Abstract
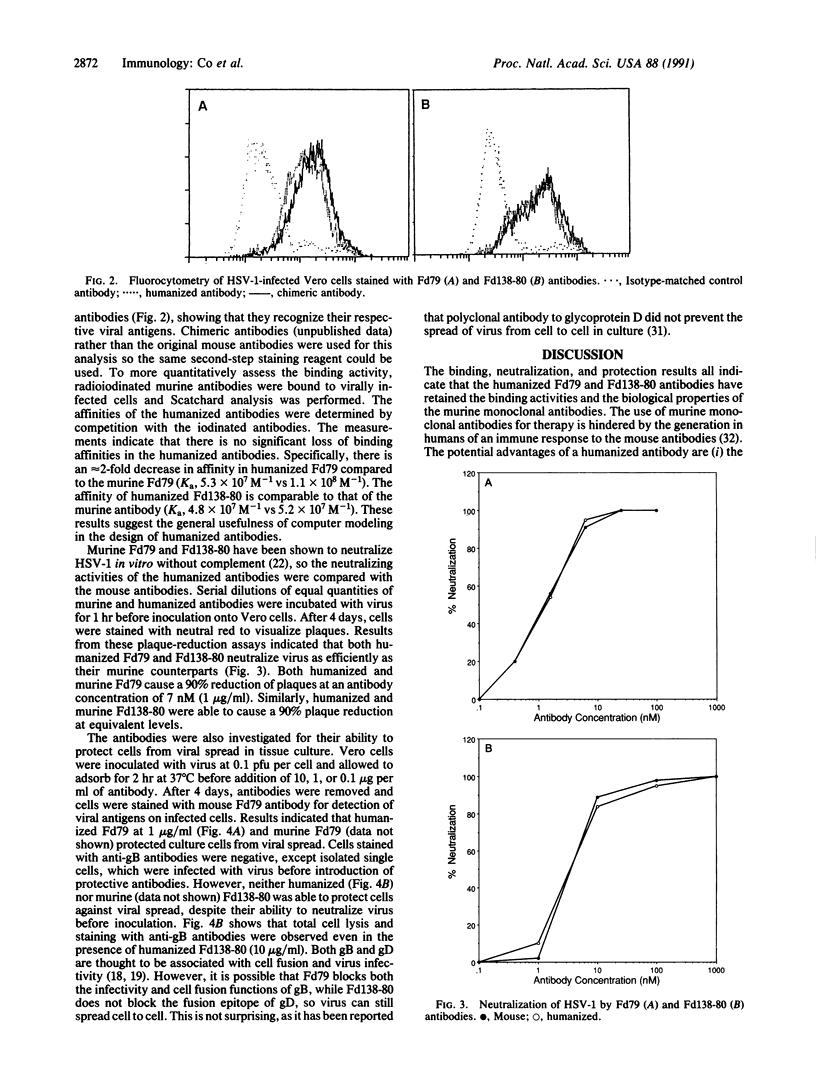
Antibody therapy holds great promise for the treatment of cancer, autoimmune disorders, and viral infections. Murine monoclonal antibodies are relatively easy to produce but are severely restricted for therapeutic use by their immunogenicity in humans. Production of human monoclonal antibodies has been problematic. Humanized antibodies can be generated by introducing the six hypervariable regions from the heavy and light chains of a murine antibody into a human framework sequence and combining it with human constant regions. We humanized, with the aid of computer modeling, two murine monoclonal antibodies against herpes simplex virus gB and gD glycoproteins. The binding, virus neutralization, and cell protection results all indicate that both humanized antibodies have retained the binding activities and the biological properties of the murine monoclonal antibodies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALTAZARD M., BAHMANYAR M. Essai pratique du sérum antirabique chez les mordus par loups enragés. Bull World Health Organ. 1955;13(5):747–772. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran N., Bacchetti S., Rawls W. E. Protection against lethal challenge of BALB/c mice by passive transfer of monoclonal antibodies to five glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 2. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1132–1137. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1132-1137.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulianne G. L., Hozumi N., Shulman M. J. Production of functional chimaeric mouse/human antibody. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):643–646. doi: 10.1038/312643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemann M., Winter G., Waldmann H., Neuberger M. S. The immunogenicity of chimeric antibodies. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2153–2157. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W. H., Gu B., Person S. Role of glycoprotein B of herpes simplex virus type 1 in viral entry and cell fusion. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2596–2604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2596-2604.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey L., Nahmias A. J., Guinan M. E., Benedetti J. K., Critchlow C. W., Holmes K. K. A trial of topical acyclovir in genital herpes simplex virus infections. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jun 3;306(22):1313–1319. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198206033062201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey L., Spear P. G. Infections with herpes simplex viruses (2). N Engl J Med. 1986 Mar 20;314(12):749–757. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603203141205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix R. D., Pereira L., Baringer J. R. Use of monoclonal antibody directed against herpes simplex virus glycoproteins to protect mice against acute virus-induced neurological disease. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):192–199. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.192-199.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller A. O., Spear P. G. Anti-glycoprotein D antibodies that permit adsorption but block infection by herpes simplex virus 1 prevent virion-cell fusion at the cell surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5454–5458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOGGAN M. D., ROIZMAN B., TURNER T. B. The effect of the temperature of incubation on the spread of Herpes simplex virus in an immune environment in cell culture. J Immunol. 1960 Feb;84:152–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale G., Dyer M. J., Clark M. R., Phillips J. M., Marcus R., Riechmann L., Winter G., Waldmann H. Remission induction in non-Hodgkin lymphoma with reshaped human monoclonal antibody CAMPATH-1H. Lancet. 1988 Dec 17;2(8625):1394–1399. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90588-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James K., Bell G. T. Human monoclonal antibody production. Current status and future prospects. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Jun 26;100(1-2):5–40. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90170-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga J., Chatterjee S., Whitley R. J. Studies on herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins using monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1986 Jun;151(2):385–389. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kümel G., Kaerner H. C., Levine M., Schröder C. H., Glorioso J. C. Passive immune protection by herpes simplex virus-specific monoclonal antibodies and monoclonal antibody-resistant mutants altered in pathogenicity. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):930–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.930-937.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letchworth G. J., 3rd, Appleton J. A. Passive protection of mice and sheep against bluetongue virus by a neutralizing monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):208–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.208-212.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. Molecular dynamics of native protein. I. Computer simulation of trajectories. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 15;168(3):595–617. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80304-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh E. Y., Elliott J. F., Cwirla S., Lanier L. L., Davis M. M. Polymerase chain reaction with single-sided specificity: analysis of T cell receptor delta chain. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):217–220. doi: 10.1126/science.2463672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews J. H., Roehrig J. T. Determination of the protective epitopes on the glycoproteins of Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus by passive transfer of monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2763–2767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf J. F., Chatterjee S., Koga J., Whitley R. J. Protection against herpetic ocular disease by immunotherapy with monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex virus glycoproteins. Intervirology. 1988;29(1):39–49. doi: 10.1159/000150027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf J. F., Koga J., Chatterjee S., Whitley R. J. Passive immunization with monoclonal antibodies against herpes simplex virus glycoproteins protects mice against herpetic ocular disease. Curr Eye Res. 1987 Jan;6(1):173–177. doi: 10.3109/02713688709020086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison S. L., Johnson M. J., Herzenberg L. A., Oi V. T. Chimeric human antibody molecules: mouse antigen-binding domains with human constant region domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6851–6855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes J. E., Lausch R. N. Monoclonal antibodies suppress replication of herpes simplex virus type 1 in trigeminal ganglia. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):656–661. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.656-661.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Schneider W. P., Selick H. E., Payne P. W., Landolfi N. F., Duncan J. F., Avdalovic N. M., Levitt M., Junghans R. P., Waldmann T. A. A humanized antibody that binds to the interleukin 2 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10029–10033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rector J. T., Lausch R. N., Oakes J. E. Use of monoclonal antibodies for analysis of antibody-dependent immunity to ocular herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):168–174. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.168-174.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riechmann L., Clark M., Waldmann H., Winter G. Reshaping human antibodies for therapy. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):323–327. doi: 10.1038/332323a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaljohn A. L., Johnson E. D., Dalrymple J. M., Cole G. A. Non-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies can prevent lethal alphavirus encephalitis. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):70–72. doi: 10.1038/297070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroff R. W., Foon K. A., Beatty S. M., Oldham R. K., Morgan A. C., Jr Human anti-murine immunoglobulin responses in patients receiving monoclonal antibody therapy. Cancer Res. 1985 Feb;45(2):879–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]