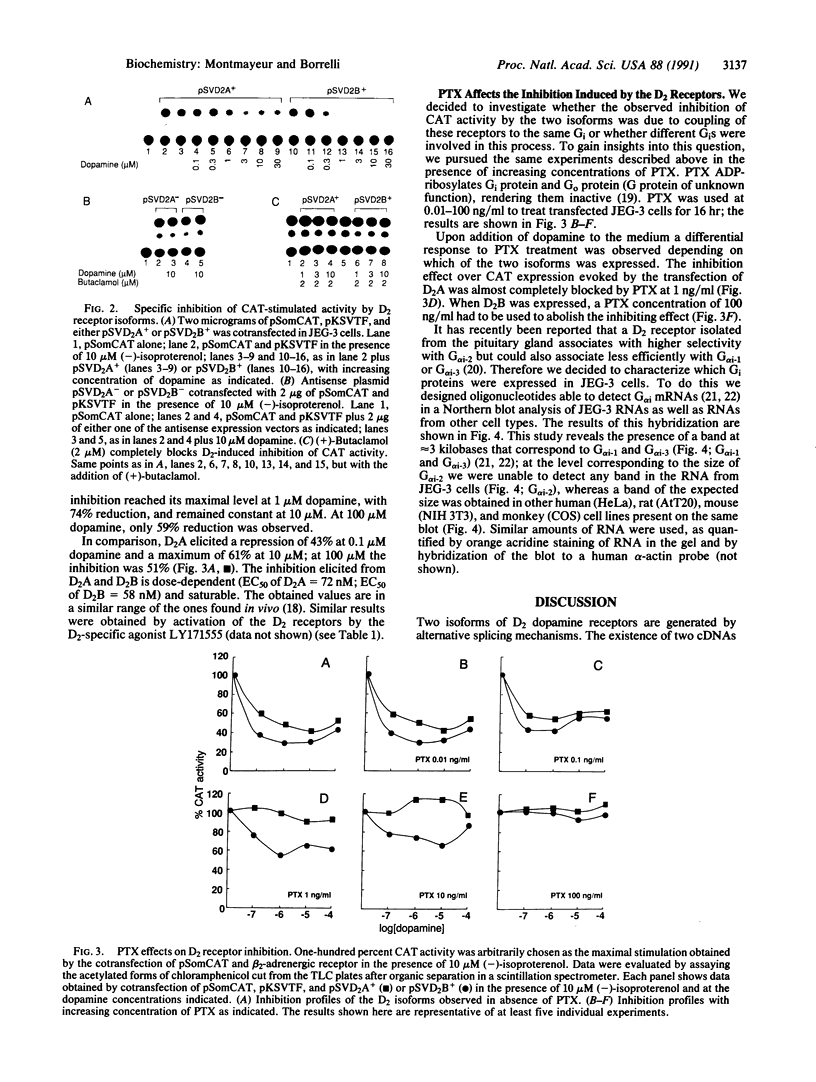
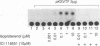Abstract
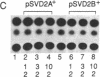
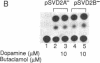
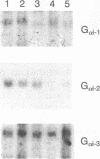
Dopaminergic D2 receptors mediate the effect of dopamine on cellular effector systems by means of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins). The major biochemical effect evoked by these receptors is the inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. As a consequence, the activation of D2 receptors lowers the intracellular cAMP level. Two cDNAs, originated by alternative splicing of the same gene, have been isolated: D2A and D2B. They code for two proteins of 444 and 415 amino acids. These proteins display high affinity for selective D2 dopamine ligands. D2A differs from D2B by an insertion of 87 nucleotides in its cDNA, which is located in a region of the protein considered important for the coupling to G proteins. To investigate functional differences between the two dopamine D2 receptor isoforms, we transiently expressed them in cultured cells. To do so we developed an assay to study membrane receptors that are coupled to the adenylyl cyclase. Using this assay, we were able to show that the stimulation of the adenylyl cyclase induced by the activation of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor is inhibited more efficiently by D2B than D2A. The effects elicited by the D2 receptors are mediated by pertussis toxin-sensitive G proteins. Treatment of transfected cells with pertussis toxin abolishes the inhibitory effects in a dose- and receptor isoform-dependent manner. Our results suggest that the two dopamine receptor isoforms are differentially coupled to G proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashkenazi A., Peralta E. G., Winslow J. W., Ramachandran J., Capon D. J. Functionally distinct G proteins selectively couple different receptors to PI hydrolysis in the same cell. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90251-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Collins S., O'Dowd B. F., Campbell P. T., de Blasi A., Kobilka B. K., MacGregor C., Irons G. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Two distinct pathways for cAMP-mediated down-regulation of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Phosphorylation of the receptor and regulation of its mRNA level. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16786–16792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Hausdorff W. P., De Blasi A., O'Dowd B. F., Kobilka B. K., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Removal of phosphorylation sites from the beta 2-adrenergic receptor delays onset of agonist-promoted desensitization. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):370–373. doi: 10.1038/333370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote T. E., Frey E. A., Grewe C. W., Kebabian J. W. Evidence that the D-2 dopamine receptor in the intermediate lobe of the rat pituitary gland is associated with an inhibitory guanyl nucleotide component. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1983;18:139–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Kobilka B. K., Daniel K. W., Nolan R. D., Lapetina E. Y., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Regan J. W. Multiple second messenger pathways of alpha-adrenergic receptor subtypes expressed in eukaryotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):63–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dal Toso R., Sommer B., Ewert M., Herb A., Pritchett D. B., Bach A., Shivers B. D., Seeburg P. H. The dopamine D2 receptor: two molecular forms generated by alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4025–4034. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delegeane A. M., Ferland L. H., Mellon P. L. Tissue-specific enhancer of the human glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene: dependence on cyclic AMP-inducible elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3994–4002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giros B., Sokoloff P., Martres M. P., Riou J. F., Emorine L. J., Schwartz J. C. Alternative splicing directs the expression of two D2 dopamine receptor isoforms. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):923–926. doi: 10.1038/342923a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Toyama R., Kozasa T., Tsukamoto T., Matsuoka M., Kaziro Y. Presence of three distinct molecular species of Gi protein alpha subunit. Structure of rat cDNAs and human genomic DNAs. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6656–6664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Molecular cloning of five GTP-binding protein cDNA species from rat olfactory neuroepithelium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14241–14249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Kobilka T. S., Daniel K., Regan J. W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Chimeric alpha 2-,beta 2-adrenergic receptors: delineation of domains involved in effector coupling and ligand binding specificity. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1310–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.2836950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Adrenergic receptors. Models for the study of receptors coupled to guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):4993–4996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K. Regulation of cAMP-inducible genes by CREB. Trends Neurosci. 1990 May;13(5):184–188. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90045-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Ransone L. J., Verma I. M. Cross-talk in signal transduction: TPA-inducible factor jun/AP-1 activates cAMP-responsive enhancer elements. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):427–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. Brain dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Sep;32(3):229–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senogles S. E., Spiegel A. M., Padrell E., Iyengar R., Caron M. G. Specificity of receptor-G protein interactions. Discrimination of Gi subtypes by the D2 dopamine receptor in a reconstituted system. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4507–4514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallar L., Muca C., Magni M., Albert P., Bunzow J., Meldolesi J., Civelli O. Differential coupling of dopaminergic D2 receptors expressed in different cell types. Stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in LtK- fibroblasts, hyperpolarization, and cytosolic-free Ca2+ concentration decrease in GH4C1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10320–10326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]