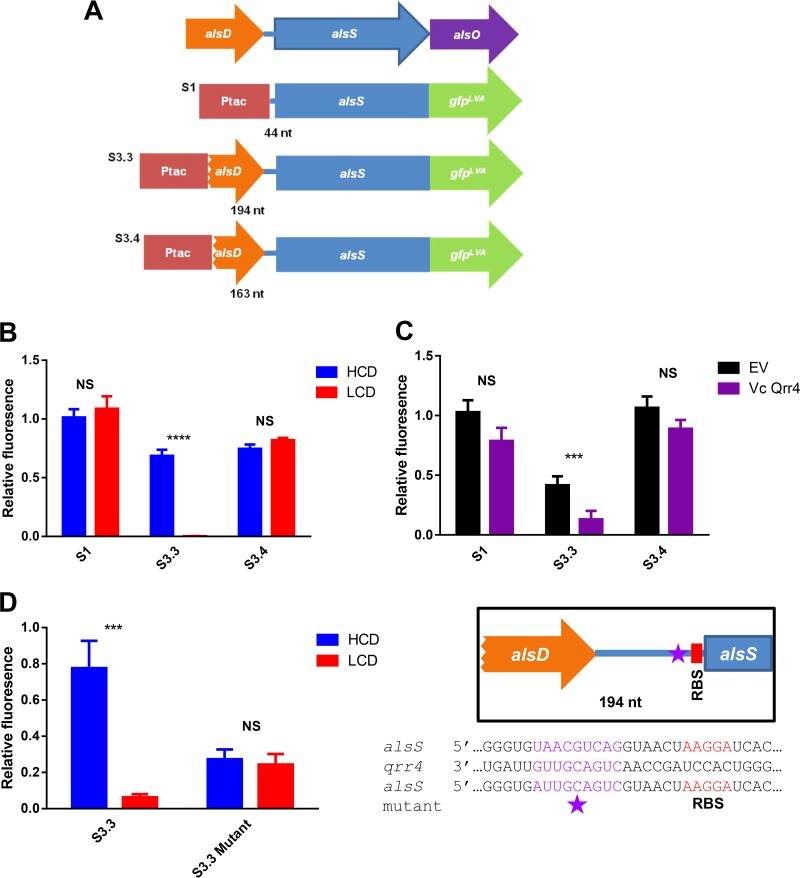
FIG 5 .
Qrr1-4 regulate alsS translation. (A) Depiction of the alsDSO operon and the different GFP translational fusions used in this study. nt, nucleotides. (B) Relative GFP fluorescence of different GFP translational fusions in V. cholerae HCD-locked (ΔluxO ΔaphA ΔhapR ΔvpsL; blue bars) and LCD-locked (luxOD61E ΔaphA ΔhapR ΔvpsL; red bars) strains. Each bar is normalized to the median FLU value of the HCD strain harboring the S1 plasmid. (C) Relative GFP fluorescence of different GFP translational fusions in E. coli strains either carrying an empty vector (EV) plasmid (black bars) or a plasmid containing rhamnose-induced V. cholerae qrr4 (purple bars). Each bar is normalized to the median FLU value of the E. coli strain carrying the S1 and EV plasmids. (D) Relative GFP fluorescence of GFP translational fusion S3.3 and S3.3 harboring nine consecutive mutations in a predicted Qrr binding site in HCD-locked (blue bars) and LCD-locked (red bars) V. cholerae strains. Each bar is normalized to the median FLU value of the HCD strain harboring the S1 plasmid. Highlighted are the location of a hypothetical Qrr binding site in alsS (purple star), the sequence of the mutant construct, and the predicted RBS. The values shown are averages of at least three replicates. Error bars denote the SEM. P values (Student’s t test): ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. NS, no statistical significance.