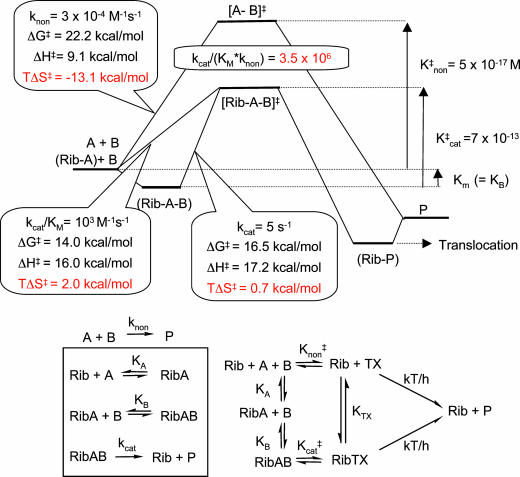
BIOCHEMISTRY. For the article “The ribosome as an entropy trap,” by Annette Sievers, Malte Beringer, Marina V. Rodnina, and Richard Wolfenden, which appeared in issue 21, May 25, 2004, of Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA (101, 7897–7901; first published May 12, 2004; 10.1073/pnas.0402488101), the authors note the following errors in Figs. 2, 4, and 6. In Fig. 2, the first-order rate constants were inadvertently overstated by a factor of 4. Thus, the overall rate enhancement achieved by the ribosome is kcat/(KM × knon) = 3.5 × 106. There is also a change in the values of Fig. 4, which result in a change in Fig. 6. In Fig. 6, knon for uncatalyzed peptide bond formation at 25°C = 3 × 10–4 M–1·s–1, ΔG≠ = 22.2 kcal/mol, ΔH≠ = 9.1 kcal/mol, and TΔS≠ =–13.1 kcal/mol. This correction reinforces the conclusion that the effect of the ribosome is to lower the entropy of activation for peptide bond formation. The corrected figures and their legends appear below.
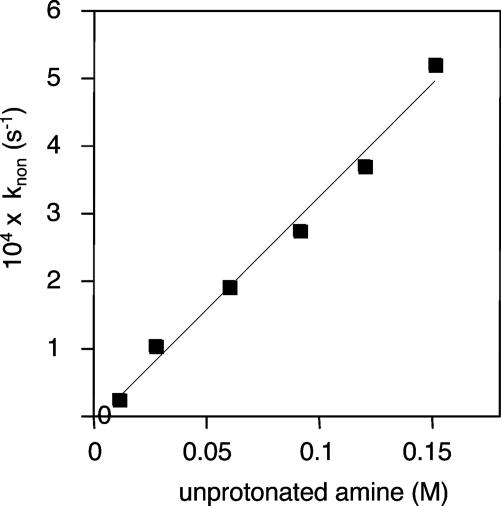
Fig. 2.
Apparent first-order rate constant of peptide bond formation, calculated from integrated 1H NMR intensities of the reactant and product, plotted as a function of unprotonated amine, with a fixed concentration (0.25 M) of total amine at varying pH values at 40°C. Similar results were obtained at fixed pH by varying the concentration of total amine (data not shown). The linear dependence of the rate shows that only one molecule of Tris participates in the ester aminolysis reaction.
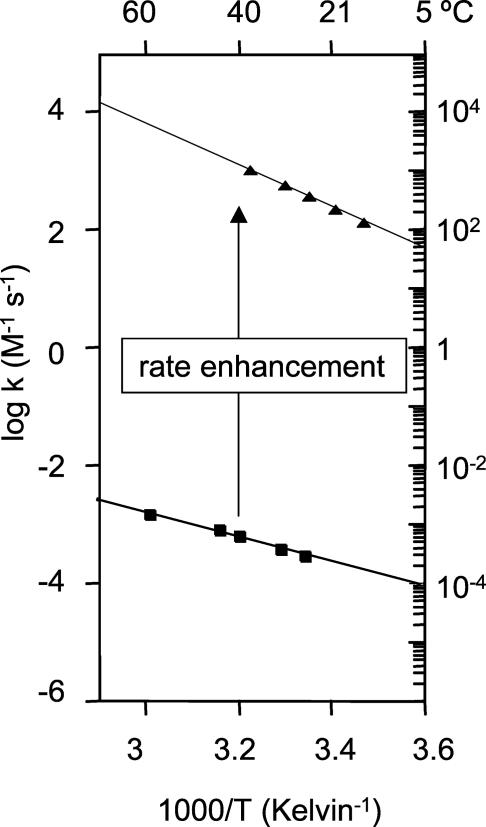
Fig. 4.
Temperature dependence of the second-order rate constants of uncatalyzed (squares) and ribosome-catalyzed (triangles) peptide bond formation. The second-order rate constants are calculated for the concentration of total amine at pH 7.5.
Fig. 6.
Activation parameters at 25°C for the second-order uncatalyzed (knon) and ribosome catalyzed peptide bond formation (kcat/KM), calculated from the concentration of total amine at pH 7.5. The broken line shows the first-order reaction in the ribosomal active site (kcat). K‡ values represent the equilibrium constant between the ground state and transition state calculated from the differences in free energy.