Abstract
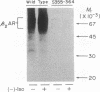
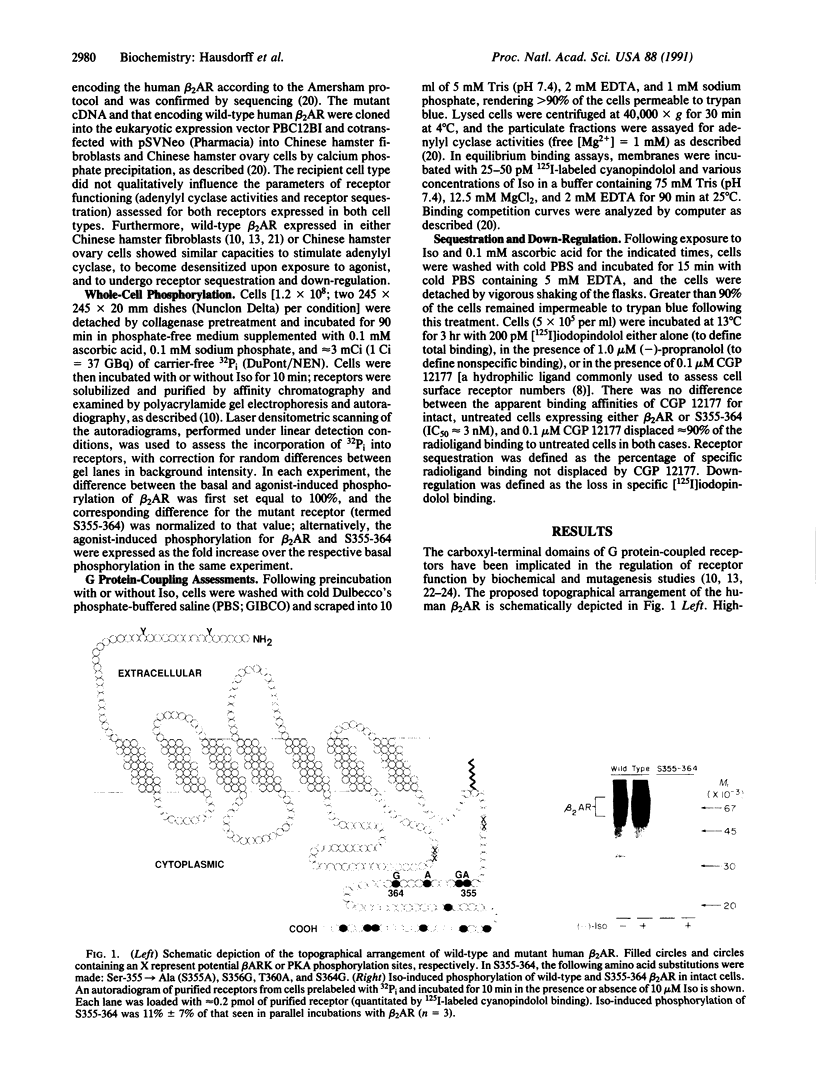
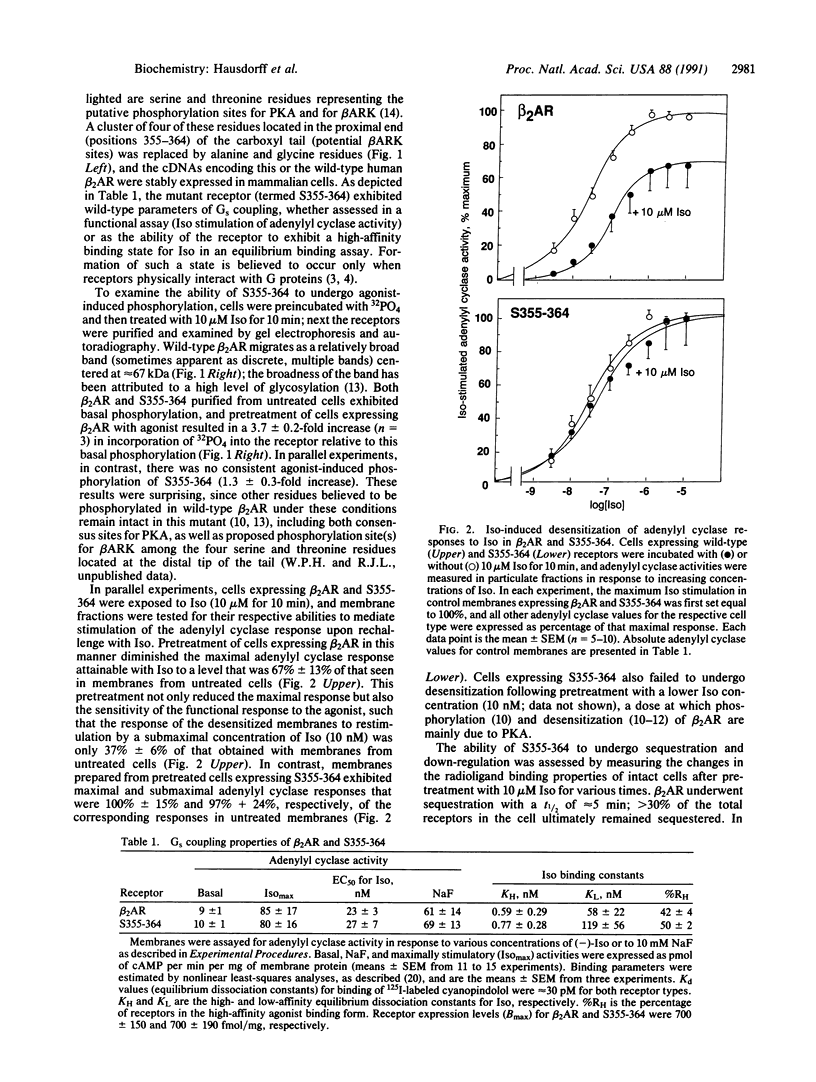
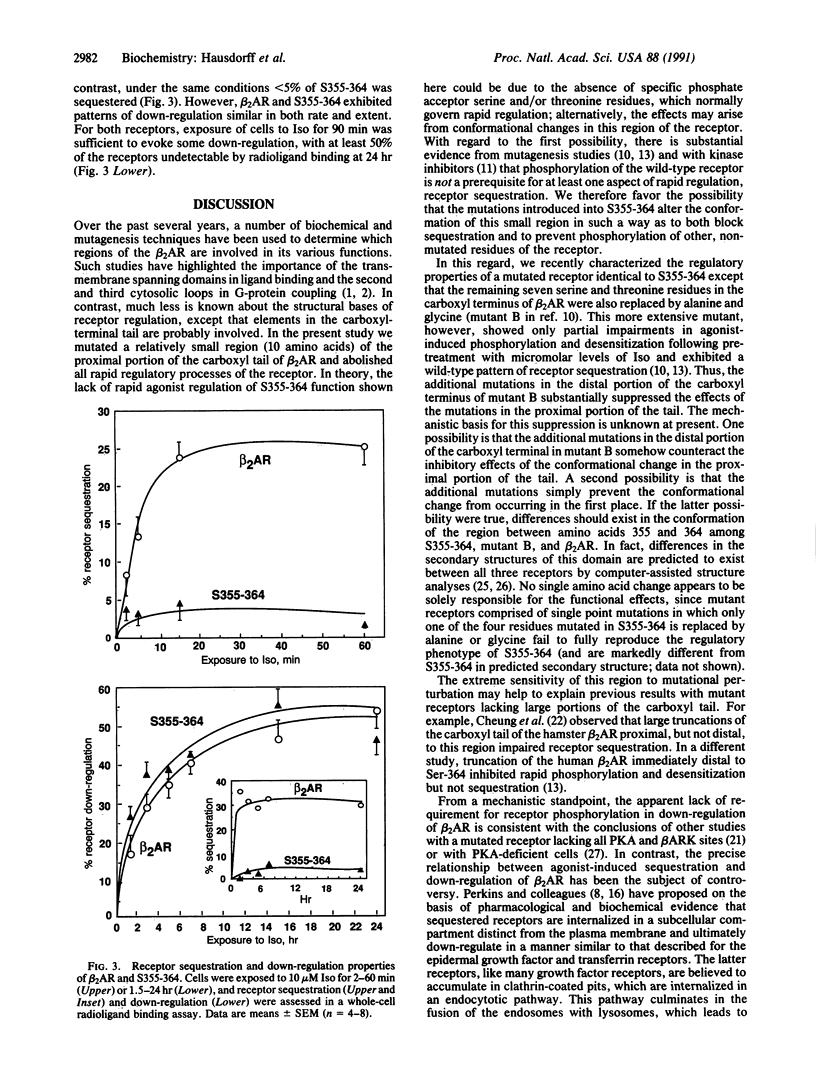
Plasma membrane receptors that couple to guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins) undergo a variety of rapid (minutes) and longer term (hours) regulatory processes induced by ligands. For the beta 2-adrenergic receptor (beta 2AR), the rapid processes include functional desensitization, mediated by phosphorylation of the receptor by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase and the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase, as well as a loss of hydrophilic ligand binding proposed to represent sequestration of receptors into a cellular compartment distinct from the plasma membrane. The slower processes include beta 2AR down-regulation (i.e., a decrease in the total cellular complement of receptors). It is not yet known whether beta 2AR phosphorylation and/or sequestration are prerequisites for down-regulation of the receptor. Like other G protein-coupled receptors, the beta 2AR molecule spans the plasma membrane seven times, and the cytoplasmic carboxyl-terminal domain has been proposed to contain molecular determinants for each of these regulatory processes. We replaced four serine and threonine residues located within a 10-amino acid segment of this domain of beta 2AR and thereby prevented agonist-promoted phosphorylation, sequestration, and rapid desensitization of the adenylyl cyclase response. In contrast, these mutations did not affect functional coupling to the stimulatory G protein Gs or long-term down-regulation. These findings thus define a small, hitherto unappreciated region of the receptor molecule that may selectively subserve its rapid regulation. In addition, with the demonstration that beta 2AR does not have to be phosphorylated or sequestered in order to enter the down-regulation pathway, the results suggest that the classical receptor endocytosis model may not be appropriate for beta 2AR regulation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benovic J. L., DeBlasi A., Stone W. C., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: primary structure delineates a multigene family. Science. 1989 Oct 13;246(4927):235–240. doi: 10.1126/science.2552582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Abramowitz J., Brown A. M. Receptor-effector coupling by G proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 7;1031(2):163–224. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90007-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Hausdorff W. P., De Blasi A., O'Dowd B. F., Kobilka B. K., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Removal of phosphorylation sites from the beta 2-adrenergic receptor delays onset of agonist-promoted desensitization. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):370–373. doi: 10.1038/333370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. T., Hnatowich M., O'Dowd B. F., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Hausdorff W. P. Mutations of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor that impair coupling to Gs interfere with receptor down-regulation but not sequestration. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;39(2):192–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. H., Sigal I. S., Dixon R. A., Strader C. D. Agonist-promoted sequestration of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor requires regions involved in functional coupling with Gs. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jan;35(1):132–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. B., Kunkel M. W., Friedman J., Goka T. J., Johnson J. A. Activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase is required for heterologous desensitization of adenylyl cyclase in S49 wild-type lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1442–1446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Bouvier M., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. The multiple membrane spanning topography of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Localization of the sites of binding, glycosylation, and regulatory phosphorylation by limited proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14282–14288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griendling K. K., Delafontaine P., Rittenhouse S. E., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Correlation of receptor sequestration with sustained diacylglycerol accumulation in angiotensin II-stimulated cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14555–14562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillet J. G., Kaveri S. V., Durieu O., Delavier C., Hoebeke J., Strosberg A. D. beta-Adrenergic agonist activity of a monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1781–1784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Wang H. Y., Malbon C. C. Agonist-induced destabilization of beta-adrenergic receptor mRNA. Attenuation of glucocorticoid-induced up-regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19928–19933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K. Agonist-induced desensitization of the beta-adrenergic receptor-linked adenylate cyclase. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Mar;35(1):5–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Bouvier M., O'Dowd B. F., Irons G. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Phosphorylation sites on two domains of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor are involved in distinct pathways of receptor desensitization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12657–12665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Turning off the signal: desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2881–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Hnatowich M., O'Dowd B. F., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. A mutation of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor impairs agonist activation of adenylyl cyclase without affecting high affinity agonist binding. Distinct molecular determinants of the receptor are involved in physical coupling to and functional activation of Gs. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1388–1393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertel C., Coulter S. J., Perkins J. P. A comparison of catecholamine-induced internalization of beta-adrenergic receptors and receptor-mediated endocytosis of epidermal growth factor in human astrocytoma cells. Inhibition by phenylarsine oxide. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12547–12553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A. From epinephrine to cyclic AMP. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):800–806. doi: 10.1126/science.2841758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Multiple pathways of rapid beta 2-adrenergic receptor desensitization. Delineation with specific inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3202–3211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Benovic J. L., Codina J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. beta-Arrestin: a protein that regulates beta-adrenergic receptor function. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1547–1550. doi: 10.1126/science.2163110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan L. C., Koachman A. M., Insel P. A. Genetic analysis of beta-adrenergic receptor internalization and down-regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):129–133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan L. C., Motulsky H. J., Insel P. A. Do agonists promote rapid internalization of beta-adrenergic receptors? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6566–6570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. W., Harden T. K. Agonist-induced desensitization of a P2Y-purinergic receptor-regulated phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19535–19539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neve K. A., Barrett D. A., Molinoff P. B. Selective regulation of beta-1 and beta-2 adrenergic receptors by atypical agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Dec;235(3):657–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Structure of the adrenergic and related receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:67–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reneke J. E., Blumer K. J., Courchesne W. E., Thorner J. The carboxy-terminal segment of the yeast alpha-factor receptor is a regulatory domain. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):221–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of transmembrane signaling by receptor phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):913–922. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90700-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Strasser R. H., Benovic J. L., Daniel K., Lefkowitz R. J. Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of the beta-adrenergic receptor regulates its functional coupling to adenylate cyclase and subcellular distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9408–9412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sigal I. S., Blake A. D., Cheung A. H., Register R. B., Rands E., Zemcik B. A., Candelore M. R., Dixon R. A. The carboxyl terminus of the hamster beta-adrenergic receptor expressed in mouse L cells is not required for receptor sequestration. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):855–863. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90623-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sigal I. S., Dixon R. A. Structural basis of beta-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J. 1989 May;3(7):1825–1832. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.7.2541037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valiquette M., Bonin H., Hnatowich M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Bouvier M. Involvement of tyrosine residues located in the carboxyl tail of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor in agonist-induced down-regulation of the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5089–5093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. Y., Berrios M., Malbon C. C. Localization of beta-adrenergic receptors in A431 cells in situ. Effect of chronic exposure to agonist. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 15;263(2):533–538. doi: 10.1042/bj2630533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]