Abstract
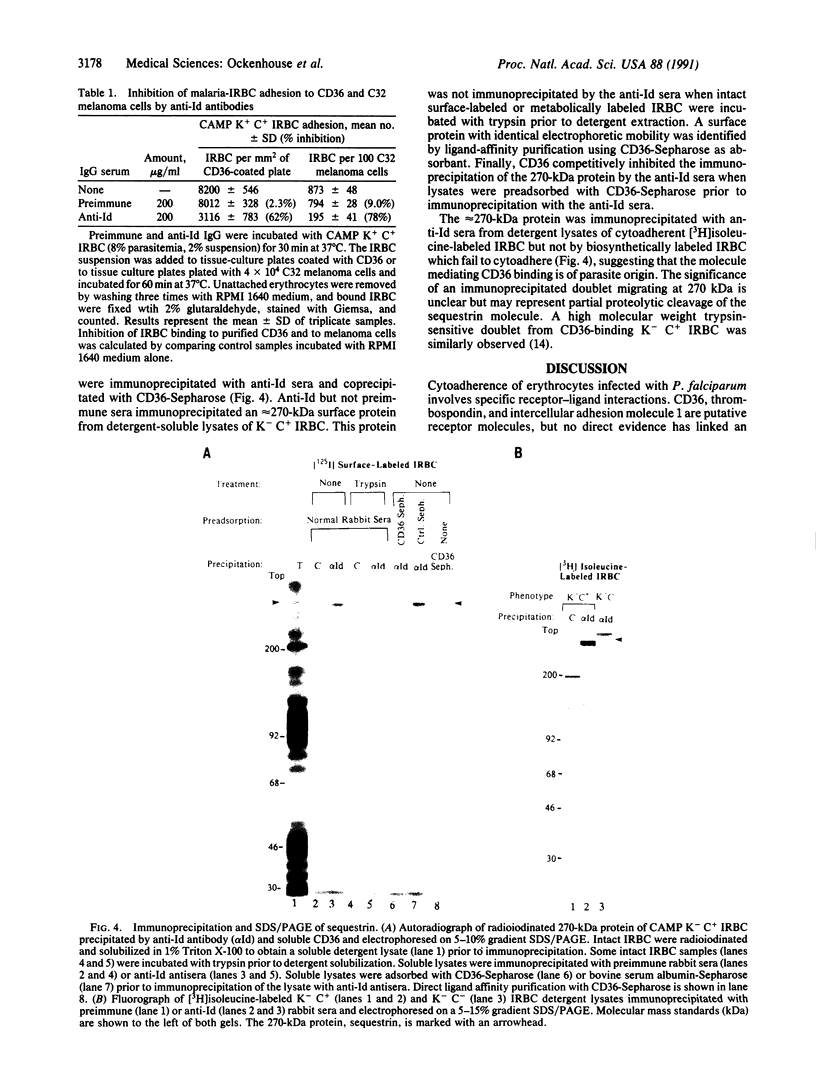
The CD36 molecule expressed by human endothelial cells is a receptor for the adhesion of erythrocytes infected with the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. A CD36-specific monoclonal antibody, OKM8, inhibits the adhesion of malaria-infected erythrocytes (IRBC) to purified CD36 and cells expressing CD36. Monospecific polyclonal anti-idiotype (anti-Id) antibodies, raised against monoclonal antibody OKM8, expressed determinants molecularly mimicking the CD36 binding domain for the adhesion of IRBC. Purified rabbit anti-Id antibodies reacted with the surface of IRBC by immunofluorescence, directly supported the adhesion of wild-type P. falciparum malaria isolates, and inhibited IRBC cytoadherence to melanoma cells. An approximately 270-kDa protein was immunoprecipitated by the anti-Id antibodies from surface-labeled and metabolically labeled IRBC and was competitively inhibited by soluble CD36. These results support the hypothesis that CD36 is a receptor and the approximately 270-kDa protein, sequestrin, is a complementary ligand involved in the adhesion of IRBC to host-cell endothelium. Sequestrin is a candidate malaria vaccine antigen, and anti-Id antibodies that recognize this molecule may be useful for passive immunotherapy of cerebral and severe P. falciparum malaria.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aley S. B., Sherwood J. A., Howard R. J. Knob-positive and knob-negative Plasmodium falciparum differ in expression of a strain-specific malarial antigen on the surface of infected erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1585–1590. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnwell J. W., Asch A. S., Nachman R. L., Yamaya M., Aikawa M., Ingravallo P. A human 88-kD membrane glycoprotein (CD36) functions in vitro as a receptor for a cytoadherence ligand on Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):765–772. doi: 10.1172/JCI114234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnwell J. W., Ockenhouse C. F., Knowles D. M., 2nd Monoclonal antibody OKM5 inhibits the in vitro binding of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes to monocytes, endothelial, and C32 melanoma cells. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3494–3497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berendt A. R., Simmons D. L., Tansey J., Newbold C. I., Marsh K. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 is an endothelial cell adhesion receptor for Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):57–59. doi: 10.1038/341057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs B. A., Culvenor J. G., Ng J. S., Kemp D. J., Brown G. V. Plasmodium falciparum: cytoadherence of a knobless clone. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Aug;69(2):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs B. A., Goozé L., Wycherley K., Wilkinson D., Boyd A. W., Forsyth K. P., Edelman L., Brown G. V., Leech J. H. Knob-independent cytoadherence of Plasmodium falciparum to the leukocyte differentiation antigen CD36. J Exp Med. 1990 Jun 1;171(6):1883–1892. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.6.1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leech J. H., Barnwell J. W., Miller L. H., Howard R. J. Identification of a strain-specific malarial antigen exposed on the surface of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1567–1575. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magowan C., Wollish W., Anderson L., Leech J. Cytoadherence by Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes is correlated with the expression of a family of variable proteins on infected erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1307–1320. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockenhouse C. F., Tandon N. N., Magowan C., Jamieson G. A., Chulay J. D. Identification of a platelet membrane glycoprotein as a falciparum malaria sequestration receptor. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1469–1471. doi: 10.1126/science.2467377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. D., Sherwood J. A., Spitalnik S. L., Panton L. J., Howard R. J., Dixit V. M., Frazier W. A., Miller L. H., Ginsburg V. Thrombospondin binds falciparum malaria parasitized erythrocytes and may mediate cytoadherence. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):64–66. doi: 10.1038/318064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sege K., Peterson P. A. Use of anti-idiotypic antibodies as cell-surface receptor probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2443–2447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talle M. A., Rao P. E., Westberg E., Allegar N., Makowski M., Mittler R. S., Goldstein G. Patterns of antigenic expression on human monocytes as defined by monoclonal antibodies. Cell Immunol. 1983 May;78(1):83–99. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandon N. N., Lipsky R. H., Burgess W. H., Jamieson G. A. Isolation and characterization of platelet glycoprotein IV (CD36). J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7570–7575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Jensen J. B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.781840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udomsangpetch R., Aikawa M., Berzins K., Wahlgren M., Perlmann P. Cytoadherence of knobless Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes and its inhibition by a human monoclonal antibody. Nature. 1989 Apr 27;338(6218):763–765. doi: 10.1038/338763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]