Abstract
It has been proposed that the acquisition of Plasmodium falciparum by man is a relatively recent event and that the sustained presence of this disease in man is unlikely to have been possible prior to the establishment of agriculture. To establish phylogenetic relationships among the Plasmodium species and to unravel the mystery of the origin of P. falciparum, we have analyzed and compared phylogenetically the small-subunit ribosomal RNA gene sequences of the species of malaria that infect humans as well as a number of those sequences from species that infect animals. Although this comparison confirmed the three established major subgroups, broadly classed as avian, simian, and rodent, we find that the human pathogen P. falciparum is monophyletic with the avian subgroup, indicating that P. falciparum and avian parasites share a relatively recent avian progenitor. The other important human pathogen, P. vivax, is very similar to a representative of the simian group of Plasmodium. The relationship between P. falciparum and the avian parasites, and the overall phylogeny of the genus, provides evidence of an exception to Farenholz's rule, which propounds synchronous speciation between host and parasite.
Full text
PDF

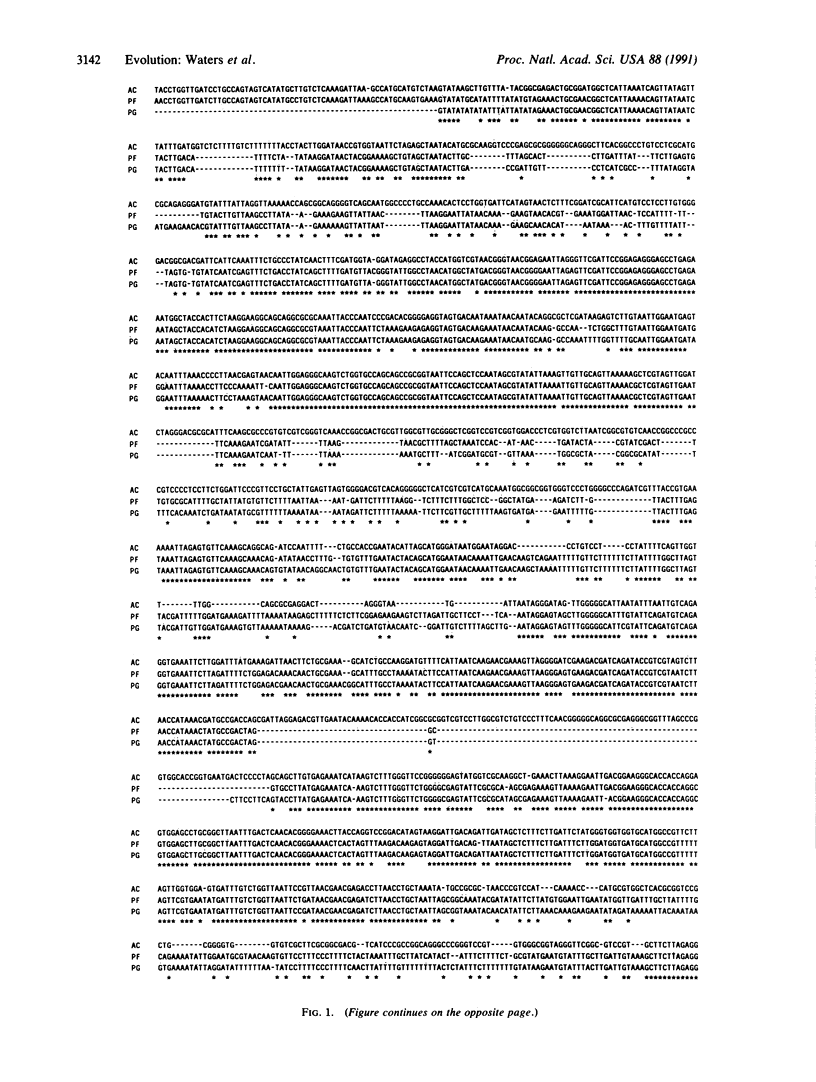
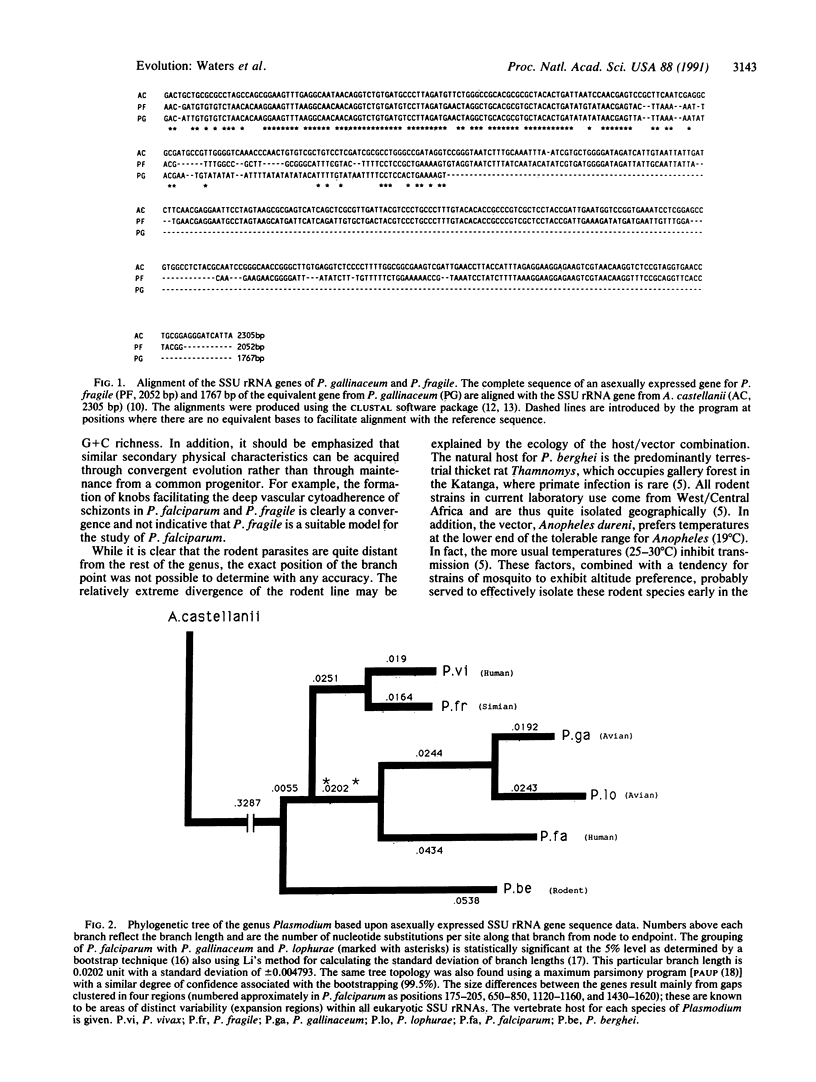
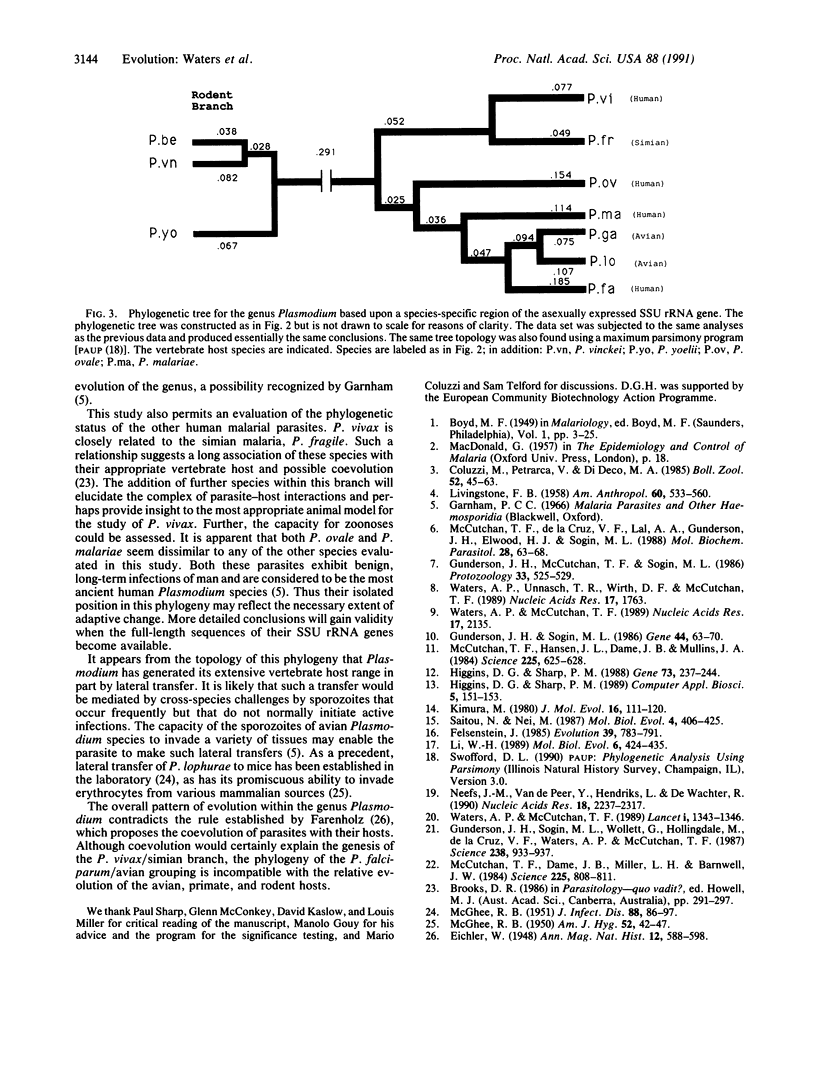
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gunderson J. H., McCutchan T. F., Sogin M. L. Sequence of the small subunit ribosomal RNA gene expressed in the bloodstream stages of Plasmodium berghei: evolutionary implications. J Protozool. 1986 Nov;33(4):525–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1986.tb05656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunderson J. H., Sogin M. L. Length variation in eukaryotic rRNAs: small subunit rRNAs from the protists Acanthamoeba castellanii and Euglena gracilis. Gene. 1986;44(1):63–70. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunderson J. H., Sogin M. L., Wollett G., Hollingdale M., de la Cruz V. F., Waters A. P., McCutchan T. F. Structurally distinct, stage-specific ribosomes occur in Plasmodium. Science. 1987 Nov 13;238(4829):933–937. doi: 10.1126/science.3672135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. Fast and sensitive multiple sequence alignments on a microcomputer. Comput Appl Biosci. 1989 Apr;5(2):151–153. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/5.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol. 1980 Dec;16(2):111–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01731581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H. A statistical test of phylogenies estimated from sequence data. Mol Biol Evol. 1989 Jul;6(4):424–435. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T. F., Dame J. B., Miller L. H., Barnwell J. Evolutionary relatedness of Plasmodium species as determined by the structure of DNA. Science. 1984 Aug 24;225(4664):808–811. doi: 10.1126/science.6382604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T. F., Hansen J. L., Dame J. B., Mullins J. A. Mung bean nuclease cleaves Plasmodium genomic DNA at sites before and after genes. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):625–628. doi: 10.1126/science.6330899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T. F., de la Cruz V. F., Lal A. A., Gunderson J. H., Elwood H. J., Sogin M. L. Primary sequences of two small subunit ribosomal RNA genes from Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Feb;28(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGHEE B. The adaptation of the avian malaria parasite Plasmodium lophurae to a continuous existence in infant mice. J Infect Dis. 1951 Jan-Feb;88(1):86–97. doi: 10.1093/infdis/88.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGHEE R. B. The ability of the avian malaria parasite, Plasmodium lophurae, to infect erythrocytes of distantly related species of animals. Am J Hyg. 1950 Jul;52(1):42–47. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefs J. M., Van de Peer Y., Hendriks L., De Wachter R. Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18 (Suppl):2237–2317. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.suppl.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters A. P., McCutchan T. F. Partial sequence of the asexually expressed SU rRNA gene of Plasmodium vivax. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2135–2135. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters A. P., McCutchan T. F. Rapid, sensitive diagnosis of malaria based on ribosomal RNA. Lancet. 1989 Jun 17;1(8651):1343–1346. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92800-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters A. P., Unnasch T. R., Wirth D. F., McCutchan T. F. Sequence of a small ribosomal RNA gene from Plasmodium lophurae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1763–1763. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



