Abstract
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to better understand the prevalence and correlates of substance use behaviors among HIV-infected adolescents in HIV care settings.
Methods
A cross-sectional sample of 2216 youth living with HIV (YLWH; ages 12-26) was recruited through the Adolescent Trials Network for HIV Interventions. Participants completed a one-time survey on sociodemographic factors, substance use and health behaviors. We used logistic regression models to understand the correlates of substance use outcomes.
Results
Overall, weekly or more frequent tobacco use was reported by 32.9% of participants, 27.5% marijuana use, and 21.3% alcohol use; and 22.5% reported any other illicit drug use. In multivariable models, young MSM had higher odds of reporting each substance use behavior, and transgender women had increased odds of marijuana and other illicit drug use. Criminal justice involvement, unstable housing, condomless sex, and suboptimal antiretroviral therapy was associated with increased risk of substance use behaviors.
Conclusions
Study findings highlight the need for regular screening for substance use in HIV care settings in order to improve access to and delivery of culturally competent substance use prevention and treatment services.
1. Introduction
HIV infection disproportionately affects young people, with individuals 16 to 24 years of age demonstrating the highest rates of new HIV infections compared to other age groups; (1) and young men of color who have sex with men (MSM) and transgender women of color carry a disproportionate burden of HIV infections (2). Several studies have documented a high prevalence of substance use behaviors among young people living with HIV (3-6). Substance use can have numerous detrimental social, psychological, and health repercussions for people living with HIV, and young people face many unique risks that place their own and others’ lives in danger. For example, alcohol and/or drug abuse has been linked to increased condomless sex (4, 7), as well as suboptimal adherence to antiretroviral therapy (ART) (8, 9), which can result in decreased CD4 cell counts, having a detectable viral load, and development of ART-resistant virus. Many youth engage in multiple substance use behaviors (10), and the presence of co-occurring substance use and psychiatric illnesses has been associated with poor drug and alcohol treatment outcomes among adolescents (11), as well as increased HIV risk behaviors.
Despite these findings, to our knowledge, large cohort studies have yet to examine the prevalence and correlates of substance use behaviors in a sample of a large cohort study of youth living with HIV (YLWH). These correlates are important to understand since they can help elucidate who is most at risk for substance use and what types of interventions might be needed to reduce risk. A range of social and structural factors including lower socioeconomic position, juvenile justice involvement, unstable housing, and lack of social support also may be important to consider, since they have been associated with increased substance use and HIV risk behaviors (12-14). Youth who are homeless or who are unstably housed are demonstrate high HIV risk behaviors due to the street-associated behaviors, which may include substance use and trading sex for drugs or money (15). In addition, many youth may not have positive role models or social support to avoid using alcohol or drugs, which can increase their risk of engaging in substance use behaviors which can interfere with their own health, as well as place others at risk for HIV (16, 17).
The purpose of the present study was two-fold: 1) to assess the prevalence, frequency, and co-occurrence of substance use behaviors in a sample of 2216 YLWH including those both perinatally and behaviorally acquired HIV infection; and 2) to examine the unique associations of tobacco, alcohol, marijuana, and other illicit substance use with three domains to inform future interventions: sociodemographic and structural factors, comorbid psychological distress (including suicidal ideation), and HIV disease and sexual risk characteristics.
2. Methods
The details of the methodology has been previously described (18, 19). Between December 2009 and January 2012, 2216 youth living with HIV were recruited to participate in a one-time cross-sectional survey. To be eligible, youth had to be: 1) between 12 and 26 years of age; 2) living with HIV/AIDS; 3) aware they were HIV-positive; 4) engaged in HIV care in one of the Adolescent Trial Network for HIV/AIDS Intervention (ATN) adolescent medicine clinical sites or affiliates; and 5) able to understand English or Spanish. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Boards (IRB) at each participating site as well as those of members of the protocol team.
2.1 Recruitment
Youth were recruited at 20 geographically diverse clinics in the urban areas that were part of the ATN, including Boston, Baltimore, Chicago, Denver, Fort Lauderdale, Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, Memphis, New Orleans, New York City, San Francisco, Tampa, Washington, DC, and San Juan, Puerto Rico. A study staff member approached all youth meeting eligibility criteria during one of their clinic visits and described the study to them. After a thorough explanation of the purpose of the study and procedures, the study staff member obtained signed informed consent or youth assent from those who agreed to participate. While the majority of IRBs granted a waiver of parental consent, written parental permission was obtained if it was required.
2.2 Procedures
Within two weeks of providing informed consent/assent, participants completed audio computer assisted self-interviews (ACASI) to assess sociodemographic, substance use, and health factors, which took 45-90 minutes to complete. Participants were compensated for their time and transportation in accordance with site IRB guidelines, which ranged from $20 to $150 (Mean = $56, Median = $50). Additionally, study staff members abstracted biomedical data (i.e., viral load, CD4 T cell counts) from participants’ medical charts.
2.3 Measures
Substance Use
We used four indicators of substance use as dependent variables in our analysis. The Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test (ASSIST) was used to collect data on the frequency of using 10 different substances over the 3 months prior to the visit (20). Dependent variables were: (1) weekly or more frequent alcohol use, (2) weekly or more frequent tobacco use, (3) weekly or more frequent marijuana use; and (4) any past three-month other illicit drug use (i.e., crack, cocaine, amphetamine, inhalants, opioids, sedatives, hallucinogens).
Sociodemographic characteristics
Participants self-reported their age, sex assigned at birth, gender identity, race and ethnicity, sexual identity, source of infection with HIV, history of incarceration, living situation, employment status, education level, and income level. Participants self-reported whether they had sex with a male in the past three months (yes/no). Participants were categorized as MSM if they: 1) were assigned a male sex at birth, 2) identified a male gender; and 3) reported any sex with another male in the past 3 months.
Social Support variables
Social support for avoiding substance use was evaluated by asking participants to rate the extent to which the agreed or disagreed with the following two statements: 1) “There are people in my life that are supportive about avoiding alcohol;” and 2) “There are people in my life that are supportive about avoiding drugs.” Participants responded on a 5-point Likert Scale ranging from 1=Strongly Disagree to 5=Strongly Agree. Both items were significantly skewed with approximately 50% reporting strongly agree; therefore, we dichotomized each variable into “Strongly Agree” versus all others.
Mental health variables
Mental health symptoms was assessed with the Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI), which is a 53-item measure that creates Global Severity Index (GSI) (21). The GSI combines information about the number of symptoms (e.g., Somatization, Obsessive-Compulsive, Depression, Anxiety) and intensity of distress, and has been used as a measure of general psychological distress and symptomatology in this sample and others (18, 22). Items have the following response options: 0=not at all, 1=a little bit, 2=moderately, 3=quite a bit, and 4=extremely. Participants were also asked whether they had ever thought of attempting suicide in their lifetime (yes/no).
HIV disease and sexual risk variables
Participants self-reported the number of missed doses of their HIV medications in the last 7 days. Consistent with prior studies (14), and to reflect the distinction between those who meet the public health goal of 100% medication adherence versus those who do not, adherence was dichotomized to indicate less than 100% adherence (1) versus 100% adherence (0).Within one week of participants completing the survey, viral load and CD4 count values were collected through a chart review. A range of viral load assays were used at different sites and the lower limit of detectability for these assays varied. Sites reported whether a participant’s viral load was undetectable, and the viral load if it was not, and were also required to specify the assay used. Previous sensitivity analyses using these data revealed no significant differences in rates of detectability based cases on in which the assay VL LLD was < 400 and those in which the assays were unknown (19). CD4 count was categorized into a 3-level variable: less than 200; 200 to 500; and 501 or higher. Participants were asked about their sexual activity with male and female partners during the past 9 months. Participants reported the number of sex partners and frequency of condom use during vaginal or anal sexual activity with HIV-positive and HIV-negative partners. We created a dichotomous variable of whether or not the participant reported engaging in condomless anal or vaginal sex with an HIV-negative male or female sexual partner in the past 90 days.
2.4 Statistical analyses
First, we examined descriptive statistics for each of the substance use outcomes and independent variables. Second, we conducted correlation analyses using the phi coefficient to examine the extent to which the substance use outcome variables were correlated with each other. Next, we fit separate bivariate logistic regression models to identify the sociodemographic, mental health, and HIV-related variables that were significantly associated with each of the substance use outcomes. Finally, we fit multivariate logistic regression models for each of the 4 substance use outcomes statistically adjusting for all sociodemographic, mental health, and HIV-related variables. All analyses were conducted in SPSS 24 with a specified p-value of 0.05.
3. Results
3.1 Sample Characteristics
Table 1 presents the characteristics of the study sample. Participants ranged in age from 12 to 26 (M=22.22, SD = 2.78). The majority of the sample were behaviorally infected with HIV (72.4%) and were members of racial/ethnic minority groups (64% Black, 19.7% Latino/Hispanic, and 7.6% Other). Less than half of the sample self-identified as straight/heterosexual (45.5%) and 63.8% reported a male gender identity; 3.2% identified as a transgender woman and 0.6% identified as a transgender man and nearly half of the sample were classified as MSM (45.2%). Of the participants classified as MSM, 74.9% (n =750) self-identified as gay, 16% (n=160) self-identified as bisexual, 5.2% (n=52) self-identified as heterosexual/straight, and 3.9% (n = 39) self-identified as queer or other. In regards to socio-structural factors, 5% reported unstable housing, 31.9% reported a history of criminal justice involvement, 31.2% were not in school, 46.3% earned less than $250 per month, and 33.4% were currently employed. Three quarters (75.2%) of the sample had detectable HIV RNA levels. Less than half (44.0%) self-reported perfect ART adherence, and 47.4% had a CD4 count of 500 or greater. Nearly one quarter (22.3%) of the sample reported condomless anal or vaginal sex with an HIV-negative person and 14.8% reported condomless anal or vaginal sex with an HIV-positive person. In regards to mental health, 31.2% had a Global Severity Index at or above the clinical cutoff of 63 and 15% reported suicidal ideation in their life time. Approximately half of the sample reported strong agreement that they had social support for avoiding drug use (60.4%) and alcohol use (49.5%).
Table 1.
Characteristics of Study Sample
| M | SD | |
|---|---|---|
|
| ||
| Mental Health Symptomst | 50.70 | 41.73 |
|
| ||
| N | % | |
| Age | ||
| 12-17 | 267 | 16.6 |
| 18-20 | 713 | 32.3 |
| 21-26 | 1125 | 51.0 |
| Source of HIV Acquisition | ||
| Perinatal | 612 | 27.6 |
| Behavioral | 1604 | 72.4 |
| Race/Ethnicity | ||
| Black | 1418 | 64.0 |
| Latino | 436 | 19.7 |
| Other | 169 | 7.6 |
| White | 192 | 8.7 |
| Sexual Identity | ||
| Straight | 1005 | 45.5 |
| Gay or Lesbian | 871 | 39.3 |
| Bisexual | 269 | 12.1 |
| Other | 71 | 3.2 |
| Gender Identity | ||
| Male | 1413 | 63.8 |
| Female | 719 | 32.4 |
| Transgender Female | 70 | 3.2 |
| Transgender Male | 14 | 0.6 |
| Males who have sex with men (MSM) | 1004 | 45.2 |
| Unstable Housing, Lifetime | 112 | 5.1 |
| Juvenile Justice Involvement, Lifetime | 707 | 31.9 |
| Education | ||
| Not in School | 689 | 31.2 |
| In School | 1142 | 51.7 |
| Graduated | 378 | 17.1 |
| Currently Employed | 735 | 33.4 |
| Suicidal Ideation, Lifetime | 335 | 15.1 |
| Drug Use Social Support | 2338 | 60.4 |
| Alcohol Use Social Support | 1097 | 49.5 |
| Alcohol Use (Weekly or Greater) | 472 | 21.3 |
| Diagnosed in the last year | 346 | 15.6 |
| CD4 Count, past 3 month | ||
| Less than 200 | 223 | 10.1 |
| 200-499 | 940 | 42.5 |
| 500 or greater | 1049 | 47.4 |
| Less than 100% ART Adherence | 579 | 44.0 |
| Detectable Viral Load | 1467 | 75.2 |
| CVAS with HIV-negative partner | 494 | 22.3 |
| Tobacco Use (Weekly or More) | 730 | 32.9 |
| Alcohol Use (Weekly or More) | 472 | 21.3 |
| Marijuana Use (Weekly or More) | 610 | 27.5 |
| Any Other Illicit Drug Use (Any Past | 499 | 22.5 |
| 3 Month) | ||
CVAS=Condomless vaginal or anal sex
=Global Severity Index
3.2 Frequency of Substance Use
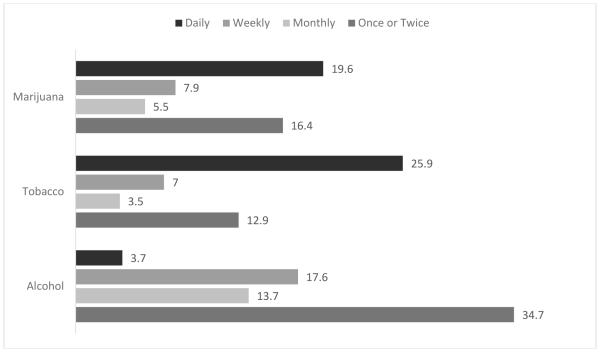
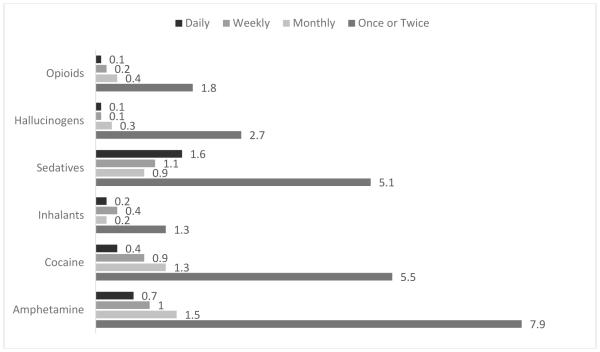
Figure 1 presents the percentages of participants who reported different frequencies of alcohol, tobacco, and marijuana use in the past 3 months. Nearly one-quarter of the sample reported at least weekly alcohol use (21.3%), with a higher percentage reporting at least weekly tobacco (32.9%) or marijuana use (27.5%). Almost 20% of participants reported daily marijuana use. Approximately one in four participants reported any other illicit drug use (22.5%) in the past 3 months (see Figure 2). There was a significant correlation between the substance use behaviors. Specifically, the phi coefficient between weekly or more frequent tobacco and marijuana use was 0.44, weekly or more frequent tobacco and alcohol use was 0.27, and weekly or more frequent marijuana and alcohol use was 0.26, ps < 0.001. The Phi Coefficients for any other illicit drug use, weekly or more frequent tobacco, weekly or more frequent alcohol, and weekly or more frequent marijuana use ranged from 0.11 to 0.16, ps < 0.001.
Figure 1.
Percentages of participants who endorsed alcohol, tobacco and marijuana use in the past 3 months
Figure 2.
Percentages of participants who endorsed any past 3 month other illicit drug use
3.3 Multivariable Models
Results of the multivariate logistic regressions are presented in Table 2 (weekly or more frequent tobacco and weekly or more frequent alcohol use) and Table 3 (weekly or more frequent marijuana and any past 3 month other illicit drug). Older age was associated with higher odds of using all substances (Table 2-3). Behaviorally infected youth had significantly greater odds of each substance use outcome in bivariate models; only the association with weekly tobacco use remained significant in multivariate models adjusting for sociodemographic, mental health, and HIV-related variables. In multivariate models, relative to Black and Latino/Hispanic participants, White participants had increased odds of weekly tobacco use, weekly alcohol use, and any past three-month other illicit drug use, relative to Black and Latino/Hispanic participants. MSM had an increased odds of engaging in each of the substance use outcomes. Gender differences were also observed with young males having increased odds of weekly alcohol and marijuana use compared to young females, whereas young transgender women had increased odds of reporting weekly marijuana use and any past three-month other illicit drug use compared to young females.
Table 2.
Bivariate and Multivariate Models for Weekly or More Frequent Tobacco and Alcohol Use
| Weekly or More Tobacco Use | Weekly or More Alcohol Use | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bivariate | Multivariate | Bivariate | Multivariate | |||||
|
| ||||||||
| OR | 95% CI | AOR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | AOR | 95% CI | |
| Age | ||||||||
| 12-17 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| 18-20 | 3.86*** | 2.70, 5.51 | 3.08*** | 1.69, 5.63 | 4.96*** | 2.75, 8.95 | 4.11* | 1.39, 12.21 |
| 21-26 | 5.56*** | 3.95, 7.83 | 3.78*** | 2.00, 7.16 | 12.98*** | 7.36, 22.89 | 10.27*** | 3.44, 30.61 |
| Route of HIV acquisition | ||||||||
| Perinatal | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Behavioral | 3.73*** | 2.93, 4.76 | 1.84** | 1.18, 2.90 | 4.33*** | 3.15, 5.95 | 1.01 | 0.57, 1.80 |
| Race/Ethnicity | ||||||||
| Black | 0.55*** | 0.40, 0.74 | 0.34*** | 0.20, 0.55 | 0.33*** | 0.24, 0.46 | 0.41** | 0.24, 0.71 |
| Latino | 0.58** | 0.41, 0.82 | 0.29*** | 0.16, 0.51 | 0.54** | 0.38, 0.77 | 0.51* | 0.28, 0.95 |
| Other | 0.58* | 0.38, 0.88 | 0.15 | 0.29, 1.20 | 0.46** | 0.29, 0.73 | 0.50 | 0.22, 1.15 |
| White | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
| MSM | 1.90*** | 1.59, 2.27 | 1.34 | 0.86, 2.10 | 3.52*** | 2.84, 4.38 | 1.93* | 1.14, 3.45 |
| Gender Identity | ||||||||
| Male | 1.59*** | 1.30, 1.95 | 1.26 | 0.80, 1.95 | 3.02*** | 2.32, 3.93 | 1.97* | 1.08, 3.57 |
| Female | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Transgender Female | 4.36*** | 2.63, 7,24 | 2.09 | 0.91, 4.78 | 1.37 | 0.30, 6.23 | 1.23 | 0.45, 3.35 |
| Transgender Male | 1.16 | 0.36, 3.75 | 1.00 | 0.10, 10.34 | 1.70 | 0.88, 3.31 | 2.78 | 0.29, 27.10 |
| Unstable Housing, Lifetime | 2.67*** | 1.72, 3.91 | 2.12* | 1.10, 4.06 | 1.66* | 1.09, 2.51 | 1.92 | 0.95, 3.89 |
| Juvenile Justice Involvement, | 3.96*** | 3.27, 4.79 | 2.96*** | 2.16, 4.06 | 1.75*** | 1.42, 2.16 | 1.21 | 0.84, 1.77 |
| Lifetime | ||||||||
| Education | ||||||||
| Not in School | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| In School | 0.38*** | 0.31, 0.47 | 0.76 | 0.54, 1.08 | 0.48*** | 0.38, 0.61 | 0.83 | 0.56, 1.23 |
| Graduated | 0.66** | 0.51, 0.86 | 0.79 | 0.50, 1.24 | 1.02 | 0.77, 1.35 | 0.72 | 0.43, 1.19 |
| Currently Employed | 0.71*** | 0.58, 0.86 | 0.63** | 0.45, 0.88 | 1.76*** | 1.43, 2.17 | 1.53* | 1.06, 2.22 |
| Mental Health Symptoms | 1.00 | 0.99, 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99, 1.01 | 1.00 | 0.99, 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99, 1.01 |
| Suicide Ideation, Lifetime | 1.74*** | 1.37, 2.21 | 1.53* | 1.03, 2.29 | 1.79*** | 1.38, 2.32 | 1.46 | 0.93, 2.30 |
| Drug Use Social Support | 0.70*** | 0.58, 0.83 | 0.55** | 0.37, 0.82 | 0.64*** | 0.52, 0.79 | 0.94 | 0.61, 1.44 |
| Alcohol Use Social Support | 0.83* | 0.70, 0.99 | 1.43 | 0.95, 2.13 | 0.44*** | 0.35, 0.54 | 0.49** | 0.31, 0.77 |
| Diagnosed in the last year | 1.45** | 1.15, 1.84 | 0.74 | 0.41, 1.34 | 1.78*** | 1.38, 2.31 | 1.23 | 0.62, 2.40 |
| CD4 Count, past 3 month | ||||||||
| Less than 200 | 0.88 | 0.64, 1.20 | 1.35 | 0.82, 2.24 | 1.01 | 0.72, 1.44 | 0.99 | 0.54, 1.82 |
| 200-499 | 0.90 | 0.75, 1.09 | 1.00 | 0.72, 1.38 | 0.94 | 0.75, 1.16 | 0.90 | 0.62, 1.30 |
| 500 or greater | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Less than 100% Adherence | 1.52** | 1.20, 1.94 | 1.62** | 1.19, 2.20 | 1.49** | 1.12, 1.98 | 1.72** | 1.20, 2.45 |
| Detectable Viral Load | 0.83 | 0.67, 1.03 | 0.72 | 0.51, 1.02 | 0.74 | 0.58, 1.05 | 0.78 | 0.52, 1.16 |
| CVAS HIV-negative partner | 1.70*** | 1.38, 2.08 | 1.70** | 1.19, 2.43 | 2.14*** | 1.71, 2.68 | 1.47* | 1.01, 2.17 |
MSM=males who have sex with men; CVAS=Condomless vaginal or anal sex
p<0.001;
p<0.01;
p<0.05
Table 3.
Bivariate and Multivariate Models for Weekly or More Frequent Marijuana Use and Any Non-Marijuana Illicit Drug Use
| Weekly or More Marijuana Use | Any past 3-month Other Illicit Drug Use | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bivariate | Multivariate | Bivariate | Multivariate | |||||
|
| ||||||||
| OR | 95% CI | AOR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | AOR | 95% CI | |
| Age | ||||||||
| 12-17 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| 18-20 | 2.86*** | 2.18, 3.74 | 2.26*** | 1.46, 3.49 | 1.90** | 1.30, 2.79 | 1.12 | 0.61, 2.05 |
| 21-26 | 3.39*** | 2.62, 4.37 | 2.02** | 1.25, 3.28 | 3.64*** | 2.55, 5.19 | 2.28* | 1.22, 4.28 |
| Route of HIV acquisition | ||||||||
| Perinatal | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Behavioral | 2.59*** | 2.13, 3.15 | 1.08 | 0.73, 1.59 | 3.06*** | 2.32, 4.04 | 1.32 | 0.80, 2.20 |
| Race/Ethnicity | ||||||||
| Black | 0.74 | 0.55, 1.01 | 0.60* | 0.37, 0.98 | 0.24*** | 0.18, 0.33 | 0.17*** | 0.10, 0.28 |
| Latino | 0.79 | 0.56, 1.12 | 0.64 | 0.37, 1.11 | 0.57** | 0.40, 0.81 | 0.48** | 0.28, 0.82 |
| Other | 0.68 | 0.45, 1.02 | 0.56 | 0.29, 1.08 | 0.35*** | 0.22, 0.56 | 0.24*** | 0.11, 0.51 |
| White | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| MSM | 2.41*** | 2.03, 2.87 | 1.41* | 1.01, 2.09 | 2.82*** | 2.29, 3.48 | 2.13** | 1.26, 3.58 |
| Gender Identity | ||||||||
| Male | 2.33*** | 1.93, 2.80 | 2.06*** | 1.42, 2.98 | 1.86*** | 1.47, 2.35 | 0.88 | 0.52, 1.47 |
| Female | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
| Transgender Female | 3.10*** | 1.86, 5.15 | 3.40** | 1.45, 7.94 | 4.15*** | 2.48, 6.95 | 3.62** | 1.56, 8.39 |
| Transgender Male | 1.02 | 0.34, 3.07 | 2.67 | 0.48, 14.81 | 2.22 | 0.68, 7.19 | 1.50 | 0.16, 14.29 |
| Unstable Housing, Lifetime | 1.62* | 1.10, 2.40 | 0.90 | 0.47, 1.71 | 2.25*** | 1.52, 3.34 | 2.20* | 1.13, 4.28 |
| Juvenile Justice Involvement, | 3.14*** | 2.60, 3.79 | 2.81*** | 2.06, 3.82 | 2.20*** | 1.79, 2.70 | 1.49* | 1.04, 2.13 |
| Lifetime | ||||||||
| Education | ||||||||
| Not in School | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| In School | 0.58*** | 0.48, 0.70 | 0.96 | 0.69, 1.34 | 0.48*** | 0.39, 0.60 | 0.91 | 0.62, 1.33 |
| Graduated | 0.88 | 0.68, 1.13 | 1.23 | 0.80, 1.89 | 0.77 | 0.58, 1.03 | 0.74 | 0.44, 1.23 |
| Currently Employed | 0.81 | 0.76, 1.09 | 0.80 | 0.59, 1.09 | 0.85 | 0.68, 1.05 | 0.59** | 0.40, 0.86 |
| Mental Health Symptoms | 1.00 | 0.99, 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99, 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99, 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99, 1.00 |
| Suicidal Ideation, Lifetime | 1.95*** | 1.53, 2.48 | 1.29 | 0.88, 1.90 | 2.25*** | 1.75, 2.89 | 2.12*** | 1.41, 3.20 |
| Drug Use Support | 0.47*** | 0.40, 0.56 | 0.30*** | 0.20, 0.43 | 0.67*** | 0.54, 0.81 | 0.67 | 0.44, 1.03 |
| Alcohol Use Support | 0.64*** | 0.54, 0.75 | 1.41 | 0.98, 2.05 | 0.75** | 0.61, 0.91 | 1.08 | 0.70, 1.66 |
| Diagnosed in the last year | 1.75*** | 1.38, 2.21 | 1.56 | 0.91, 2.67 | 1.21 | 0.93, 1.58 | 0.83 | 0.48, 1.81 |
| CD4 Count | ||||||||
| Less than 200 | 0.88 | 0.66, 1.17 | 1.13 | 0.72, 1.79 | 1.07 | 0.76, 1.50 | 1.00 | 0.56, 1.79 |
| 200-499 | 0.90 | 0.76, 1.07 | 1.03 | 0.77, 1.37 | 0.92 | 0.75, 1.14 | 1.02 | 0.72, 1.44 |
| 500 or greater | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Less than 100% Adherence | 1.75*** | 1.40, 2.18 | 1.91*** | 1.44, 2.52 | 1.32* | 1.01, 1.73 | 1.44* | 1.03, 2.01 |
| Detectable Viral Load | 0.87 | 0.70, 1.06 | 0.95 | 0.69, 1.30 | 0.92 | 0.72, 1.18 | 1.01 | 0.69, 1.47 |
| CVAS HIV-negative partner | 1.69*** | 1.38, 2.08 | 1.23 | 0.87, 1.73 | 2.01*** | 1.61, 2.51 | 1.34 | 0.92, 1.97 |
MSM= males who have sex with men; CVAS=Condomless vaginal or anal sex
p<0.001;
p<0.01;
p<0.05
Lifetime criminal justice involvement was associated with increased odds of weekly tobacco use, marijuana use, and any past three-month other illicit drug use. Furthermore, unstable housing was associated with increased odds of reporting weekly tobacco use and any past three-month other illicit drug use. Being employed was associated with increased odds of engaging in weekly alcohol use and reduced odds of weekly tobacco use and any past three-month other illicit drug use.
With regards to mental health variables, suicidal ideation was associated with increased odds of reporting weekly or more frequent tobacco use and any past three-month other illicit drug use. Social support for avoiding alcohol use was associated with reduced odds of reporting weekly alcohol use, and social support for avoiding drugs was associated with reduced odds of reporting weekly tobacco and marijuana use.
Reporting less than 100% ART adherence was associated with increased odds of reporting each of the substance use behaviors; whereas, viral load and CD4 were not associated with any of the substance use behaviors. Engaging in condomless anal or vaginal sex with an HIV-uninfected partner was associated with increased odds of reporting weekly alcohol and tobacco use.
4. Discussion
This study is among the first to describe the prevalence and correlates of different substance use behaviors in a large cohort study of both perinatally and behaviorally YLWH enrolled in HIV care settings. Study findings suggest that sociodemographic characteristics, HIV disease and sexual risk characteristics, and comorbid mental and behavioral health factors are associated with substance use behaviors, but these some of these factors differ depending on the specific substance use behavior. Given the high prevalence of substance use behaviors in this sample of YLWH, our study findings support the need for regular screening for substance use in primary care settings where YLWH are treated. This is particularly important as not all HIV primary care clinics routinely screen patients for alcohol and other substance use (23).
Notably, one in four youth reported daily tobacco use and approximately one-third of the youth used tobacco on a daily or weekly basis, which is substantially higher than their HIV-negative counterparts (24). Approximately one in five youth reported weekly or more frequent alcohol use, marijuana use, and past three-month other illicit drug use. This sample of YLWH exhibited similar levels of other illicit drugs to the U.S. general population of youth; however, they reported slightly higher levels of marijuana and alcohol use (25), which is particularly troubling given that engaging in substance use behaviors at a younger age has been associated with increased risk of substance dependence, psychiatric disorders, and even mortality (26). Furthermore, we found a high co-occurrence of substance use with particularly high strong Phi Coefficient correlations between tobacco and marijuana use. Given that existing substance use interventions have only produced modest effects (27), there is a critical need to address substance use among these vulnerable YLWH and to ensure that effective tobacco control strategies and other substance use prevention and treatment programs are developed, tested, and implemented.
Our results mirror national survey data that indicate that young people of color are significantly less likely to engage in weekly substance use compared to their white counterparts (28). However, prior research indicates that while rates of substance use among Black youth may be lower than white youth, Black adolescents and adults experience a higher prevalence of substance-related problems than their white counterparts (29, 30). Such disparities have been attributed to young people of color being less likely to receive substance use treatment compared to their white counterparts (28). Structural factors such as poverty, incarceration, as well as exposure to community violence have been shown to exacerbate substance use and HIV risk among youth of color (31). Thus, research is warranted to better understand substance use trajectories across the lifespan and identify critical barriers to the receipt of substance use screening and treatment for people of color living with HIV.
Disparities have been noted in substance use by sexual identity and gender identity among youth in United States. Consistent with prior research (32, 33), young MSM were more likely to report marijuana, alcohol, tobacco, and other illicit drug use compared to other youth, and young transgender women were more likely to report weekly or more frequent marijuana use and any other illicit drug use compared to young cisgender females. As such, future research is warranted to better understand the social context of young people’s lives, including elucidating the ways in which multiple and interlocking forms of stigma heighten risk for substance-related problems over the life course in order to reduce substance use disparities among sexual and gender minority populations.
Structural factors, and in particular a history of incarceration, were significantly associated with many of the substance use outcomes. Prevention programs for youth in the juvenile justice system are useful in addressing substance use and HIV-related risks. However, many of these young people frequently experience social and environmental distress including exposure to violence, limited economic resources, and family problems including parental substance abuse (34). Thus youth with a history of incarceration may particularly benefit from brief substance use screening and interventions in HIV care settings in order to reduce substance use behaviors, as well as potentially impact the high rates of recidivism.
Over half of the sample indicated that they had social support in avoiding alcohol or drugs. In bivariate analyses, social support was significantly associated with reduced odds of engaging in each substance use behavior; however, social support was only protective against alcohol and marijuana use in fully adjusted models. These findings highlight the importance of social support in young peoples’ lives to reduce the burden of substance use problems in this high risk-group. HIV care settings may be able to reduce substance use for YLWH if they sponsor clinic support group for youth and provide supportive adult role models and/or peer buddies. These strategies, may increase social support for avoiding substances. Future research is warranted to better understand how different types and sources of support may reduce substance use behaviors among YLWH.
Consistent with previous research documenting the substance use and HIV risk behaviors among people living with HIV, including youth (4, 14, 35), we found that engaging in any condomless intercourse was significantly associated with an increased odds of engaging in weekly alcohol and tobacco use, whereas there was no significant association of condomless intercourse with marijuana use and other illicit drug use. Alcohol use may impair young people’s decision making and lower their inhibitions, which has the potential increase their potential for engaging in high-risk behaviors (36). Thus, substance use screening and linkage to substance use treatment targeting alcohol use may be particularly effective in reducing substance use and HIV risk behaviors among YLWH.
In multivariate models, we found that suboptimal ART adherence was significantly associated with increased odds of alcohol, tobacco, and marijuana use, as well as any past three-month other illicit drug use; however, viral load and CD4 was not associated with these substance use behaviors. Our findings add to the limited research available on substance use and ART adherence among YLWH (37). Studies among adults living with HIV have found self-report measures of suboptimal ART adherence to be significantly associated with substance use (38). It is plausible that we did not find significant associations between substance use and HIV clinical markers, such as viral load and CD4, because the YLWH were already engaged in HIV care. Nonetheless, these findings suggest that brief substance use screening and interventions in HIV care settings are urgently needed to improve HIV treatment, prevention and adherence outcomes.
4.1 Limitations
This study findings must be interpreted within several limitations. First, the cross-sectional design of the study limits, which precludes us for making causal inferences. Although ACASI technology was used to mitigate social desirability bias, self-report data is still subject to social desirability and recall bias. Additionally, we did not formally adjust for numerous tests; therefore, study findings with marginal p-values, such as the association between social support and avoiding alcohol and weekly tobacco use, should be interpreted with caution. Furthermore, this is a non-probability sample of youth who were aware of their HIV status and linked to medical services which limits generalizability to the broader population of youth living with HIV.
4.2 Conclusions
Despite these limitations, this study provides important insights into the prevalence and correlates of substance use among YLWH, which has practical implications for research and clinical services. Future research is warranted to better understand the structural and social factors associated with substance use behaviors among YLWH, particularly among young MSM and transgender women. Specifically, we found that social support to avoid substance use was protective against certain substance use behaviors. A better understanding of the different types and sources of support, as well as identifying which groups are in most need of social support, may guide supportive services. Additionally, the important link between structural factors, such as juvenile justice involvement and substance use, merits further investigation and draws attention to the importance of structural interventions in HIV prevention efforts (39). Given the high prevalence of substance use among youth living with HIV seen in primary care, clinicians should be trained to use screening tools and interventions for substance use problems in order to identify youth in need of additional evaluation and treatment.
References
- 1.Center for Disease Control and Prevention CDC Fact Sheet New HIV infections in the United States. 2012 [Google Scholar]
- 2.Phillips G, Wohl A, Xavier J, Jones K, Hidalgo J. Epidemiologic data on young men who color who have sex with men. AIDS Patient Care STDs. 2011;25(Supple 1):S3–S8. doi: 10.1089/apc.2011.9882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hosek SG, Harper GW, Domanico R. Predictors of medication adherence among HIV-infected youth. Psychology, Health, & Medicine. 2005;10(2):166–179. doi: 10.1080/1354350042000326584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bruce D, Kahana SY, Fernández MI, Harper GW, ATN Alcohol use predicts sexual risk behavior with HIV-negative or partners of unknown status among young HIV-positive men who have sex with men. AIDS Care. 2013;25(5):559–65. doi: 10.1080/09540121.2012.720363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Alperen J, Brummel S, Tassiopoulos K, Mellins CA, Kacanek D, Smith R, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for substance use among perinatally HIV-infected and perinatally exposured but uninfected youth. J Adolesc Health. 2014;54(3):341–349. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2013.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Elkington KS, Bauermeister JA, Santamaria EK, Dolezal C, Mellins CA. Substance use and the development of sexual risk behaviors in youth perinatally exposed to HIV. J Pediatr Psychol. 2014;41(2) doi: 10.1093/jpepsy/jsu103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Elkington KS, Bauermeister JA, Robbins RN, Gromadzka O, Abrams EJ, Wiznia A, et al. Individual and contextual factors of sexual risk in youth perinatally infected with HIV. AIDS Patient Care STDs. 2012;26:411–422. doi: 10.1089/apc.2012.0005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mellins CA, Havens JF, McCaskill EO, Leu CS, Brudney K, Chesney MA. Mental health, substance use and disclosure are signficantly associated with treatment adherence of HIV-infected mothers. Psychol Health Med. 2002;7:451–460. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Power R, Koopman C, Volk J, Israelski DM, Stone L, Chesney MA, et al. Social support, substance use, and denial in relationship to antiretroviral treatment adherence among HIV-infected persons. AIDS Patient Care STDs. 2003;17:245–252. doi: 10.1089/108729103321655890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Agrawal A, Budney AJ, Lynskey MT. The co-occurring use and misuse of cannabis and tobacco: A review. Addiction. 2012;107(7):1221–1233. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2012.03837.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Grella CE, Hser Y, Joshi V, Rounds-Bryant J. Drug treatment outcomes for adolescents with comorbid mental and substance use disorders. J Nerv Mental Dis. 2001;189(6):384–392. doi: 10.1097/00005053-200106000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Udell W, Donenberg G, Emerson E. Parents matter in HIV risk among probabtion youth. J Fam Psychol. 2011;25:785–789. doi: 10.1037/a0024987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wasserman GA, McReynolds LS, Ko S, Katz LM, Carpenter JR. Gender differences in pediatric disorders at juvenile probation intake. Am J Public Health. 2005;95:131–137. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2003.024737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fernandez MI, Huskzti HC, Wilson PA, Kahana S, Nichols S, Gonin R, et al. Profiles of risk among HIV-infected youth in clinical settings. AIDS Behav. 2015;19(5):918–930. doi: 10.1007/s10461-014-0876-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mastro TD, Cunningham J, Medrana T, van Dam J. Youth and HIV: the intersection of homelessness, orphanhood, injection drug use, and sexual risk. AIDS. 2012;26:111–113. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32834dcfa0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bird JD, Kuhns L, Garofalo R. The impact of role models on health outcomes for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender youth. J Adolesc Health. 2012;50:353–357. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2011.08.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yancey AK, Siegel JM, McDaniel KL. Role models, ethnic identity, and health-risk behaviors in urban adolescents. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2002;156:55–61. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.156.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Brown LK, Whiteley L, Harper GW, Nichols S, Amethys N, PRevention CAPTfTAMTNfHA Psychological symptoms among 2032 youth living with HIV: A multisite study. AIDS Patient Care STDs. 2015;29(4):212–219. doi: 10.1089/apc.2014.0113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kahana S, Fernandez MI, Wilson PA, Bauermeister JA, Lee S, Wilson CM, et al. Rates and correlates of antiretroviral therapy use and biorlogic suprression amog perinatally and behaviorally HIV infected youth linked to care in the United States. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015;68(169-177) doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000000408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.World Health Organization The Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test (ASSIST): Development, reliability and feasibility. Addiction. 2002;97:1183–1194. doi: 10.1046/j.1360-0443.2002.00185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Derogatis LR. BSI Brief Symptom Inventory: Administration, Scoring, and Procedures Manual. PsychCorp; Bloomington, MN: 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lam PK, Naar-King S, Wright K. Social support and disclosure as predictors of mental health in HIV-positive youth. AIDS Patient Care STDs. 2007;21:20–29. doi: 10.1089/apc.2006.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Surah S, Kieran J, O’Dea S, et al. Use of the Alcohol Use Identification Test (AUDIT) to determine the prevalence of alcohol misuse among HIV-infected individuals. Int J STDs AIDS. 2013;24(7):517–521. doi: 10.1177/0956462412473885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Youth Risk Behavioral Surveillance - United States, 2007. MMWR. 2008;57(SS04):1–131. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Johnston LD, O'Malley P, Bachman JG, Schulenberg JE. Monitoring the Future national results on adolescent drug use: Overview of key findings, 2011. Institute for Social Research, The University of Michigan; Ann Arbor: 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Swahn MH, Bossarte RM, Ashby JS, Meyers J. Pre-teen alcohol use initiation and suicide attempts among middle and high school students: findings from the 2006 Georgia Student Health Survey. Addict Behav. 2010;35:452–458. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2009.12.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Naar-King S, Wright K, Parsons JT. Health Choices: Motivational enhancement therapy for health risk behaviors in HIV positive youth. AIDS Educat Prev. 2006;18(1):1–11. doi: 10.1521/aeap.2006.18.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Johnston LD, O'Malley PM, Bachman JG, Jerald G, Schulenberg JE. Monitoring the Future National Survey Results on Drug Use, 1975-2010. Volume 1, Secondary School Students. Institute of Social Research. 2011 [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bachman JG, Wallace JM, Kurth CL, Johnston LD, O’Malley PM, Neighbors HW. Racial/Ethnic differences in smoking, drinking, and illicit drug use among American high school seniors. Am J Public Health. 1991;81:371–377. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.3.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Welte JW, Barnes GM. Alcohol use among adolescent minority groups. J Studies Alcohol. 1987;48:329–336. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1987.48.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Quinn K, Voisin DR, Bouris A, Schneirder J. Psychological distress, drug use, sex risks, and medication adherence among young HIV-positive Black men who have sex with men: Exposure to community violence matters. AIDS Care. 2016 doi: 10.1080/09540121.2016.1153596. E-pub ahead of print. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Garofalo R, Deleon J, Osmer E, Doll M, Harper GW. Overlooked, misunderstood and at-risk: Exploring the lives and HIV risk of ethnic minority male-to-female trangender youth. J Adolesc Health. 2006;38(3):230–236. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2005.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Goldbach JT, Scrager SM, Dunlap SL, Holloway IW. The application of minority stress theory to marijuana use among sexual minority adolescents. Subst Use Mis. 2015;50(3):366–375. doi: 10.3109/10826084.2014.980958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Espinosa EM, Sorensen JR, Lopez MA. Youth pathways to placement: The influence of gender, mental health needs and trauma on confinement in juveline justice system. J Youth Adolesc. 2013;42(12):1824–1836. doi: 10.1007/s10964-013-9981-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Mimiaga MJ, Reisner SL, Grasso C, Crane HM, Safren SA, Kitahata MM, et al. Substance use among HIV-infected patients engaged in primary care in the United States: Findings from the Centers for AIDS Research Network of Integrated Clinical Systems Cohort. Am J Public Health. 2013;103:1457–1467. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2012.301162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mustanski B, Byck GR, Newcomb ME, Henry D, Bolland J, Dick D. HIV information and behavioral skills moderate the effects of relationship type and substance use on HIV risk behaviors among African American youth. AIDS Patient Care STDs. 2013;27(6):342–351. doi: 10.1089/apc.2012.0468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Murphy DA, Belzer M, Durako SJ, Sarr M, Wilson CM, Muenz LR. Longitudinal antiretroviral adherence among adolescents infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2005;159:764–770. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.159.8.764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tucker JS, Burnam MA, Sherbourne CS, Kung F, Gifford AL. Substance use and mental health correlates of nonadherence to antiretroviral medications in a sample of patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Am J Med. 2003;114(7):573–580. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(03)00093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sumartojo E. Structural factors in HIV prevention: concepts, examples, and implications for research. AIDS. 2000;14(Suppl 1) doi: 10.1097/00002030-200006001-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]