Abstract
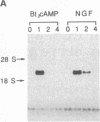
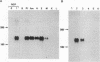
PC3 is an immediate early gene induced by nerve growth factor in PC12 cells, a cell line derived from a tumor of the adrenal medulla that undergoes neuronal differentiation in the presence of nerve growth factor. This induction is independent of new protein synthesis as it can occur in the presence of cycloheximide. PC3 is also induced with similar kinetics, but at lower levels, by membrane depolarization (both in vivo and in vitro) and epidermal growth factor. It is induced at much lower levels by fibroblast growth factor and interleukin 6. In vivo it is found expressed in tissues, such as brain at embryonic day 13.5, placenta, amnion, and spleen, which are proliferating and/or differentiating. The deduced protein sequence from the cDNA indicates the presence of a signal peptide, suggesting that PC3 is secreted.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson E. D., Deller M. J., Warshaw J. B. Functional EGF receptors are present on mouse embryo tissues. Nature. 1981 Jun 25;291(5817):656–659. doi: 10.1038/291656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloe L., Levi-Montalcini R. Nerve growth factor-induced transformation of immature chromaffin cells in vivo into sympathetic neurons: effect of antiserum to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1246–1250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Axel R. Molecular probes for the development and plasticity of neural crest derivatives. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):649–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel D. P., Sheng M., Lau L. F., Greenberg M. E. Growth factors and membrane depolarization activate distinct programs of early response gene expression: dissociation of fos and jun induction. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):304–313. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein D. E., Greene L. A. Evidence for RNA synthesis-dependent and -independent pathways in stimulation of neurite outgrowth by nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6059–6063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler C. E., Herschman H. R. Tumor promoter modulation of epidermal growth factor- and nerve growth factor-induced adhesion and growth factor binding of PC-12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Nov;105(2):275–285. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041050211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Angel P., Karin M. Jun-B differs in its biological properties from, and is a negative regulator of, c-Jun. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90754-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. J., McNurlan M. A. Regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation by interferons. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 1;226(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2260345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Gordon M. B., Rubino K. L., Sambucetti L. C. Isolation and characterization of the c-fos(rat) cDNA and analysis of post-translational modification in vitro. Oncogene. 1987;2(1):79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernfors P., Hallbök F., Ebendal T., Shooter E. M., Radeke M. J., Misko T. P., Persson H. Developmental and regional expression of beta-nerve growth factor receptor mRNA in the chick and rat. Neuron. 1988 Dec;1(10):983–996. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Greene L. A., Ziff E. B. Nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor induce rapid transient changes in proto-oncogene transcription in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14101–14110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., Devereux J., Burgess R. R. The codon preference plot: graphic analysis of protein coding sequences and prediction of gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):539–549. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich G., Meyer T. E. Nerve growth factor (NGF) is present in human placenta and semen, but undetectable in normal and Paget's disease blood: measurements with an anti-mouse-NGF enzyme immunoassay using a recombinant human NGF reference. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 30;155(1):482–486. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard D. G., Ziff E. B., Greene L. A. Identification and characterization of mRNAs regulated by nerve growth factor in PC12 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3156–3167. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Angeletti P. U. Nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jul;48(3):534–569. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.3.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi A., Eldridge J. D., Paterson B. M. Molecular cloning of a gene sequence regulated by nerve growth factor. Science. 1985 Jul 26;229(4711):393–395. doi: 10.1126/science.3839317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisonpierre P. C., Belluscio L., Friedman B., Alderson R. F., Wiegand S. J., Furth M. E., Lindsay R. M., Yancopoulos G. D. NT-3, BDNF, and NGF in the developing rat nervous system: parallel as well as reciprocal patterns of expression. Neuron. 1990 Oct;5(4):501–509. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masiakowski P., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor induces the genes for two proteins related to a family of calcium-binding proteins in PC12 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1277–1281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt J. A nerve growth factor-induced gene encodes a possible transcriptional regulatory factor. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):797–799. doi: 10.1126/science.3672127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt J. Nerve growth factor induces a gene homologous to the glucocorticoid receptor gene. Neuron. 1988 May;1(3):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90138-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Cohen D. R., Hempstead J. L., Curran T. Mapping patterns of c-fos expression in the central nervous system after seizure. Science. 1987 Jul 10;237(4811):192–197. doi: 10.1126/science.3037702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandiella-Alonso A., Malgaroli A., Vicentini L. M., Meldolesi J. Early rise of cytosolic Ca2+ induced by NGF in PC12 and chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):48–51. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81529-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raedler E., Raedler A. Autoradiographic study of early neurogenesis in rat neocortex. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1978 Sep 27;154(3):267–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00345657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Kenney J., Kowalski W. J., Friesel R., Mehlman T., Maciag T. Interaction of endothelial cell growth factor with heparin: characterization by receptor and antibody recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6138–6142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler M., Schwab M. E. Specific retrograde transport of nerve growth factor (NGF) from neocortex to nucleus basalis in the rat. Brain Res. 1984 May 21;300(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91338-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton D. L., Reichardt L. F. Expression of the beta-nerve growth factor gene correlates with the density of sympathetic innervation in effector organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7951–7955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Greenberg M. E. The regulation and function of c-fos and other immediate early genes in the nervous system. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90106-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. P., Varon S., Shooter E. M. Multiple forms of the nerve growth factor protein and its subunits. Biochemistry. 1968 Sep;7(9):3259–3268. doi: 10.1021/bi00849a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirone F., Shooter E. M. Early gene regulation by nerve growth factor in PC12 cells: induction of an interferon-related gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2088–2092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisden W., Errington M. L., Williams S., Dunnett S. B., Waters C., Hitchcock D., Evan G., Bliss T. V., Hunt S. P. Differential expression of immediate early genes in the hippocampus and spinal cord. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):603–614. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90118-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]