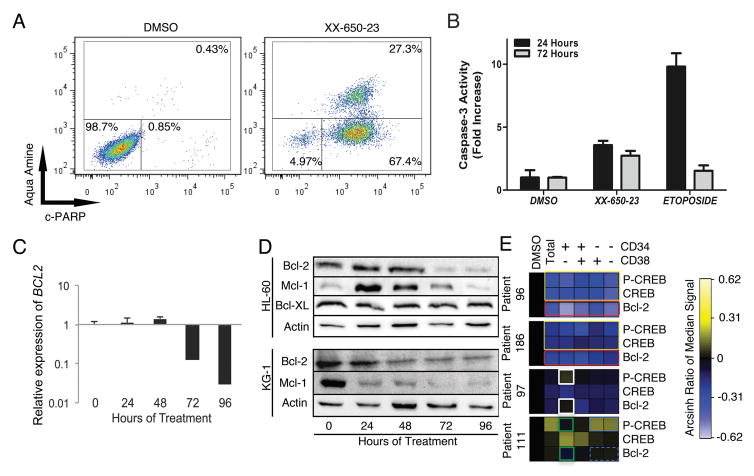
Fig. 5. CREB Inhibition in AML Cells Induces Apoptosis.
A) HL-60 cells clearly showed early apoptotic (c-PARP+/aqua amine−) or late apoptotic (c-PARP+/aqua amine+) populations following 72 hours of treatment with 2 μ XX-650-23. Representative flow cytometric plots of three independent experiments are shown. B) Caspase-3 activity is activated in response to XX-650-23 treatment in HL60 cells. Data are graphed as mean ± SD (n = 2). C) RT-PCR showed BCL2 expression decreases at 72 hours after XX-650-23 treatment in HL-60 cells. Data are graphed as mean ± SEM (n = 3). D) Western blot analysis shows a decrease in Bcl-2 protein expression following 72 hours of treatment, no change in Bcl-XL expression, and an initial increase followed by a decrease in Mcl-1 expression in HL-60 cells. In KG-1 cells, Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 also showed decreased expression following XX-650-23 treatment. E) Heatmap representing expression of p-CREB (Ser133), total CREB (CREB) and Bcl-2 in four primary AML samples treated with DMSO or XX-650-23 as analyzed by mass cytometry. Expression shown as Arcsin ratio to DMSO control (first column). Gated cell populations based on CD34 and/or CD38 as indicated above heatmap. Patient 96 and 186 demonstrate downregulation of Bcl-2 in all cell populations in response to XX-650-23 (red box) as well as decreases in total CREB and p-CREB (yellow boxes). Patient 97 demonstrates activation of p-CREB in a cell specific manner (white boxes) as well as no effect on Bcl-2 expression in CD34+CD38− population. In contrast, p-CREB and Bcl-2 expression levels were downregulated in CD34+CD38− population (green boxes) in Patient 111, even though p-CREB level was increased (blue box) and Bcl-2 expression level was not changed (blue dashed box) in mature populations.