Abstract
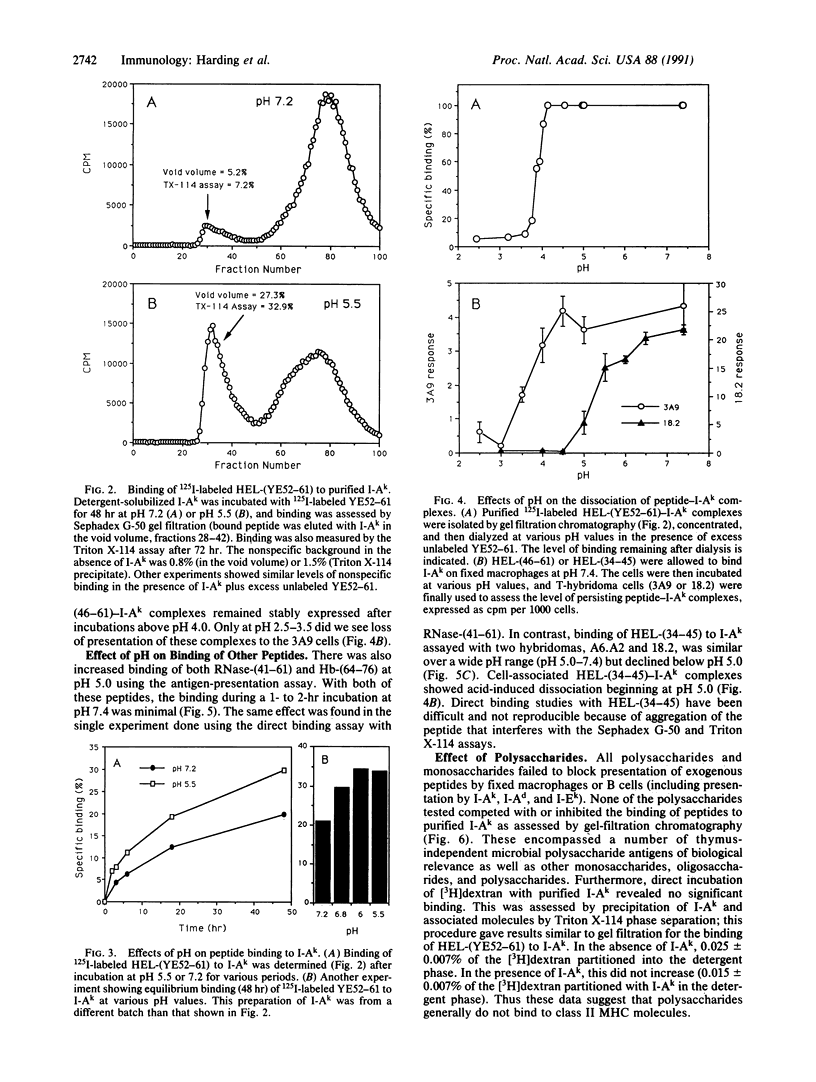
The binding of immunogenic peptides to class II major histocompatibility molecules was examined at various pH values. We studied binding of peptides containing residues 52-61 from hen egg lysozyme (HEL) to I-Ak on fixed peritoneal macrophages or to solubilized affinity-purified I-Ak. Optimum binding occurred at pH 5.5-6.0 with accelerated kinetics relative to pH 7.4; equilibrium binding was also higher at pH 5.5-6.0 than at 7.4. Similar enhancement at pH 5-6 was observed for the binding of hemoglobin-(64-76) to I-Ek and of ribonuclease-(41-61) to I-Ak. In contrast, the binding of HEL-(34-45) to I-Ak was minimally enhanced at acid pH. Dissociation of cell-associated or purified peptide-I-Ak complexes was minimal between pH 5.5 and 7.4, with increased dissociation only at or below pH 4.0 [HEL-(46-61)] or pH 5.0 [HEL-(34-45)]. Thus, optimum peptide binding occurs at pH values similar to the endosomal environment, where the complexes appear to be formed during antigen processing. In addition, we examined the effect of a number of polysaccharides on the binding of peptide to I-Ak. None of these competed with the HEL peptide 125I-labeled YE52-61 for binding to I-Ak. [3H]Dextran also failed to bind purified I-Ak. Polysaccharides do not appear to bind to class II major histocompatibility complex molecules, which explains the T-cell independence of polysaccharide antigens.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen P. M., Beller D. I., Braun J., Unanue E. R. The handling of Listeria monocytogenes by macrophages: the search for an immunogenic molecule in antigen presentation. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):323–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen P. M., Matsueda G. R., Evans R. J., Dunbar J. B., Jr, Marshall G. R., Unanue E. R. Identification of the T-cell and Ia contact residues of a T-cell antigenic epitope. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):713–715. doi: 10.1038/327713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen P. M., Strydom D. J., Unanue E. R. Processing of lysozyme by macrophages: identification of the determinant recognized by two T-cell hybridomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2489–2493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babbitt B. P., Allen P. M., Matsueda G., Haber E., Unanue E. R. Binding of immunogenic peptides to Ia histocompatibility molecules. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):359–361. doi: 10.1038/317359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashford D., Karplus M. pKa's of ionizable groups in proteins: atomic detail from a continuum electrostatic model. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 6;29(44):10219–10225. doi: 10.1021/bi00496a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Sette A., Colon S. M., Jenis D. M., Grey H. M. Isolation and characterization of antigen-Ia complexes involved in T cell recognition. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1071–1077. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90822-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho A., Gronowicz E., Bullock W. W., Möller G. Mechanism of thymus-independent immunocyte triggering. Mitogenic activation of B cells results in specific immune responses. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):74–92. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett T. P., Saper M. A., Bjorkman P. J., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Specificity pockets for the side chains of peptide antigens in HLA-Aw68. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):692–696. doi: 10.1038/342692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glimcher L. H., Schroer J. A., Chan C., Shevach E. M. Fine specificity of cloned insulin-specific T cell hybridomas: evidence supporting a role for tertiary conformation. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2868–2874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guagliardi L. E., Koppelman B., Blum J. S., Marks M. S., Cresswell P., Brodsky F. M. Co-localization of molecules involved in antigen processing and presentation in an early endocytic compartment. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):133–139. doi: 10.1038/343133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Collins D. S., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Unanue E. R. Liposome-encapsulated antigens are processed in lysosomes, recycled, and presented to T cells. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90647-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Roof R. W., Unanue E. R. Turnover of Ia-peptide complexes is facilitated in viable antigen-presenting cells: biosynthetic turnover of Ia vs. peptide exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4230–4234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Unanue E. R. Antigen processing and intracellular Ia. Possible roles of endocytosis and protein synthesis in Ia function. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):12–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Unanue E. R. Low-temperature inhibition of antigen processing and iron uptake from transferrin: deficits in endosome functions at 18 degrees C. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):323–329. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Unanue E. R., Slot J. W., Schwartz A. L., Geuze H. J. Functional and ultrastructural evidence for intracellular formation of major histocompatibility complex class II-peptide complexes during antigen processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5553–5557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. E. Regulation of antigen presentation by acidic pH. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1779–1784. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. E. Stable association of processed antigen with antigen-presenting cell membranes. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):420–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G., Humphrey J. H. The immunological properties of haptens coupled to thymus-independent carrier molecules. I. The characteristics of the immune response to dinitrophenyl-lysine-substituted pneumococcal polysaccharide (SIII) and levan. Eur J Immunol. 1974 May;4(5):370–377. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert L. E., Unanue E. R. Analysis of the interaction of peptide hen egg white lysozyme (34-45) with the I-Ak molecule. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):802–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. M., Watts T. H. On the dissociation and reassociation of MHC class II-foreign peptide complexes. Evidence that brief transit through an acidic compartment is not sufficient for binding site regeneration. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1829–1834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leyva-Cobian F., Unanue E. R. Intracellular interference with antigen presentation. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1445–1450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz R. G., Allen P. M. Direct evidence for functional self-protein/Ia-molecule complexes in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5220–5223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz R. G., Tyler A. N., Allen P. M. T cell recognition of bovine ribonuclease. Self/non-self discrimination at the level of binding to the I-Ak molecule. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4124–4128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luescher I. F., Unanue E. R. Purification and photoaffinity labeling of the I-Ak histocompatibility molecule. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Dec 31;135(1-2):233–245. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90277-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä O., Péterfy F., Outschoorn I. G., Richter A. W., Seppälä I. Immunogenic properties of alpha (1----6) dextran, its protein conjugates, and conjugates of its breakdown products in mice. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Jun;19(6):541–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. A., Lettice L. A., Rota P., Santos-Aguado J., Rothbard J., McMichael A. J., Strominger J. L. Comparison between two peptide epitopes presented to cytotoxic T lymphocytes by HLA-A2. Evidence for discrete locations within HLA-A2. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4098–4103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof R. W., Luescher I. F., Unanue E. R. Phospholipids enhance the binding of peptides to class II major histocompatibility molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1735–1739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein L. J., Stein K. E. Murine immune response to the Neisseria meningitidis group C capsular polysaccharide. I. Ontogeny. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4352–4356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A. L. Cell biology of intracellular protein trafficking. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:195–229. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein K. E., Zopf D. A., Johnson B. M., Miller C. B., Paul W. E. The immune response to an isomaltohexosyl-protein conjugate, a thymus-dependent analogue of alpha(1 replaced by 6) dextran. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1350–1354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler H. K., Unanue E. R. Decrease in macrophage antigen catabolism caused by ammonia and chloroquine is associated with inhibition of antigen presentation to T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):175–178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



