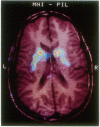
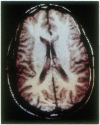
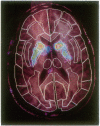
Abstract
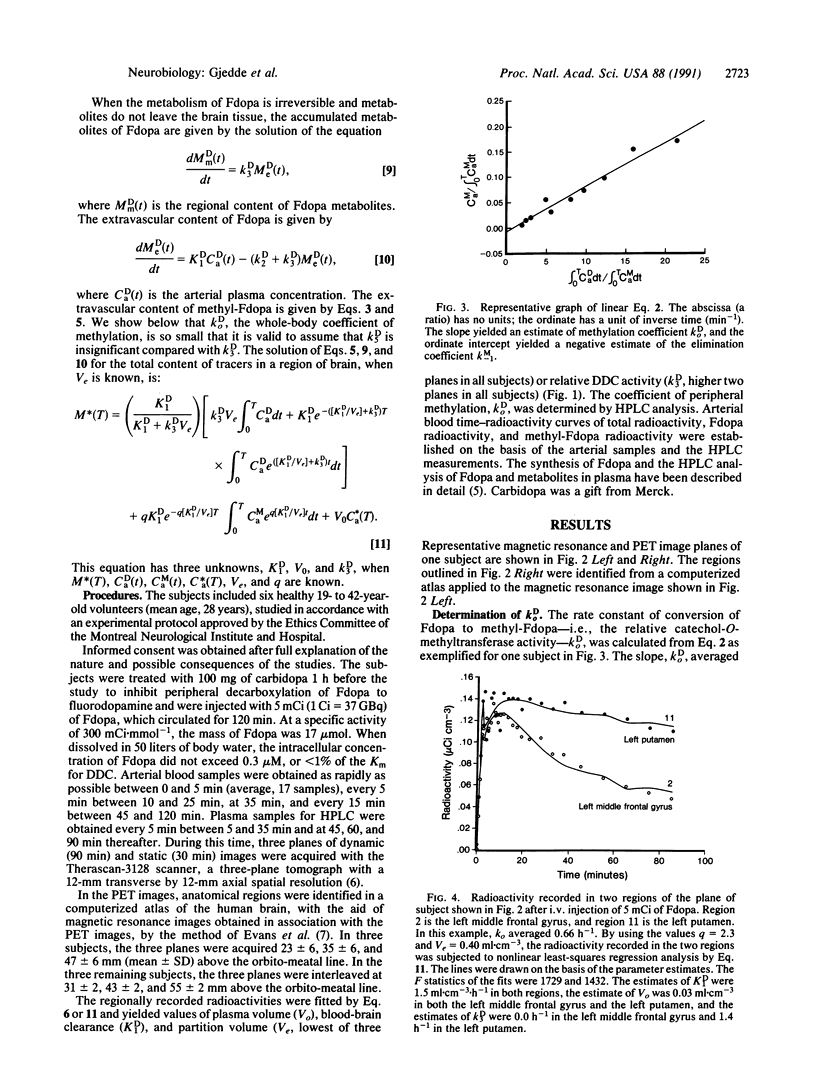
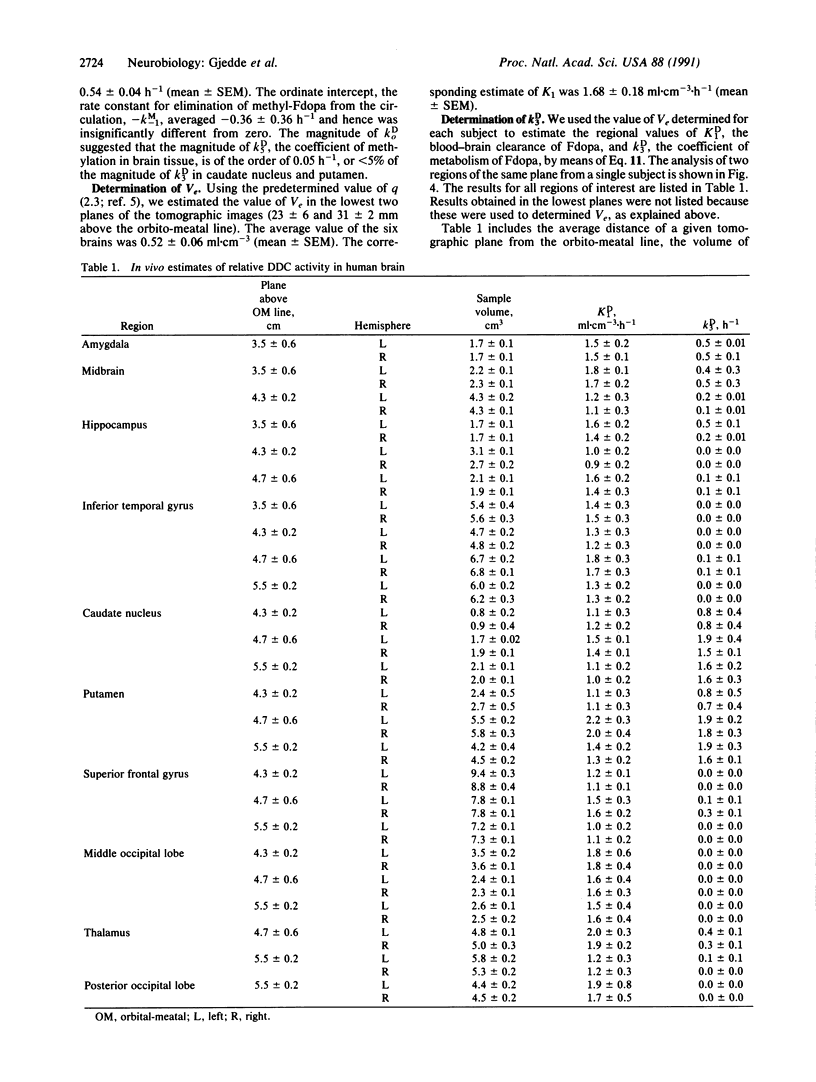
Monoaminergic neurons use dopa decarboxylase (DDC; aromatic-L-amino-acid carboxy-lyase, EC 4.1.1.28) to form dopamine from L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-dopa). We measured regional dopa decarboxylase activity in brains of six healthy volunteers with 6-[18F]fluoro-L-dopa and positron emission tomography. We calculated the enzyme activity, relative to its Km, with a kinetic model that yielded the relative rate of conversion of 6-[18F]fluoro-L-dopa to [18F]fluorodopamine. Regional values of relative dopa decarboxylase activity ranged from nil in occipital cortex to 1.9 h-1 in caudate nucleus and putamen, in agreement with values obtained in vitro.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Evans A. C., Beil C., Marrett S., Thompson C. J., Hakim A. Anatomical-functional correlation using an adjustable MRI-based region of interest atlas with positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1988 Aug;8(4):513–530. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1988.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firnau G., Sood S., Chirakal R., Nahmias C., Garnett E. S. Cerebral metabolism of 6-[18F]fluoro-L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine in the primate. J Neurochem. 1987 Apr;48(4):1077–1082. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05629.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnett E. S., Firnau G., Chan P. K., Sood S., Belbeck L. W. [18F]fluoro-dopa, an analogue of dopa, and its use in direct external measurements of storage, degradation, and turnover of intracerebral dopamine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):464–467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnett E. S., Firnau G., Nahmias C. Dopamine visualized in the basal ganglia of living man. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):137–138. doi: 10.1038/305137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. J., Huang S. C., Phelps M. E. Quantitation in positron emission computed tomography: 1. Effect of object size. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1979 Jun;3(3):299–308. doi: 10.1097/00004728-197906000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. M., Ellis J. R., Jr, Eden M. Analysis of emission tomographic scan data: limitations imposed by resolution and background. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1984 Jun;8(3):514–522. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198406000-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenders K. L., Poewe W. H., Palmer A. J., Brenton D. P., Frackowiak R. S. Inhibition of L-[18F]fluorodopa uptake into human brain by amino acids demonstrated by positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol. 1986 Aug;20(2):258–262. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K. G., Hornykiewicz O. Occurrence and distribution of aromatic L-amino acid (L-DOPA) decarboxylase in the human brain. J Neurochem. 1972 Jun;19(6):1549–1559. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb05099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovenberg W., Victor S. J. Regulation of tryptophan and tyrosine hydroxylase. Life Sci. 1974 Jun 16;14(12):2337–2353. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay A. V., Davies P., Dewar A. J., Yates C. M. Regional distribution of enzymes associated with neurotransmission by monoamines, acetylcholine and GABA in the human brain. J Neurochem. 1978 Apr;30(4):827–839. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb10791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R., Palmer M. R., Patlak C. S., Calne D. B. Nigrostriatal function in humans studied with positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol. 1989 Oct;26(4):535–542. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazziotta J. C., Phelps M. E., Plummer D., Kuhl D. E. Quantitation in positron emission computed tomography: 5. Physical--anatomical effects. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1981 Oct;5(5):734–743. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198110000-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., McGeer E. G. Enzymes associated with the metabolism of catecholamines, acetylcholine and gaba in human controls and patients with Parkinson's disease and Huntington's chorea. J Neurochem. 1976 Jan;26(1):65–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oreland L., Arai Y., Stenström A. The effect of deprenyl (selegiline) on intra- and extraneuronal dopamine oxidation. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1983;95:81–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1983.tb01518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith J., Dyve S., Kuwabara H., Guttman M., Diksic M., Gjedde A. Blood-brain transfer and metabolism of 6-[18F]fluoro-L-dopa in rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1990 Sep;10(5):707–719. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1990.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riederer P., Jellinger K. Neurochemical insights into monoamine oxidase inhibitors, with special reference to deprenyl (selegiline). Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1983;95:43–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1983.tb01516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoepp D. D., Azzaro A. J. Specificity of endogenous substrates for types A and B monoamine oxidase in rat striatum. J Neurochem. 1981 Jun;36(6):2025–2031. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb10829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe J. A., Rewcastle N. B., Lloyd K. G., Hornykiewicz O., Hill M., Tasker R. R. Striatonigral degeneration. Response to levodopa therapy with pathological and neurochemical correlation. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Jul;19(3):275–286. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]