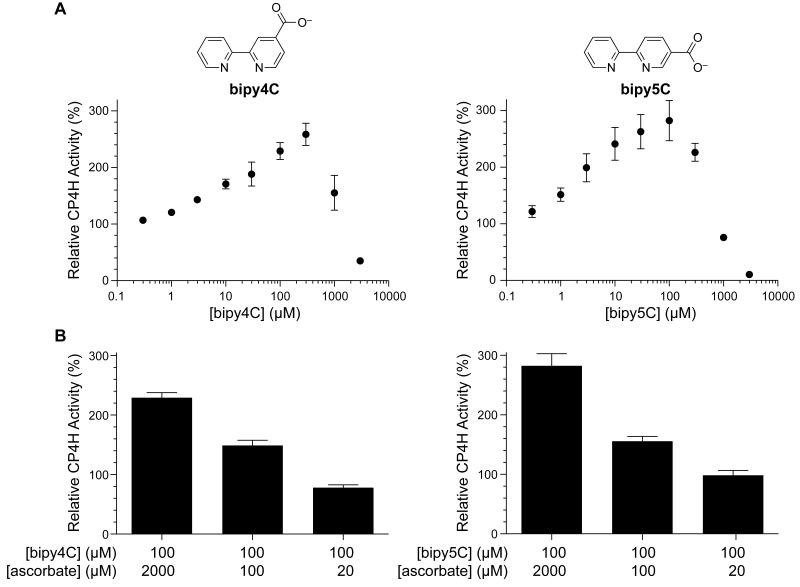
Figure 1.
Activation of CP4H1 by bipy4C and bipy5C is dose-dependent and requires the Vitamin C cofactor. (A) Dose–response curves for activation (and inhibition) of CP4H1 by bipymonoCs. CP4H assays were performed in the presence and absence of activator (0.3–3000 μM) and ascorbate (2 mM), and in the presence of a saturating concentration of α-ketoglutarate (1 mM). Relative activity values are the mean (±SE) of three independent experiments) and represent the ratio of enzymatic activity in the presence and absence of activator. (B) Dependence of the activation observed by bipy4C and bipy5C on ascorbate concentration. CP4H assays were performed in the presence and absence of activator (100 μM) and ascorbate (20 μM–2 mM), and in the presence of 1 mM α-ketoglutarate. Relative activity values are the mean (±SE) of three independent experiments) and represent the ratio of CP4H activity observed in the presence and absence of activator.