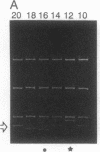
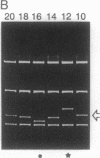
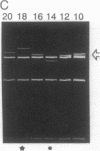
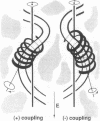
Abstract
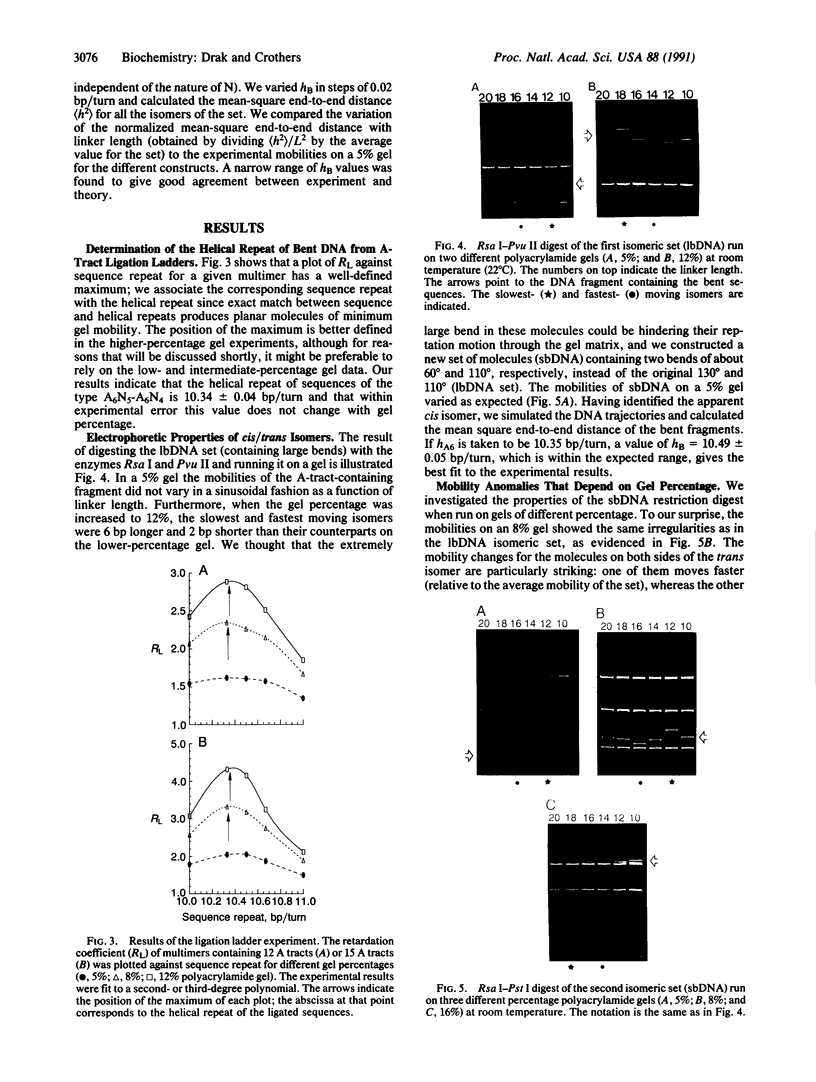
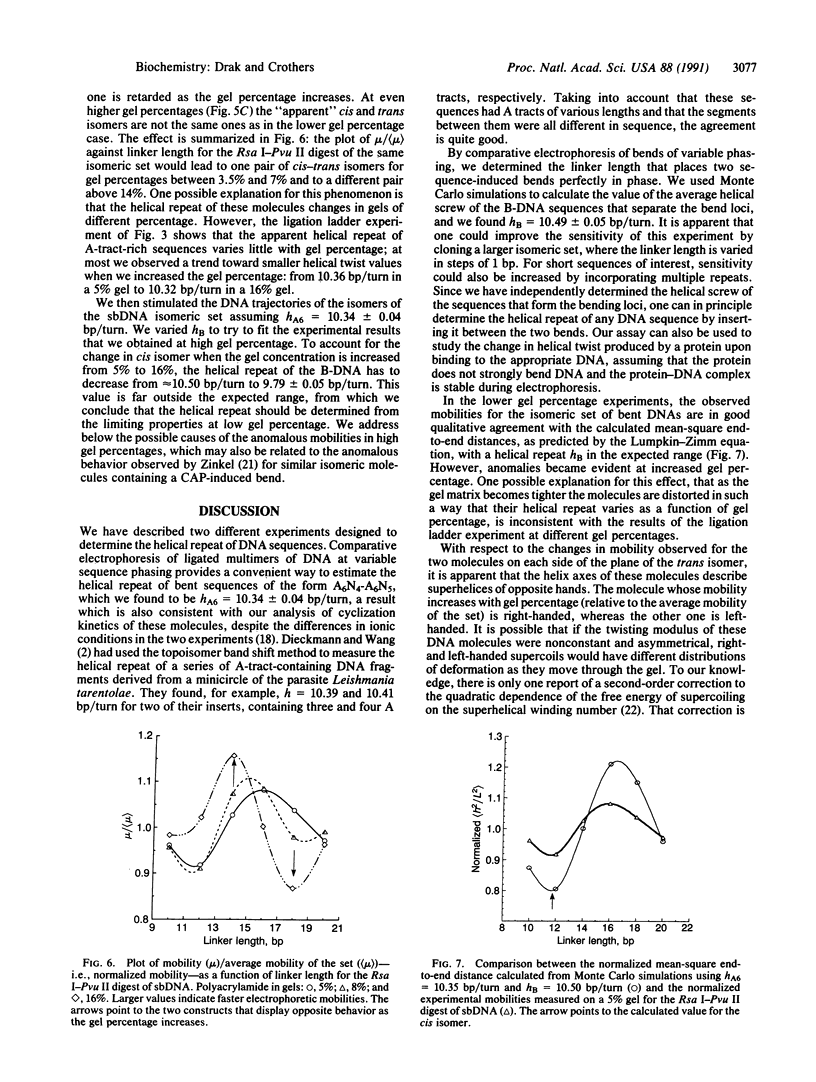
We determined a value of 10.34 +/- 0.04 base pairs (bp) per turn for the helical repeat of bent DNA sequences of the form A6N4-A6N5 by estimating the sequence repeat required to produce a planar curve, as judged from the maximum in the electrophoretic mobility anomaly of multimers containing different sequence repeats (10.00, 10.33, 10.50, 10.67, and 11.00 bp per turn). This result provides the basis for a method to evaluate the helical repeat of any DNA segment by comparative electrophoresis measurements. The sequence of interest is placed between two A-tract bends and the phasing is varied over an entire helical turn. Knowledge of the number of base pairs between the bends in the cis isomer, which has the lowest electrophoretic mobility, allows calculation of the average helical repeat of the inserted sequence. In the course of these experiments we observed an unexpected dependence of electrophoretic mobility on the shape of DNA molecules: in high-percentage polyacrylamide gels, those bent molecules for which we deduced a right-handed superhelical form are less retarded than their homologous left-handed isomers. To explain this finding we propose that superhelical chirality influences the choice of DNA migration pathway, leading to rotation of the DNA molecule relative to the local coordinate frame in the gel. High-percentage gels have sufficiently close contact with the right-handed DNA helical twist to differentiate the frictional consequences of right- and left-handed twisting motions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer W., Vinograd J. Interaction of closed circular DNA with intercalative dyes. II. The free energy of superhelix formation in SV40 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):419–435. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Nature of Col E 1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.667-676.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S., Wang J. C. On the sequence determinants and flexibility of the kinetoplast DNA fragment with abnormal gel electrophoretic mobilities. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M. G., Crothers D. M. CAP and RNA polymerase interactions with the lac promoter: binding stoichiometry and long range effects. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):141–158. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. DNA sequence determinants of CAP-induced bending and protein binding affinity. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):824–829. doi: 10.1038/333824a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Crothers D. M. Chemical determinants of DNA bending at adenine-thymine tracts. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3745–3748. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Drak J., Rice J. A., Crothers D. M. Determination of the extent of DNA bending by an adenine-thymine tract. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4227–4234. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman L. S., Frisch H. L. Why does the electrophoretic mobility of DNA in gels vary with the length of the molecule? Biopolymers. 1982 May;21(5):995–997. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene S. D., Zimm B. H. Understanding the anomalous electrophoresis of bent DNA molecules: a reptation model. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):396–399. doi: 10.1126/science.2756426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumpkin O. J., Déjardin P., Zimm B. H. Theory of gel electrophoresis of DNA. Biopolymers. 1985 Aug;24(8):1573–1593. doi: 10.1002/bip.360240812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumpkin O. J. Mobility of DNA in gel electrophoresis. Biopolymers. 1982 Nov;21(11):2315–2316. doi: 10.1002/bip.360211116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini J. C., Levene S. D., Crothers D. M., Englund P. T. Bent helical structure in kinetoplast DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAYMOND S., NAKAMICHI M. Electrophoresis in synthetic gels. I. Relation of gel structure to resolution. Anal Biochem. 1962 Jan;3:23–30. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A. Anomalous electrophoretic mobility of restriction fragments containing the att region. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):523–529. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90264-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn K., Blattner F. R. Direct evidence for DNA bending at the lambda replication origin. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):416–422. doi: 10.1126/science.2951850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. Comparative gel electrophoresis measurement of the DNA bend angle induced by the catabolite activator protein. Biopolymers. 1990 Jan;29(1):29–38. doi: 10.1002/bip.360290106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. DNA bend direction by phase sensitive detection. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):178–181. doi: 10.1038/328178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]