Abstract
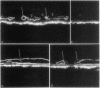
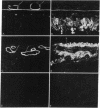
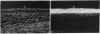
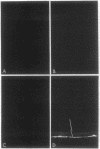
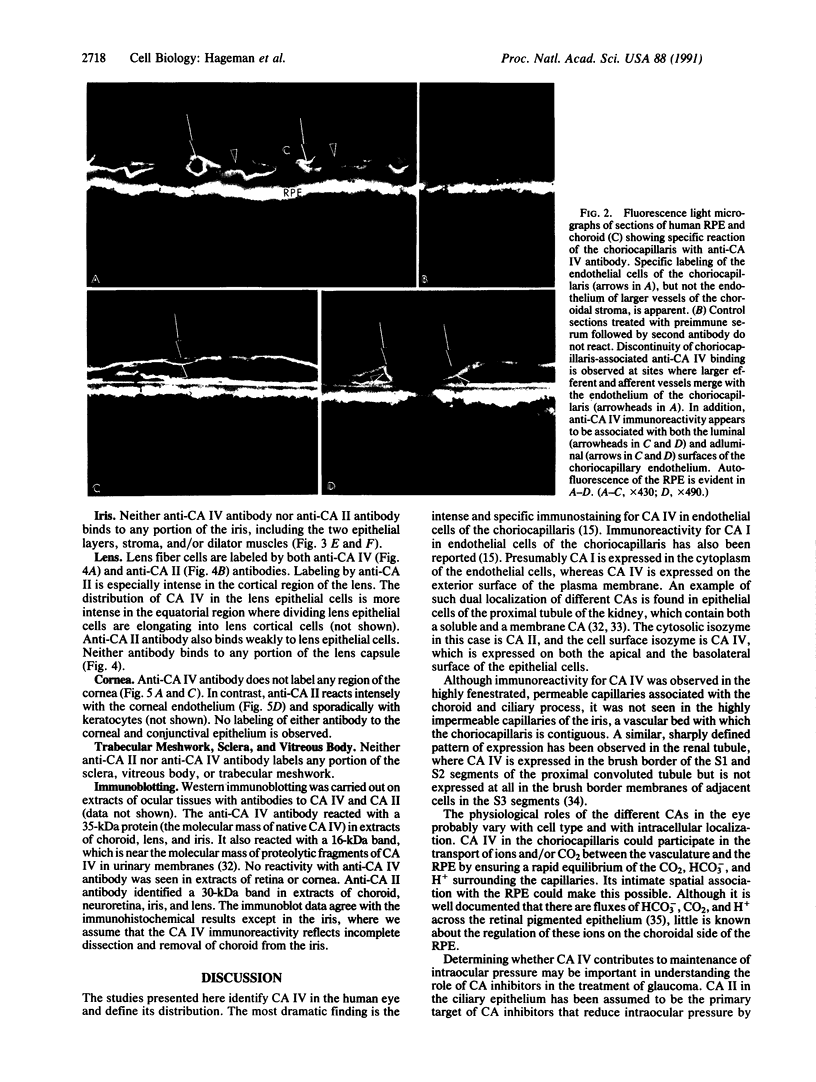
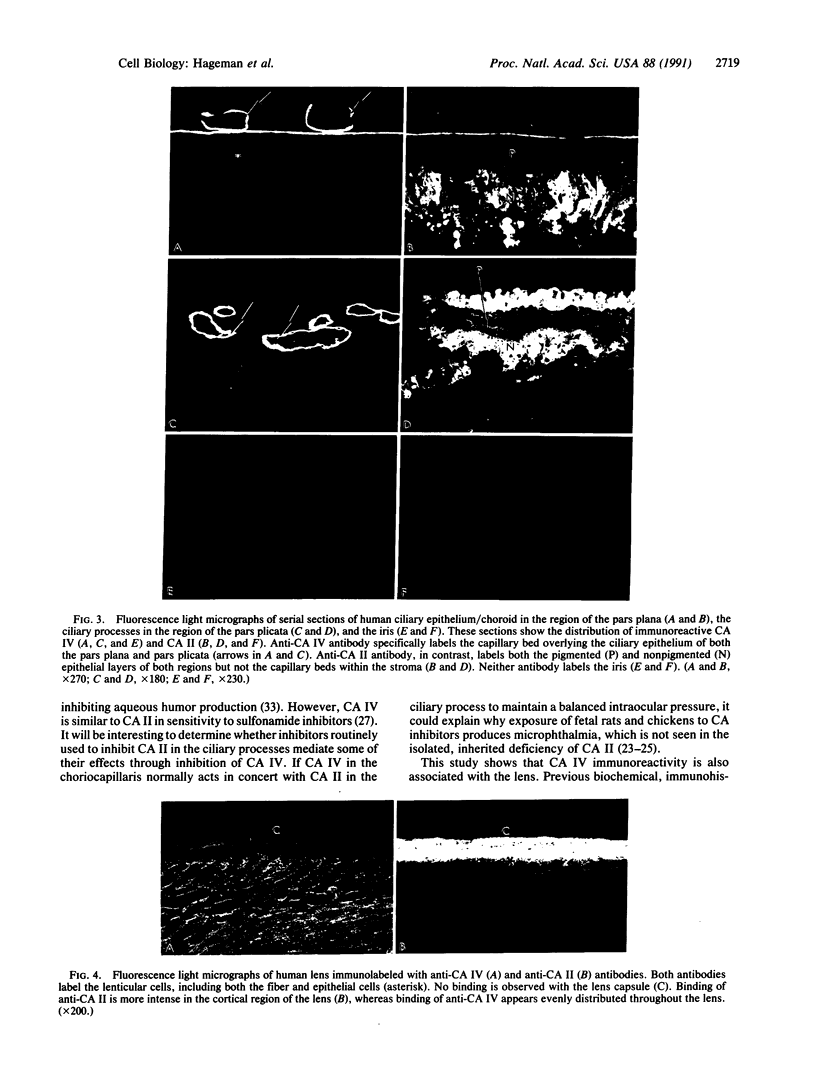
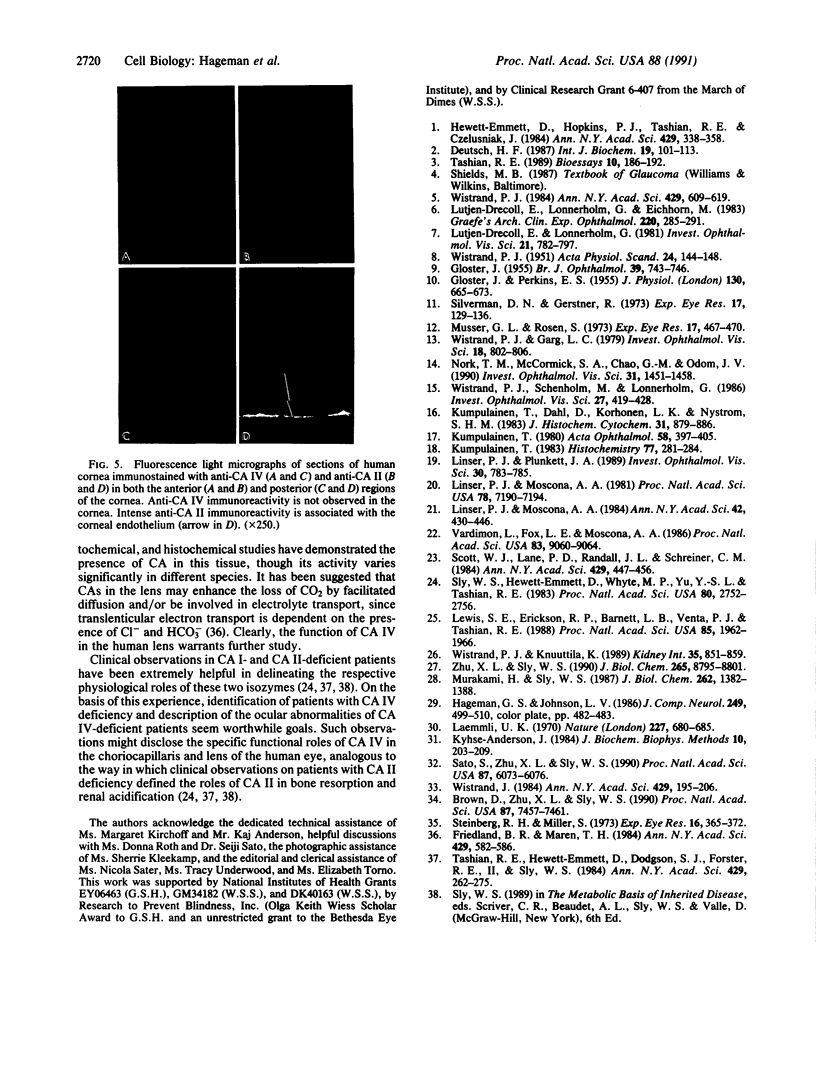
Carbonic anhydrase (CA) activity plays an important role in controlling aqueous humor production in the eye and in regulating intraocular pressure. Prior studies identified the soluble isozymes CA II and CA I in the human eye and also suggested a distinct membrane-associated CA. We used an antibody to CA IV, the membrane-anchored isozyme from human lung, to study CA IV in eye tissues and to compare its distribution with that of CA II. We found intense immunostaining for CA IV associated with endothelial cells of one specific uveal capillary bed, the choriocapillaris. CA IV was not detected in endothelial cells of the contiguous capillaries of the iris or in endothelial cells of other vessels. Immunoreactivity for CA IV was also intense in epithelial and fiber cells of the lens but was not detectable in the neuroretina, the ciliary process (except for capillaries), and the cornea, all sites where immunostaining with anti-CA II antibody was intense. These studies indicate that the membrane-associated CA in human eye, which was suspected from histochemical studies, is CA IV. Defining the physiological role of this ocular isozyme remains a challenge.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown D., Zhu X. L., Sly W. S. Localization of membrane-associated carbonic anhydrase type IV in kidney epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7457–7461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch H. F. Carbonic anhydrases. Int J Biochem. 1987;19(2):101–113. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(87)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland B. R., Maren T. H. The role of carbonic anhydrase in lens ion transport and metabolism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;429:582–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb12391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOSTER J. Investigation of the carbonic anhydrase content of the cornea of the rabbit. Br J Ophthalmol. 1955 Dec;39(12):743–746. doi: 10.1136/bjo.39.12.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOSTER J., PERKINS E. S. Carbonic anhydrase in the lens and in the ciliary body and iris of albino rabbits. J Physiol. 1955 Dec 29;130(3):665–673. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman G. S., Johnson L. V. Biochemical characterization of the major peanut-agglutinin-binding glycoproteins in vertebrate retinae. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Jul 22;249(4):499-510, 482-3. doi: 10.1002/cne.902490406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewett-Emmett D., Hopkins P. J., Tashian R. E., Czelusniak J. Origins and molecular evolution of the carbonic anhydrase isozymes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;429:338–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb12359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumpulainen T. Carbonic anhydrase isoenzyme C in the human retina. An immunohistochemical study. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1980 Jun;58(3):397–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1980.tb05739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumpulainen T., Dahl D., Korhonen L. K., Nyström S. H. Immunolabeling of carbonic anhydrase isoenzyme C and glial fibrillary acidic protein in paraffin-embedded tissue sections of human brain and retina. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Jul;31(7):879–886. doi: 10.1177/31.7.6406590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumpulainen T. Immunohistochemical demonstration of carbonic anhydrase isoenzyme C in the epithelium of the human ciliary processes. Histochemistry. 1983;77(2):281–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00506571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyhse-Andersen J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Dec;10(3-4):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. E., Erickson R. P., Barnett L. B., Venta P. J., Tashian R. E. N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea-induced null mutation at the mouse Car-2 locus: an animal model for human carbonic anhydrase II deficiency syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1962–1966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linser P. J., Plunkett J. A. A role for carbonic anhydrase in early eye morphogenesis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1989 Apr;30(4):783–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linser P., Moscona A. A. Carbonic anhydrase C in the neural retina: transition from generalized to glia-specific cell localization during embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7190–7194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linser P., Moscona A. A. Variable CA II compartmentalization in vertebrate retina. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;429:430–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb12369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütjen-Drecoll E., Lönnerholm G. Carbonic anhydrase distribution in the rabbit eye by light and electron microscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981 Dec;21(6):782–797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütjen-Drecoll E., Lönnerholm G., Eichhorn M. Carbonic anhydrase distribution in the human and monkey eye by light and electron microscopy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1983;220(6):285–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00231357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami H., Sly W. S. Purification and characterization of human salivary carbonic anhydrase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1382–1388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser G. L., Rosen S. Carbonic anhydrase activity in primate photoreceptors. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Apr;15(4):467–470. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90138-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nork T. M., McCormick S. A., Chao G. M., Odom J. V. Distribution of carbonic anhydrase among human photoreceptors. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1990 Aug;31(8):1451–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Zhu X. L., Sly W. S. Carbonic anhydrase isozymes IV and II in urinary membranes from carbonic anhydrase II-deficient patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6073–6076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. J., Jr, Lane P. D., Randall J. L., Schreiner C. M. Malformations in nonlimb structures induced by acetazolamide and other inhibitors of carbonic anhydrase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;429:447–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb12370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. N., Gerster R. The detection and localization of carbonic anhydrase in the rabbit cornea. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Oct 24;17(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sly W. S., Hewett-Emmett D., Whyte M. P., Yu Y. S., Tashian R. E. Carbonic anhydrase II deficiency identified as the primary defect in the autosomal recessive syndrome of osteopetrosis with renal tubular acidosis and cerebral calcification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2752–2756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. H., Miller S. Aspects of electrolyte transport in frog pigment epithelium. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Aug 24;16(5):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashian R. E., Hewett-Emmett D., Dodgson S. J., Forster R. E., 2nd, Sly W. S. The value of inherited deficiencies of human carbonic anhydrase isozymes in understanding their cellular roles. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;429:262–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb12346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashian R. E. The carbonic anhydrases: widening perspectives on their evolution, expression and function. Bioessays. 1989 Jun;10(6):186–192. doi: 10.1002/bies.950100603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardimon L., Fox L. E., Moscona A. A. Developmental regulation of glutamine synthetase and carbonic anhydrase II in neural retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9060–9064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISTRAND P. J. Carbonic anhydrase in the anterior uvea of the rabbit. Acta Physiol Scand. 1951;24(2-3):145–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1951.tb00833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistrand P. J., Garg L. C. Evidence of a high-activity C type of carbonic anhydrase in human ciliary processes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1979 Aug;18(8):802–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistrand P. J., Knuuttila K. G. Renal membrane-bound carbonic anhydrase. Purification and properties. Kidney Int. 1989 Mar;35(3):851–859. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistrand P. J. Properties of membrane-bound carbonic anhydrase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;429:195–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb12333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistrand P. J., Schenholm M., Lönnerholm G. Carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes CA I and CA II in the human eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1986 Mar;27(3):419–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistrand P. J. The use of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors in ophthalmology and clinical medicine. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;429:609–619. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb12398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X. L., Sly W. S. Carbonic anhydrase IV from human lung. Purification, characterization, and comparison with membrane carbonic anhydrase from human kidney. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8795–8801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]