase. An inhibition of 50% was seen with peptide 2.1 at a 0.4 mM concentration. Peptides from other regions of the SPARC protein did not produce this effect. Maximum inhibition of [3H]thymidine uptake by SPARC and peptide 2.1 occurred during the early-to-middle G1 phase of the endothelial-cell cycle. From 0-12 hr after release from G0 phase, cells exhibited delayed entry into S phase, which normally occurred at 24 +/- 2 hr. These results were further corroborated by flow cytometry. In the presence of SPARC at 20 micrograms/ml, 72% fewer cells were in S phase after a 24-hr period; a similar, but less marked, reduction was seen with peptide 2.1. Peptide 2.1 did not cause cell rounding, whereas peptide 1.1, a highly efficient inhibitor of endothelial-cell spreading, exhibited essentially no activity with respect to cell-cycle progression. It therefore appears that the transient, inhibitory effect of SPARC on the entry of endothelial cells into S phase does not depend on the overt changes in cell shape mediated through cytoskeletal rearrangement.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolander M. E., Young M. F., Fisher L. W., Yamada Y., Termine J. D. Osteonectin cDNA sequence reveals potential binding regions for calcium and hydroxyapatite and shows homologies with both a basement membrane protein (SPARC) and a serine proteinase inhibitor (ovomucoid). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2919–2923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellot J. J., Jr, Pukac L. A., Caleb B. L., Wright T. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. Heparin selectively inhibits a protein kinase C-dependent mechanism of cell cycle progression in calf aortic smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3147–3155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng C. Y. Purification of a calcium binding protein (rat SPARC) from primary Sertoli cell-enriched culture medium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 30;167(3):1393–1399. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90677-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccarelli C., Philipson L., Sorrentino V. Regulation of expression of growth arrest-specific genes in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1525–1529. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziadek M., Paulsson M., Aumailley M., Timpl R. Purification and tissue distribution of a small protein (BM-40) extracted from a basement membrane tumor. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Dec 1;161(2):455–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J., Taylor W., Paulsson M., Sage H., Hogan B. Calcium binding domains and calcium-induced conformational transition of SPARC/BM-40/osteonectin, an extracellular glycoprotein expressed in mineralized and nonmineralized tissues. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 3;26(22):6958–6965. doi: 10.1021/bi00396a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. C., von Hippel P. H. Calculation of protein extinction coefficients from amino acid sequence data. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 1;182(2):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90602-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith J. C., McCormick J. J., Yen A. Endothelial cell cycle kinetics. Changes in culture and correlation with endothelial properties. Lab Invest. 1984 Dec;51(6):643–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimark R. L., Schwartz S. M. The role of membrane-membrane interactions in the regulation of endothelial cell growth. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1934–1940. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman I. M., Castellot J. J., Jr Regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell growth by endothelial-synthesized extracellular matrices. Arteriosclerosis. 1987 Sep-Oct;7(5):463–469. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.7.5.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P. W., Harper S. J., McVey J. H., Hogan B. L. In vivo expression of mRNA for the Ca++-binding protein SPARC (osteonectin) revealed by in situ hybridization. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):473–482. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E. Fibronectin controls capillary endothelial cell growth by modulating cell shape. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3579–3583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer J. C., Wojta J., Christ G., Binder B. R. Functional inhibition of endogenously produced urokinase decreases cell proliferation in a human melanoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5424–5428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane T. F., Sage E. H. Functional mapping of SPARC: peptides from two distinct Ca+(+)-binding sites modulate cell shape. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3065–3076. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitman D. C., Fiscus R. R., Murad F. Forskolin, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, and cyclic AMP analogs inhibit proliferation of cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1986 May;127(2):237–243. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041270208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liau G., Chan L. M. Regulation of extracellular matrix RNA levels in cultured smooth muscle cells. Relationship to cellular quiescence. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10315–10320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majack R. A., Bornstein P. Heparin and related glycosaminoglycans modulate the secretory phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1688–1695. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majack R. A., Clowes A. W. Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell migration by heparin-like glycosaminoglycans. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Mar;118(3):253–256. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041180306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maness P. F., Walsh R. C., Jr Dihydrocytochalasin B disorganizes actin cytoarchitecture and inhibits initiation of DNA synthesis in 3T3 cells. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason I. J., Taylor A., Williams J. G., Sage H., Hogan B. L. Evidence from molecular cloning that SPARC, a major product of mouse embryo parietal endoderm, is related to an endothelial cell 'culture shock' glycoprotein of Mr 43,000. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1465–1472. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04383.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley C. G., Kingdon H. S. Use of 3 H-thymidine for measurement of DNA synthesis in rat liver--a warning. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jan;45(1):298–305. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch P. S., Kubbies M., Chen Y. C., Schindler D., Hoehn H. BrdU-Hoechst flow cytometry: a unique tool for quantitative cell cycle analysis. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Feb;174(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90302-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen C. D., Means A. R. Calmodulin is required for cell-cycle progression during G1 and mitosis. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):73–82. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03350.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid B. J., Haggitt R. C., Rubin C. E., Rabinovitch P. S. Barrett's esophagus. Correlation between flow cytometry and histology in detection of patients at risk for adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jul;93(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly C. F., Kindy M. S., Brown K. E., Rosenberg R. D., Sonenshein G. E. Heparin prevents vascular smooth muscle cell progression through the G1 phase of the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6990–6995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Johnson C., Bornstein P. Characterization of a novel serum albumin-binding glycoprotein secreted by endothelial cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3993–4007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Tupper J., Bramson R. Endothelial cell injury in vitro is associated with increased secretion of an Mr 43,000 glycoprotein ligand. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Jun;127(3):373–387. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041270305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Vernon R. B., Decker J., Funk S., Iruela-Arispe M. L. Distribution of the calcium-binding protein SPARC in tissues of embryonic and adult mice. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Jun;37(6):819–829. doi: 10.1177/37.6.2723400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Vernon R. B., Funk S. E., Everitt E. A., Angello J. SPARC, a secreted protein associated with cellular proliferation, inhibits cell spreading in vitro and exhibits Ca+2-dependent binding to the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):341–356. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen J., Domenicucci C., Goldberg H. A., Sodek J. Immunohistochemical localization of SPARC (osteonectin) and denatured collagen and their relationship to remodelling in rat dental tissues. Arch Oral Biol. 1990;35(5):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(90)90180-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher W. The role of extracellular proteases in cell proliferation and differentiation. Lab Invest. 1987 Dec;57(6):607–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorgente N., Bullard D. L., Jakovljevic L., Dorey K. Endogenous regulation of endothelial cell proliferation. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1984 Nov;17(6):573–582. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1984.tb00616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino V., Pepperkok R., Davis R. L., Ansorge W., Philipson L. Cell proliferation inhibited by MyoD1 independently of myogenic differentiation. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):813–815. doi: 10.1038/345813a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termine J. D., Kleinman H. K., Whitson S. W., Conn K. M., McGarvey M. L., Martin G. R. Osteonectin, a bone-specific protein linking mineral to collagen. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. B., Sage H. The calcium-binding protein SPARC is secreted by Leydig and Sertoli cells of the adult mouse testis. Biol Reprod. 1989 Jun;40(6):1329–1340. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod40.6.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. Positive and negative controls on cell growth. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8263–8269. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewer U. M., Albrechtsen R., Fisher L. W., Young M. F., Termine J. D. Osteonectin/SPARC/BM-40 in human decidua and carcinoma, tissues characterized by de novo formation of basement membrane. Am J Pathol. 1988 Aug;132(2):345–355. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]