Abstract
High-affinity, membrane-associated inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate (IP4) and inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) binding proteins were solubilized and isolated utilizing a heparin-agarose resin followed by an IP4 affinity resin. The IP6 receptor comprises a protein complex of 115-, 105-, and 50-kDa subunits, all of which comigrate under native conditions. The Kd of the receptor for IP6 is 12 nM, whereas inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate (IP5), IP4, and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) are 50%, 30%, and 15%, respectively, as potent. Two protein complexes copurify with the IP4 receptor fraction. A 182/123-kDa complex elutes first from the affinity column followed by a 174/84-kDa protein complex, which elutes at higher salt. Both complexes show high affinity for IP4 (Kd = 3-4 nM). IP5, IP6, and IP3 display approximately 25%, 10%, and 0.1%, respectively, the affinity of IP4. Ligand binding to IP6 and IP4 receptors is inhibited 50% by heparin at 0.1 microgram/ml. IP4 receptor proteins are stoichiometrically phosphorylated by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C, whereas negligible phosphorylation is observed for the IP6 receptor.
Full text
PDF

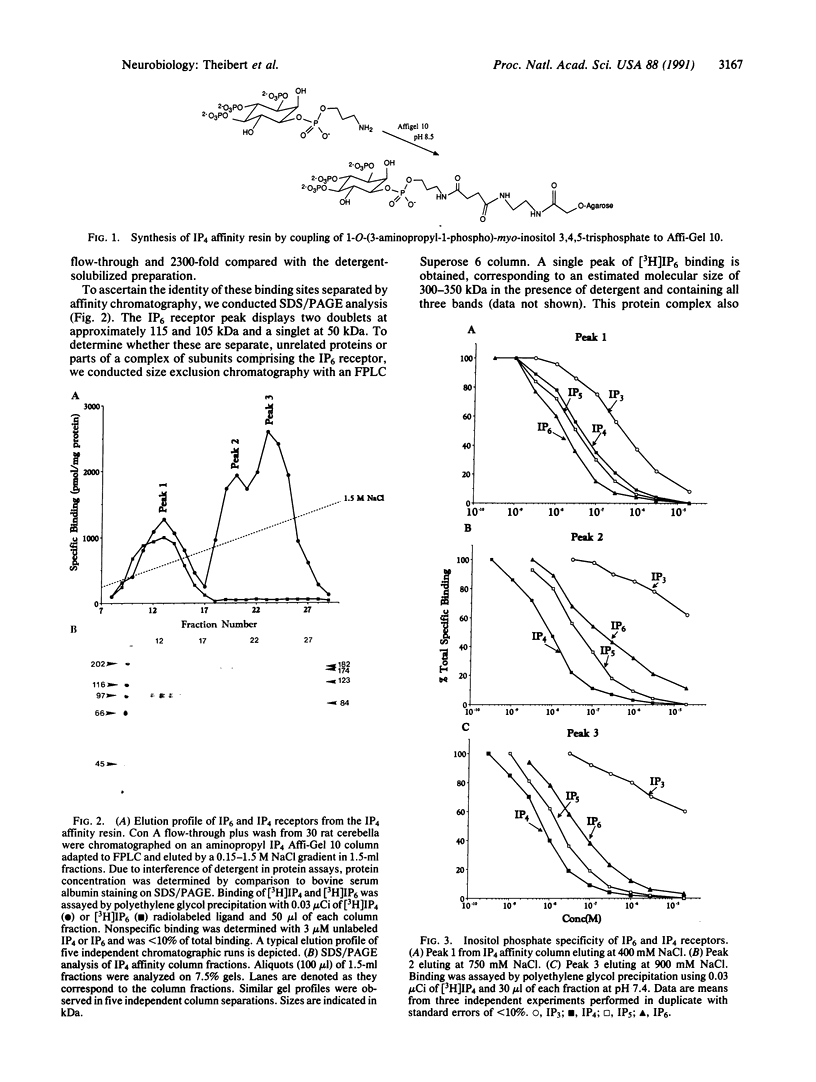
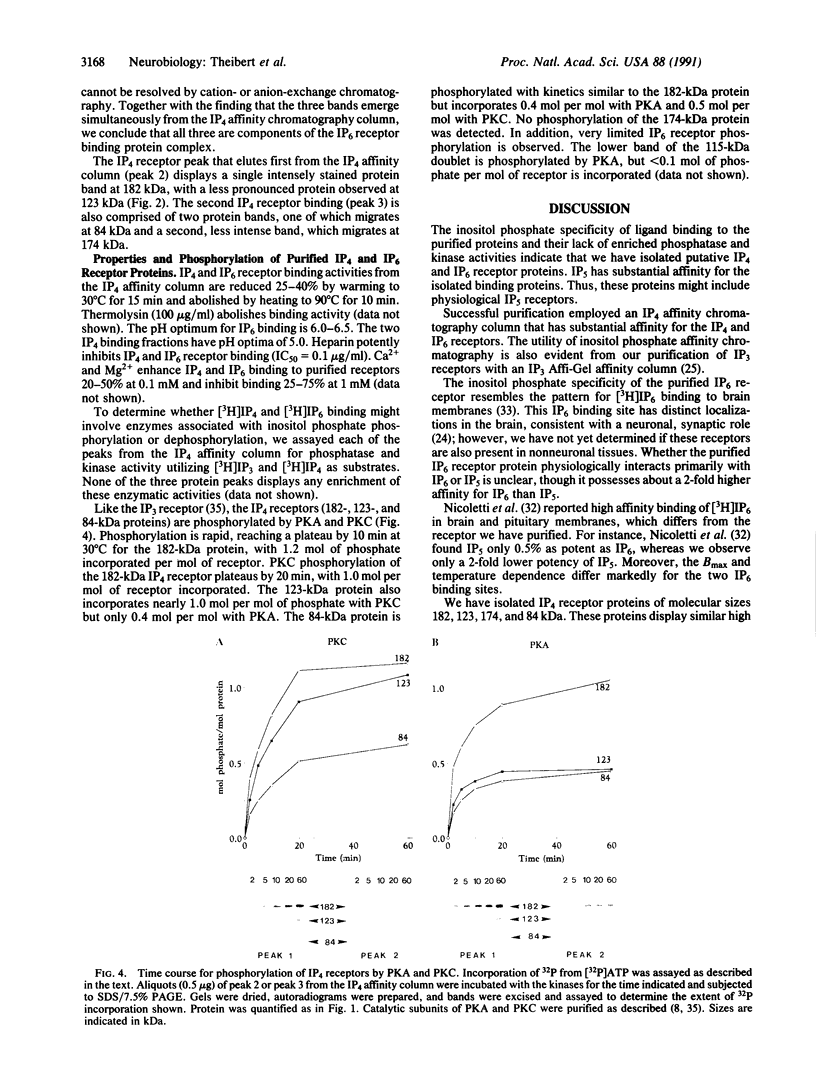

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balla T., Hunyady L., Baukal A. J., Catt K. J. Structures and metabolism of inositol tetrakisphosphates and inositol pentakisphosphate in bovine adrenal glomerulosa cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9386–9390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford P. G., Irvine R. F. Specific binding sites for [3H]inositol(1,3,4,5)tetrakisphosphate on membranes of HL-60 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):680–685. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90421-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Nahorski S. R. Neurotransmitter and depolarization-stimulated accumulation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate mass in rat cerebral cortex slices. J Neurochem. 1990 Jun;54(6):2138–2141. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changya L., Gallacher D. V., Irvine R. F., Petersen O. H. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate act by different mechanisms when controlling Ca2+ in mouse lacrimal acinar cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81425-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danoff S. K., Ferris C. D., Donath C., Fischer G. A., Munemitsu S., Ullrich A., Snyder S. H., Ross C. A. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors: distinct neuronal and nonneuronal forms derived by alternative splicing differ in phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2951–2955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donié F., Hülser E., Reiser G. High-affinity inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate receptor from cerebellum: solubilization, partial purification and characterization. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jul 30;268(1):194–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81006-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donié F., Reiser G. A novel, specific binding protein assay for quantitation of intracellular inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate (InsP4) using a high-affinity InsP4 receptor from cerebellum. FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 28;254(1-2):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enyedi P., Williams G. H. Heterogenous inositol tetrakisphosphate binding sites in the adrenal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):7940–7942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. D., Huganir R. L., Bredt D. S., Cameron A. M., Snyder S. H. Inositol trisphosphate receptor: phosphorylation by protein kinase C and calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinases in reconstituted lipid vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2232–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. D., Huganir R. L., Supattapone S., Snyder S. H. Purified inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor mediates calcium flux in reconstituted lipid vesicles. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):87–89. doi: 10.1038/342087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi T., Yoshikawa S., Miyawaki A., Wada K., Maeda N., Mikoshiba K. Primary structure and functional expression of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-binding protein P400. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):32–38. doi: 10.1038/342032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C. A., Mah S., Williamson J. R. Formation and metabolism of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate in liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8100–8103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Reynolds D. J., Poyner D. R., Hanley M. R. Identification of a novel inositol phosphate recognition site: specific [3H]inositol hexakisphosphate binding to brain regions and cerebellar membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 16;167(2):819–827. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92099-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop J. P., Blakeley D. M., Brown K. D., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J. Effects of bombesin and insulin on inositol (1,4,5)trisphosphate and inositol (1,3,4)trisphosphate formation in Swiss 3T3 cells. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):703–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90513-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. D., Dean N. M., Boynton A. L. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate induces Ca2+ sequestration in rat liver cells. Science. 1988 Nov 25;242(4882):1176–1178. doi: 10.1126/science.2847317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. 'Quantal' Ca2+ release and the control of Ca2+ entry by inositol phosphates--a possible mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80692-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. The inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate pathway--demonstration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 3-kinase activity in animal tissues. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):631–634. doi: 10.1038/320631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Moor R. M. Micro-injection of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate activates sea urchin eggs by a mechanism dependent on external Ca2+. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):917–920. doi: 10.1042/bj2400917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji H., Sandberg K., Baukal A. J., Catt K. J. Metabolism of inositol pentakisphosphate to inositol hexakisphosphate in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20185–20188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson R. A., Hansen C. A., Williamson J. R. Purification of D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7465–7471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Sim S. S., Kim J. W., Moon K. H., Kim J. H., Rhee S. G. Purification and properties of D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase from rat brain. Susceptibility to calpain. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9434–9440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignery G. A., Newton C. L., Archer B. T., 3rd, Südhof T. C. Structure and expression of the rat inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12679–12685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignery G. A., Südhof T. C. The ligand binding site and transduction mechanism in the inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate receptor. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3893–3898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07609.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. J., Murray K. J., England P. J., Downes C. P., Michell R. H. Partial purification and some properties of rat brain inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):157–163. doi: 10.1042/bj2510157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. P., Gallacher D. V., Irvine R. F., Petersen O. H. Synergism of inositol trisphosphate and tetrakisphosphate in activating Ca2+-dependent K+ channels. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):653–655. doi: 10.1038/330653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti F., Bruno V., Cavallaro S., Copani A., Sortino M. A., Canonico P. L. Specific binding sites for inositolhexakisphosphate in brain and anterior pituitary. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 May;37(5):689–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti F., Bruno V., Fiore L., Cavallaro S., Canonico P. L. Inositol hexakisphosphate (phytic acid) enhances Ca2+ influx and D-[3H]aspartate release in cultured cerebellar neurons. J Neurochem. 1989 Oct;53(4):1026–1030. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Meldolesi J., Milner T. A., Satoh T., Supattapone S., Snyder S. H. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor localized to endoplasmic reticulum in cerebellar Purkinje neurons. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):468–470. doi: 10.1038/339468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Hawkins P. T., Barker C. J., Downes C. P. Synthesis of myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate from inositol phosphates generated by receptor activation. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):721–733. doi: 10.1042/bj2530721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supattapone S., Danoff S. K., Theibert A., Joseph S. K., Steiner J., Snyder S. H. Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of a brain inositol trisphosphate receptor decreases its release of calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8747–8750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supattapone S., Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H. Solubilization, purification, and characterization of an inositol trisphosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1530–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura H., Hughes A. R., Thastrup O., Putney J. W., Jr Activation of calcium entry by the tumor promoter thapsigargin in parotid acinar cells. Evidence that an intracellular calcium pool and not an inositol phosphate regulates calcium fluxes at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12266–12271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theibert A. B., Supattapone S., Ferris C. D., Danoff S. K., Evans R. K., Snyder S. H. Solubilization and separation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate- and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-binding proteins and metabolizing enzymes in rat brain. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 15;267(2):441–445. doi: 10.1042/bj2670441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theibert A. B., Supattapone S., Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Meek J. L., Snyder S. H. Demonstration of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate receptor binding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1283–1289. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80272-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallejo M., Jackson T., Lightman S., Hanley M. R. Occurrence and extracellular actions of inositol pentakis- and hexakisphosphate in mammalian brain. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):656–658. doi: 10.1038/330656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]