Abstract
We describe the formation of homologously paired joint molecules in an in vitro reaction that is dependent on the concerted actions of purified RecA and RecBCD proteins and is stimulated by single-stranded DNA-binding protein (SSB). RecBCD enzyme initiates the process by unwinding the linear double-stranded DNA to produce single-stranded DNA, which is trapped by SSB and RecA. RecA uses this single-stranded DNA to catalyze the invasion of a supercoiled double-stranded DNA molecule, forming a homologously paired joint molecule. At low RecBCD enzyme concentrations, the rate-limiting step is the unwinding of duplex DNA by RecBCD, whereas at higher RecBCD concentrations, the rate-limiting step is RecA-catalyzed strand invasion. The behavior of mutant RecA proteins in this in vitro reaction parallels their in vivo phenotypes, suggesting that this reaction may define biochemical steps that occur during homologous recombination by the RecBCD pathway in vivo.
Full text
PDF
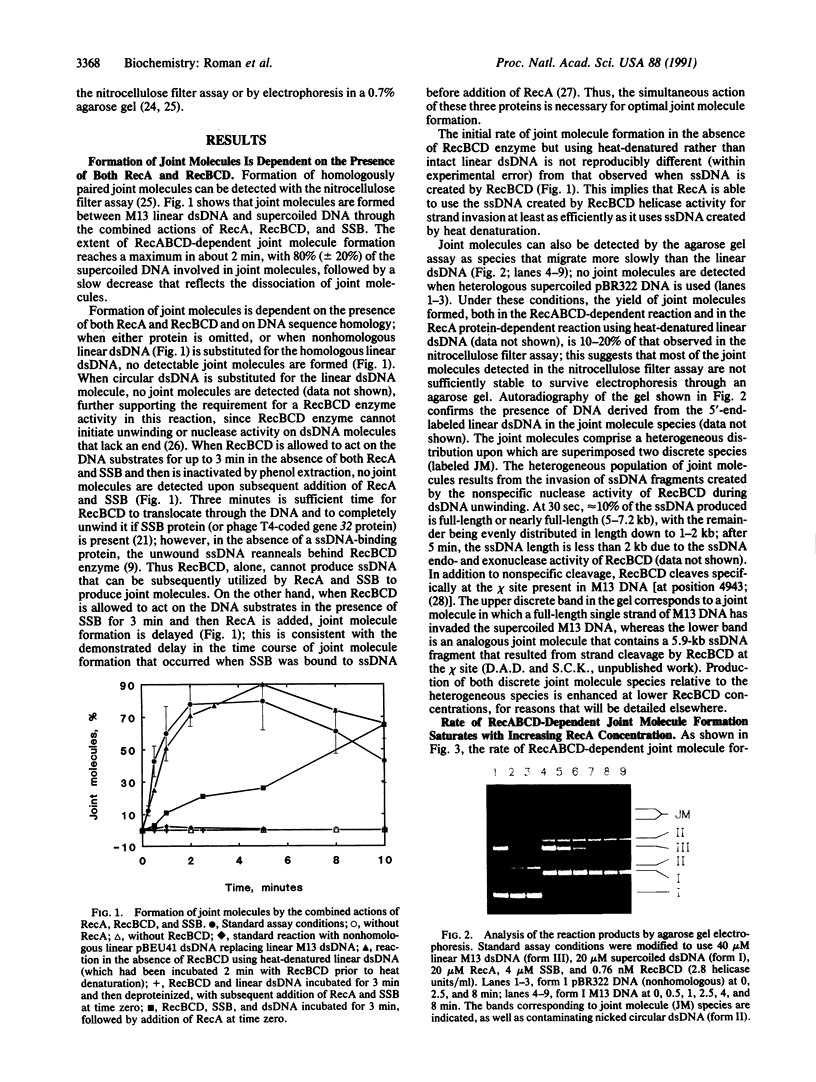
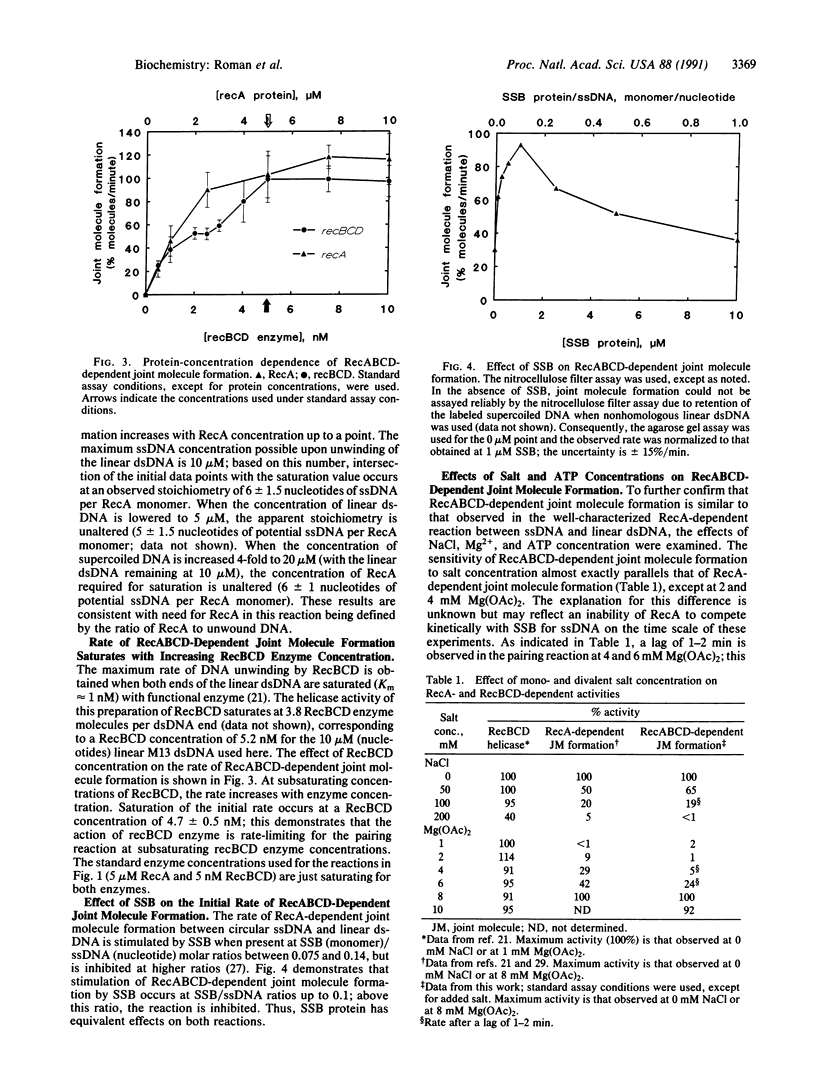
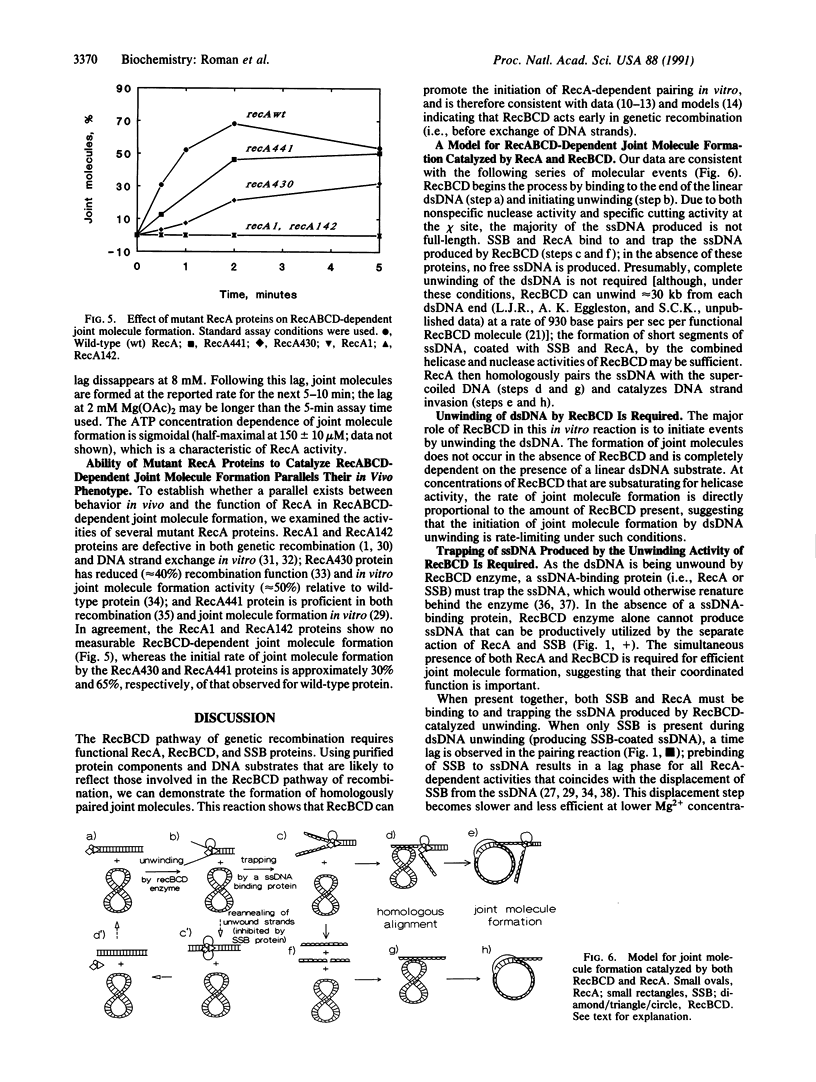

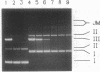
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beattie K. L., Wiegand R. C., Radding C. M. Uptake of homologous single-stranded fragments by superhelical DNA. II. Characterization of the reaction. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):783–803. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90271-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK A. J., MARGULIES A. D. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF RECOMBINATION-DEFICIENT MUTANTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:451–459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellazzi M., George J., Buttin G. Prophage induction and cell division in E. coli. I. Further characterization of the thermosensitive mutation tif-1 whose expression mimics the effect of UV irradiation. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(2):139–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00269133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J. Recombination deficient mutants of E. coli and other bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:67–86. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. M., Lehman I. R. Enzymes of general recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:229–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. M., Soltis D. A., Livneh Z., Lehman I. R. On the role of single-stranded DNA binding protein in recA protein-promoted DNA strand exchange. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2577–2585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichler D. C., Lehman I. R. On the role of ATP in phosphodiester bond hydrolysis catalyzed by the recBC deoxyribonuclease of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):499–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerson P. T., Howard-Flanders P. Cotransduction with thy of a gene required for genetic recombination in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1729–1731. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1729-1731.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassberg J., Meyer R. R., Kornberg A. Mutant single-strand binding protein of Escherichia coli: genetic and physiological characterization. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):14–19. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.14-19.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J., Shores C. G. RecA protein rapidly crystallizes in the presence of spermidine: a valuable step in its purification and physical characterization. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):158–162. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., Theriot L. Mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 defective in DNA repair and in genetic recombination. Genetics. 1966 Jun;53(6):1137–1150. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.6.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczykowski S. C., Burk D. L., Krupp R. A. Biochemical events essential to the recombination activity of Escherichia coli RecA protein. I. Properties of the mutant RecA142 protein. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 20;207(4):719–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90239-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczykowski S. C., Krupp R. A. Effects of Escherichia coli SSB protein on the single-stranded DNA-dependent ATPase activity of Escherichia coli RecA protein. Evidence that SSB protein facilitates the binding of RecA protein to regions of secondary structure within single-stranded DNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):97–113. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90630-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavery P. E., Kowalczykowski S. C. Properties of recA441 protein-catalyzed DNA strand exchange can be attributed to an enhanced ability to compete with SSB protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):4004–4010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. G., Evans N. P., Buckman C. Formation of recombinant lacZ+ DNA in conjugational crosses with a recB mutant of Escherichia coli K12 depends on recF, recJ, and recO. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Aug;209(1):135–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00329848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menetski J. P., Kowalczykowski S. C. Biochemical properties of the Escherichia coli recA430 protein. Analysis of a mutation that affects the interaction of the ATP-recA protein complex with single-stranded DNA. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 20;211(4):845–855. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90078-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morand P., Blanco M., Devoret R. Characterization of lexB mutations in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):572–582. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.572-582.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch K. M., Linn S. A unified mechanism for the nuclease and unwinding activities of the recBC enzyme of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2641–2648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. D., McLaughlin T., Low B. Transduction versus "conjuduction": evidence for multiple roles for exonuclease V in genetic recombination in Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1043–1047. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman L. J., Kowalczykowski S. C. Characterization of the helicase activity of the Escherichia coli RecBCD enzyme using a novel helicase assay. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2863–2873. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman L. J., Kowalczykowski S. C. Formation of heteroduplex DNA promoted by the combined activities of Escherichia coli recA and recBCD proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18340–18348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman L. J., Kowalczykowski S. C. Relationship of the physical and enzymatic properties of Escherichia coli recA protein to its strand exchange activity. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7375–7385. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusche J. R., Konigsberg W., Howard-Flanders P. Isolation of altered recA polypeptides and interaction with ATP and DNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):949–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruyechan W. T., Wetmur J. G. Studies on the cooperative binding of the Escherichia coli DNA unwinding protein to single-stranded DNA. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5529–5534. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert H. S., Porter R. D. Enhanced recombination between lambda plac5 and F42lac: identification of cis- and trans-acting factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7500–7504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R., Amundsen S. K., Chaudhury A. M., Cheng K. C., Ponticelli A. S., Roberts C. M., Schultz D. W., Taylor A. F. Roles of RecBC enzyme and chi sites in homologous recombination. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:485–495. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. Homologous recombination in procaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Mar;52(1):1–28. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.1.1-28.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. F., Smith G. R. Substrate specificity of the DNA unwinding activity of the RecBC enzyme of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90414-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A., Smith G. R. Unwinding and rewinding of DNA by the RecBC enzyme. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlin B. E., Clark A. J. Overproduction of the Escherichia coli recA protein without stimulation of its proteolytic activity. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):386–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.386-390.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. C., Cassuto E., Howard-Flanders P. recA protein promotes homologous-pairing and strand-exchange reactions between duplex DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2100–2104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey S. D., Porter R. D. General recombination in Escherichia coli K-12: in vivo role of RecBC enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):29–34. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.29-34.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]