Abstract
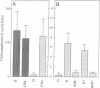
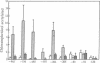
We have developed a transient gene expression assay system in the aquatic monocot Lemna gibba in which DNA was introduced into intact tissue by particle bombardment. Constructs based on the Lemna rbcS gene SSU5B, which is positively regulated by phytochrome in vivo, also showed phytochrome regulation in the transient assay system. Reporter gene expression increased 12-fold over dark levels in response to a single treatment with red light. This increase was not observed if far-red light was immediately followed by the red light. A 5' deletion analysis of the promoter defined a region from position -205 to position -83 relative to the start of transcription as necessary to observe the phytochrome response. This region contains the binding site for the light-induced binding activity (LRF-1) found in Lemna nuclear extracts. Upstream of position -205, we found evidence for the presence of at least two upstream activating sequences and a silencer.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruce W. B., Christensen A. H., Klein T., Fromm M., Quail P. H. Photoregulation of a phytochrome gene promoter from oat transferred into rice by particle bombardment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9692–9696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce W. B., Quail P. H. cis-acting elements involved in photoregulation of an oat phytochrome promoter in rice. Plant Cell. 1990 Nov;2(11):1081–1089. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.11.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzby J. S., Yamada T., Tobin E. M. A light-regulated DNA-binding activity interacts with a conserved region of a Lemna gibba rbcS promoter. Plant Cell. 1990 Aug;2(8):805–814. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.8.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callis J., Fromm M., Walbot V. Introns increase gene expression in cultured maize cells. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1183–1200. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castresana C., Garcia-Luque I., Alonso E., Malik V. S., Cashmore A. R. Both positive and negative regulatory elements mediate expression of a photoregulated CAB gene from Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):1929–1936. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03030.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald R. G., Cashmore A. R. Mutation of either G box or I box sequences profoundly affects expression from the Arabidopsis rbcS-1A promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1717–1726. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08295.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluhr R., Kuhlemeier C., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Organ-specific and light-induced expression of plant genes. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1106–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4754.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin P. M., Chua N. H. Localization of a phytochrome-responsive element within the upstream region of pea rbcS-3A. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5565–5568. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuliano G., Pichersky E., Malik V. S., Timko M. P., Scolnik P. A., Cashmore A. R. An evolutionarily conserved protein binding sequence upstream of a plant light-regulated gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7089–7093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. A., Klein T. M., Roth B. A., Fromm M. E., Cone K. C., Radicella J. P., Chandler V. L. Transactivation of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes following transfer of B regulatory genes into maize tissues. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2517–2522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon-Kamm W. J., Spencer T. M., Mangano M. L., Adams T. R., Daines R. J., Start W. G., O'Brien J. V., Chambers S. A., Adams W. R., Jr, Willetts N. G. Transformation of Maize Cells and Regeneration of Fertile Transgenic Plants. Plant Cell. 1990 Jul;2(7):603–618. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.7.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Kay S. A., Chua N. H. Sequence-specific interactions of a pea nuclear factor with light-responsive elements upstream of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2543–2549. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein T. M., Roth B. A., Fromm M. E. Regulation of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes introduced into intact maize tissues by microprojectiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6681–6685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlemeier C., Cuozzo M., Green P. J., Goyvaerts E., Ward K., Chua N. H. Localization and conditional redundancy of regulatory elements in rbcS-3A, a pea gene encoding the small subunit of ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4662–4666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlemeier C., Fluhr R., Green P. J., Chua N. H. Sequences in the pea rbcS-3A gene have homology to constitutive mammalian enhancers but function as negative regulatory elements. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):247–255. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E., Chua N. H. GT-1 binding site confers light responsive expression in transgenic tobacco. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):471–474. doi: 10.1126/science.2330508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E., Kano-Murakami Y., Gilmartin P., Niner B., Chua N. H. A metal-dependent DNA-binding protein interacts with a constitutive element of a light-responsive promoter. Plant Cell. 1990 Sep;2(9):857–866. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.9.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy F., Boutry M., Hsu M. Y., Wong M., Chua N. H. The 5'-proximal region of the wheat Cab-1 gene contains a 268-bp enhancer-like sequence for phytochrome response. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2537–2542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler U., Cashmore A. R. Photoregulated gene expression may involve ubiquitous DNA binding proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3415–3427. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverthorne J., Tobin E. M. Demonstration of transcriptional regulation of specific genes by phytochrome action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1112–1116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverthorne J., Wimpee C. F., Yamada T., Rolfe S. A., Tobin E. M. Differential expression of individual genes encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in Lemna gibba. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Jul;15(1):49–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00017723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberon X., Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. IV. Deletion derivatives of pBR322 and pBR325. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90328-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiekema W. J., Wimpee C. F., Tobin E. M. Nucleotide sequence encoding the precursor of the small subunit of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Lemna gibba L.G-3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):8051–8061. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.8051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]