Abstract
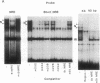
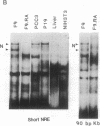
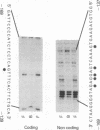
Transcription of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I genes is negatively regulated in undifferentiated F9 mouse embryonal carcinoma cells via the conserved upstream regulatory region. This region contains constitutive enhancers and an inducible enhancer, the interferon consensus sequence (ICS), that is responsible for interferon-induced transcription. A series of mutations in the ICS, but not in the enhancer elements, resulted in an increase in expression of the MHC class I promoter in F9 cells. However, these ICS mutants did not increase promoter activity in F9 cells differentiated after retinoic acid treatment. Results of mobility-shift DNA-binding assays and methylation interference experiments showed that undifferentiated F9 cells contained a factor(s) that bound to a sequence within the 5' and central part of the ICS. This binding site, termed the MHC negative regulatory element (NRE), coincided with the site of mutations that increased promoter activity in F9 cells and was distinct from the element to which interferon-response factors bind. The factor(s) that binds to the MHC NRE was not detected in differentiated F9 cells treated with retinoic acid or in other cells expressing MHC class I genes. Finally, introduction of concatenated, double-stranded NRE oligomers, but not oligomers of unrelated sequences, into F9 cells abolished negative regulation of the MHC class I promoter activity, providing evidence that the NRE binding factor is responsible for repression of the MHC class I genes in F9 cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler S., Waterman M. L., He X., Rosenfeld M. G. Steroid receptor-mediated inhibition of rat prolactin gene expression does not require the receptor DNA-binding domain. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):685–695. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90406-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artzt K., Jacob F. Letter: Absence of serologically detectable H-2 on primitive teratocarcinoma cells in culture. Transplantation. 1974 Jun;17(6):632–634. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197406000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Binding of a nuclear factor to a regulatory sequence in the promoter of the mouse H-2Kb class I major histocompatibility gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):305–313. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniahmad A., Muller M., Steiner C., Renkawitz R. Activity of two different silencer elements of the chicken lysozyme gene can be compensated by enhancer elements. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2297–2303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02504.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barklis E., Mulligan R. C., Jaenisch R. Chromosomal position or virus mutation permits retrovirus expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):391–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90596-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Flavell R. A., Sharp P. A. A gamma-interferon-induced factor that binds the interferon response sequence of the MHC class I gene, H-2Kb. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1139–1144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke P. A., Hirschfeld S., Shirayoshi Y., Kasik J. W., Hamada K., Appella E., Ozato K. Developmental and tissue-specific expression of nuclear proteins that bind the regulatory element of the major histocompatibility complex class I gene. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1309–1321. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremisi C., Babinet C. Negative regulation of early polyomavirus expression in mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):761–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.761-763.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Martin P. L., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Eukaryotic gene transcription with purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:582–598. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driggers P. H., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Mak W. H., Marks M. S., Levi B. Z., Flanagan J. R., Appella E., Ozato K. An interferon gamma-regulated protein that binds the interferon-inducible enhancer element of major histocompatibility complex class I genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3743–3747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamant F., Gurin C. C., Sorge J. A. An embryonic DNA-binding protein specific for the promoter of the retrovirus long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3548–3553. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. R., Krieg A. M., Max E. E., Khan A. S. Negative control region at the 5' end of murine leukemia virus long terminal repeats. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):739–746. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Yamaguchi Y., Ogawa E., Shigesada K., Satake M., Ito Y. A ubiquitous repressor interacting with an F9 cell-specific silencer and its functional suppression by differentiated cell-specific positive factors. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Mar;1(3):135–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautsch J. W., Wilson M. C. Delayed de novo methylation in teratocarcinoma suggests additional tissue-specific mechanisms for controlling gene expression. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):32–37. doi: 10.1038/301032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W., Maxam A. The nucleotide sequence of the lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3581–3584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Rigby P. W., Lane D. P. Negative regulation of viral enhancers in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggarty A., Ponton A., Paterno G. D., Daigneault L., Skup D. An embryonic DNA-binding protein specific for a region of the human IFN beta 1 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10575–10592. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Fujita T., Miyamoto M., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Furia A., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Structurally similar but functionally distinct factors, IRF-1 and IRF-2, bind to the same regulatory elements of IFN and IFN-inducible genes. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël A., Kimura A., Kieran M., Yano O., Kanellopoulos J., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. A common positive trans-acting factor binds to enhancer sequences in the promoters of mouse H-2 and beta 2-microglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2653–2657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh S., Ozawa K., Kondoh S., Soeda E., Israel A., Shiroki K., Fujinaga K., Itakura K., Gachelin G., Yokoyama K. Identification of sequences responsible for positive and negative regulation by E1A in the promoter of H-2Kbm1 class I MHC gene. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):127–135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly F., Condamine H. Tumor viruses and early mouse embryos. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 29;651(2-3):105–141. doi: 10.1016/0304-419X(82)90009-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Staudt L., Robbins P., Kuang A., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Repression of the IgH enhancer in teratocarcinoma cells associated with a novel octamer factor. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):544–546. doi: 10.1126/science.2536195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression of eukaryotic promoters. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E., Davis B., Overhauser J., Chao E., Fan H. Non-function of a Moloney murine leukaemia virus regulatory sequence in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):470–472. doi: 10.1038/308470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R. Teratocarcinomas and mammalian embryogenesis. Science. 1980 Aug 15;209(4458):768–776. doi: 10.1126/science.6250214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Rogers B. J. Isolation of male embryonal carcinoma cells and their chromosome replication patterns. Dev Biol. 1982 Feb;89(2):503–508. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90338-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki J., Appella E., Ozato K. Negative regulation of the major histocompatibility class I gene in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9537–9541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima R. G. Developmental expression of murine extra-embryonic endodermal cytoskeletal proteins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3414–3421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Wan Y. J., Orrison B. M. Mouse major histocompatibility class I gene expression begins at midsomite stage and is inducible in earlier-stage embryos by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2427–2431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Fromental C., Chambon P. A trans-acting factor represses the activity of the polyoma virus enhancer in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells. Oncogene Res. 1987 Jul;1(2):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirayoshi Y., Burke P. A., Appella E., Ozato K. Interferon-induced transcription of a major histocompatibility class I gene accompanies binding of inducible nuclear factors to the interferon consensus sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5884–5888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J., Lockett T. J., Kelly J., Lewy D. Competition studies with repressors and activators of viral enhancer function in F9 mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4307–4324. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Smith K. K., Marotti K. R. Hormonal induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells: generation of parietal endoderm by retinoic acid and dibutyryl cAMP. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90471-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukiyama T., Niwa O., Yokoro K. Mechanism of suppression of the long terminal repeat of Moloney leukemia virus in mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4670–4676. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Imler J. L., Chatton B., Schatz C., Wasylyk C. Negative and positive factors determine the activity of the polyoma virus enhancer alpha domain in undifferentiated and differentiated cell types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7952–7956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Lis J. T. A consensus sequence polymer inhibits in vivo expression of heat shock genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3200–3206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]