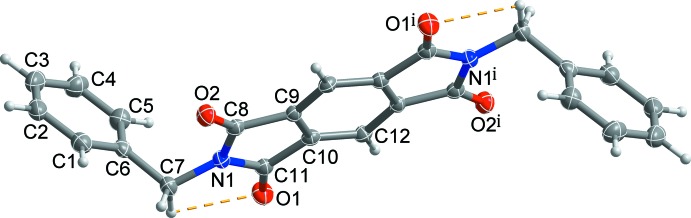
The title compound, C24H16N2O4 (systematic name: 2,6-dibenzylpyrrolo[3,4-f]isoindole-1,3,5,7(2H,6H)-tetraone), lies about a crystallographic inversion center at the center of the pyromellitic diimide moiety which is planar. In the crystal, intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯π interactions lead to the formation of a two-dimensional supramolecular network.
Keywords: crystal structure, pyromellitic diimide derivative, hydrogen bonding, two-dimensional network
Abstract
The title compound, C24H16N2O4 [systematic name: 2,6-dibenzylpyrrolo[3,4-f]isoindole-1,3,5,7(2H,6H)-tetraone], consists of a central pyromellitic diimide moiety with terminal benzyl groups at the N-atom positions. The molecule is located about an inversion centre, so the asymmetric unit contains one half-molecule. In the molecule, both terminal phenyl groups, tilted by 72.97 (4)° with respect to the mean plane of the central pyromellitic diimide moiety (r.m.s. deviation = 0.0145 Å), are oriented away from each other, forming an elongated S-shaped conformation. In the crystal, molecules are connected via weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯π interactions, resulting in the formation of supramolecular layers extending parallel to the ab plane.
Chemical context
As a result of their potential applications in organic photovoltaics (Huang et al., 2014 ▸) and as molecular electronic devices (Guo et al., 2014 ▸) and energy storage devices (Song et al., 2010 ▸), several π-conjugated, redox-active aromatic diimides including pyromellitic diimides, naphthalene diimides and perylene diimides have received considerable attention from materials chemists. Additionally, π-conjugated aromatic diimides and their derivatives are used as rigid structural components in supramolecular assemblies for the exploitation of supramolecular interactions such as hydrogen-bonding and halogen–π interactions (Hay & Custelcean, 2009 ▸; Lu et al., 2007 ▸; Gamez et al., 2007 ▸). Recently, our group reported a copper(I) coordination polymer with a pyromellitic diimide ligand, namely N,N′-bis[3-(methylthio)propyl]pyromellitic diimide, and revealed the presence of halogen–π interactions between the chlorine atoms of a dichloromethane solvent molecule of crystallization and pyromellitic diimide rings (Park et al., 2011 ▸). In an extension of our studies of pyromellitic diimide derivatives, we have prepared the title compound by the reaction of pyromellitic dianhydride with 2-phenyethylamine and we report its crystal structure here.
Structural commentary
The molecular structure of the title compound consists of a central pyromellitic diimide ring system with terminal benzyl groups on each of the inversion-related nitrogen atoms (Fig. 1 ▸). As the molecule is located about a crystallographic inversion centre, the asymmetric unit of the compound comprises one half-molecule. Short intramolecular C—H⋯O contacts (Table 1 ▸) enclose S(5) rings and may contribute to the planarity of the pyromellitic diimide ring system (r.m.s. deviation = 0.0145 Å). The two terminal phenyl groups in the molecule are oriented away from each other, forming an elongated S-shaped conformation. The terminal phenyl ring is tilted by 72.97 (4)° with respect to the mean plane of the central pyromellitic diimide moiety.
Figure 1.
A view of the molecular structure of the title compound, showing the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are presented as small spheres of arbitrary radius and yellow dashed lines represent the intramolecular C—H⋯O short contacts. [Symmetry code; (i) −x + 2, −y + 1, −z.]
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C7—H7B⋯O1 | 0.99 | 2.53 | 2.917 (2) | 103 |
| C12—H12⋯O2i | 0.95 | 2.45 | 3.401 (2) | 178 |
| C7—H7B⋯Cg1ii | 0.99 | 2.60 | 3.478 (2) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal, adjacent molecules are connected by weak C12—H12⋯O2 hydrogen bonds, Table 1 ▸ (yellow dashed lines in Fig. 2 ▸), forming inversion dimers. Inversion symmetry links these into a chain propagating along [ 10]. Neighboring chains are linked through intermolecular C—H⋯π interactions between a methylene H atom and the terminal phenyl ring, resulting in the formation of supramolecular layers extending parallel to the ab plane (black dashed lines in Fig. 3 ▸ and Table 1 ▸). These layers are separated from each other by 3.104 (3) Å. No intermolecular π–π interactions are found between the pyromellitic diimide moieties.
10]. Neighboring chains are linked through intermolecular C—H⋯π interactions between a methylene H atom and the terminal phenyl ring, resulting in the formation of supramolecular layers extending parallel to the ab plane (black dashed lines in Fig. 3 ▸ and Table 1 ▸). These layers are separated from each other by 3.104 (3) Å. No intermolecular π–π interactions are found between the pyromellitic diimide moieties.
Figure 2.
Chains of the title compound formed through intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (yellow dashed lines).
Figure 3.
Supramolecular layers of the title compound formed through intermolecular C—H⋯π interactions (black dashed lines) between the chains generated by intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (yellow dashed lines). H atoms not involved in intermolecular interactions have been omitted for clarity.
Synthesis and crystallization
The title compound was synthesized by the reaction of pyromellitic dianhydride with 2-phenylethylamine according to a literature procedure (Kang et al., 2015 ▸). X-ray quality single crystals were obtained by slow evaporation of a dichloromethane solution of the title compound.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. All H atoms were positioned geometrically with d(C—H) = 0.95 Å for Csp 2—H and 0.99 Å for methylene, and were refined as riding with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C).
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C24H16N2O4 |
| M r | 396.39 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 173 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 6.1500 (5), 4.7475 (3), 31.002 (2) |
| β (°) | 90.461 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 905.14 (11) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.10 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.50 × 0.06 × 0.02 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker 2013 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.661, 0.746 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 4593, 2016, 1444 |
| R int | 0.034 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.650 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.048, 0.119, 1.04 |
| No. of reflections | 2016 |
| No. of parameters | 136 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.25, −0.22 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016017710/sj5513sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016017710/sj5513Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016017710/sj5513Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1515263
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
This work was supported from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) project (2012R1A4A1027750 and 2015R1D1A3A01020410).
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C24H16N2O4 | F(000) = 412 |
| Mr = 396.39 | Dx = 1.454 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.1500 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 874 reflections |
| b = 4.7475 (3) Å | θ = 2.6–24.8° |
| c = 31.002 (2) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| β = 90.461 (3)° | T = 173 K |
| V = 905.14 (11) Å3 | Needle, colourless |
| Z = 2 | 0.50 × 0.06 × 0.02 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 1444 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| φ and ω scans | Rint = 0.034 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker 2013) | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 1.3° |
| Tmin = 0.661, Tmax = 0.746 | h = −6→7 |
| 4593 measured reflections | k = −2→6 |
| 2016 independent reflections | l = −38→40 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.119 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0529P)2 + 0.089P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2016 reflections | Δρmax = 0.25 e Å−3 |
| 136 parameters | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.9145 (2) | 0.9617 (3) | 0.09759 (4) | 0.0314 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.4737 (2) | 0.2514 (3) | 0.04921 (4) | 0.0282 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.6589 (2) | 0.6176 (3) | 0.08217 (5) | 0.0218 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.2783 (3) | 0.3279 (4) | 0.15445 (6) | 0.0303 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.1617 | 0.3659 | 0.1350 | 0.036* | |
| C2 | 0.2505 (4) | 0.1311 (4) | 0.18711 (7) | 0.0363 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.1157 | 0.0354 | 0.1901 | 0.044* | |
| C3 | 0.4206 (4) | 0.0760 (4) | 0.21524 (7) | 0.0399 (6) | |
| H3 | 0.4021 | −0.0568 | 0.2378 | 0.048* | |
| C4 | 0.6175 (4) | 0.2130 (4) | 0.21071 (6) | 0.0356 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.7346 | 0.1724 | 0.2299 | 0.043* | |
| C5 | 0.6439 (3) | 0.4094 (4) | 0.17812 (6) | 0.0298 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.7792 | 0.5036 | 0.1751 | 0.036* | |
| C6 | 0.4739 (3) | 0.4699 (4) | 0.14973 (6) | 0.0233 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.4994 (3) | 0.6895 (4) | 0.11523 (6) | 0.0252 (4) | |
| H7A | 0.3565 | 0.7201 | 0.1011 | 0.030* | |
| H7B | 0.5432 | 0.8691 | 0.1290 | 0.030* | |
| C8 | 0.8499 (3) | 0.7687 (3) | 0.07548 (6) | 0.0213 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.9507 (3) | 0.6455 (3) | 0.03618 (5) | 0.0199 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.8168 (3) | 0.4283 (3) | 0.02169 (5) | 0.0186 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.6279 (3) | 0.4093 (3) | 0.05118 (5) | 0.0211 (4) | |
| C12 | 1.1389 (3) | 0.7249 (3) | 0.01520 (5) | 0.0202 (4) | |
| H12 | 1.2303 | 0.8725 | 0.0253 | 0.024* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0344 (9) | 0.0305 (7) | 0.0293 (7) | −0.0060 (6) | 0.0023 (6) | −0.0098 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0247 (8) | 0.0285 (7) | 0.0316 (7) | −0.0056 (6) | 0.0030 (6) | −0.0014 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0230 (9) | 0.0219 (7) | 0.0204 (8) | 0.0001 (6) | 0.0034 (6) | −0.0008 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0264 (11) | 0.0300 (9) | 0.0346 (11) | 0.0002 (8) | 0.0036 (9) | −0.0041 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0402 (14) | 0.0287 (10) | 0.0401 (12) | −0.0023 (10) | 0.0169 (10) | −0.0015 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0580 (17) | 0.0307 (10) | 0.0313 (12) | 0.0042 (11) | 0.0151 (11) | 0.0035 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0460 (14) | 0.0341 (10) | 0.0267 (10) | 0.0039 (10) | −0.0045 (9) | 0.0039 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0301 (12) | 0.0315 (9) | 0.0279 (10) | −0.0028 (9) | −0.0009 (9) | −0.0003 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0258 (11) | 0.0228 (8) | 0.0214 (9) | 0.0009 (8) | 0.0049 (8) | −0.0046 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0248 (11) | 0.0269 (9) | 0.0240 (9) | 0.0025 (8) | 0.0043 (8) | −0.0009 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0227 (10) | 0.0198 (8) | 0.0214 (9) | 0.0011 (7) | −0.0010 (8) | 0.0016 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0211 (10) | 0.0184 (8) | 0.0202 (9) | 0.0011 (7) | −0.0025 (7) | 0.0010 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0187 (9) | 0.0181 (7) | 0.0190 (8) | 0.0005 (7) | 0.0001 (7) | 0.0024 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0239 (10) | 0.0194 (8) | 0.0199 (9) | 0.0012 (8) | −0.0021 (7) | 0.0027 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0229 (11) | 0.0182 (7) | 0.0195 (9) | −0.0014 (7) | −0.0019 (7) | 0.0005 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C8 | 1.210 (2) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| O2—C11 | 1.210 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.391 (2) |
| N1—C11 | 1.391 (2) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C8 | 1.393 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.503 (2) |
| N1—C7 | 1.465 (2) | C7—H7A | 0.9900 |
| C1—C6 | 1.387 (3) | C7—H7B | 0.9900 |
| C1—C2 | 1.389 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.491 (2) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9500 | C9—C12 | 1.385 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.382 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.392 (2) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C10—C12i | 1.384 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.383 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.487 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C12—C10i | 1.384 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.385 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C11—N1—C8 | 111.98 (15) | N1—C7—C6 | 114.25 (14) |
| C11—N1—C7 | 124.05 (15) | N1—C7—H7A | 108.7 |
| C8—N1—C7 | 123.68 (14) | C6—C7—H7A | 108.7 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 121.05 (19) | N1—C7—H7B | 108.7 |
| C6—C1—H1 | 119.5 | C6—C7—H7B | 108.7 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 119.5 | H7A—C7—H7B | 107.6 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.4 (2) | O1—C8—N1 | 125.37 (17) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.3 | O1—C8—C9 | 128.58 (17) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.3 | N1—C8—C9 | 106.04 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.40 (19) | C12—C9—C10 | 122.98 (16) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.8 | C12—C9—C8 | 129.19 (15) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.8 | C10—C9—C8 | 107.81 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.9 (2) | C12i—C10—C9 | 122.44 (16) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C12i—C10—C11 | 129.49 (16) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C9—C10—C11 | 108.03 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.59 (19) | O2—C11—N1 | 125.35 (18) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.7 | O2—C11—C10 | 128.50 (16) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.7 | N1—C11—C10 | 106.14 (15) |
| C1—C6—C5 | 118.72 (17) | C10i—C12—C9 | 114.59 (15) |
| C1—C6—C7 | 120.50 (17) | C10i—C12—H12 | 122.7 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.77 (17) | C9—C12—H12 | 122.7 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.1 (3) | N1—C8—C9—C12 | 178.00 (17) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.7 (3) | O1—C8—C9—C10 | −179.63 (17) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.8 (3) | N1—C8—C9—C10 | −0.36 (18) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.2 (3) | C12—C9—C10—C12i | −0.4 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.7 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C12i | 178.05 (15) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −177.86 (17) | C12—C9—C10—C11 | −178.18 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.6 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.31 (18) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 178.03 (17) | C8—N1—C11—O2 | −178.89 (16) |
| C11—N1—C7—C6 | 71.0 (2) | C7—N1—C11—O2 | −4.8 (3) |
| C8—N1—C7—C6 | −115.62 (18) | C8—N1—C11—C10 | −0.08 (18) |
| C1—C6—C7—N1 | −115.50 (19) | C7—N1—C11—C10 | 173.99 (14) |
| C5—C6—C7—N1 | 65.9 (2) | C12i—C10—C11—O2 | 1.1 (3) |
| C11—N1—C8—O1 | 179.57 (16) | C9—C10—C11—O2 | 178.61 (17) |
| C7—N1—C8—O1 | 5.5 (3) | C12i—C10—C11—N1 | −177.67 (16) |
| C11—N1—C8—C9 | 0.27 (18) | C9—C10—C11—N1 | −0.15 (18) |
| C7—N1—C8—C9 | −173.83 (14) | C10—C9—C12—C10i | 0.4 (3) |
| O1—C8—C9—C12 | −1.3 (3) | C8—C9—C12—C10i | −177.73 (16) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C7—H7B···O1 | 0.99 | 2.53 | 2.917 (2) | 103 |
| C12—H12···O2ii | 0.95 | 2.45 | 3.401 (2) | 178 |
| C7—H7B···Cg1iii | 0.99 | 2.60 | 3.478 (2) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) x+1, y+1, z; (iii) x, y+1, z.
References
- Brandenburg, K. (2010). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2013). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Gamez, P., Mooibroek, T. J., Teat, S. J. & Reedijk, J. (2007). Acc. Chem. Res. 40, 435–444. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Guo, X., Facchetti, A. & Marks, T. J. (2014). Chem. Rev. 114, 8943–9021. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hay, B. P. & Custelcean, R. (2009). Cryst. Growth Des. 9, 2539–2545.
- Huang, H., Zhou, N., Ortiz, R. P., Chen, Z., Loser, S., Zhang, S., Guo, X., Casado, J., López Navarrete, J. T., Yu, X., Facchetti, A. & Marks, T. J. (2014). Adv. Funct. Mater. 24, 2782–2793.
- Kang, G., Jeon, Y., Lee, K. Y., Kim, J. & Kim, T. H. (2015). Cryst. Growth Des. 15, 5183–5187.
- Lu, Y.-X., Zou, J.-W., Wang, Y.-H. & Yu, Q.-S. (2007). Chem. Phys. 334, 1–7.
- Park, G., Yang, H., Kim, T. H. & Kim, J. (2011). Inorg. Chem. 50, 961–968. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Song, Z., Zhan, H. & Zhou, Y. (2010). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 8444–8448. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016017710/sj5513sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016017710/sj5513Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016017710/sj5513Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1515263
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report